Advancements in Quantum Circuit Design for ARIA: Implementation and Security Evaluation
-
摘要: 随着量子计算的兴起与飞速发展, 它以其独特的并行计算能力和叠加特性冲击着传统密码算法的安全性。评估经典密码算法在量子计算环境下的抗量子攻击能力并设计出相应改进策略,已成为当前密码学领域的研究热点。该文以韩国分组密码算法标准ARIA为研究对象,基于塔域分解完成ARIA算法4种S盒的量子电路设计,所设计的S盒量子电路在NCT门集下仅需21个量子比特,是现有需要量子比特数最少的ARIA算法S盒量子电路实现方案。针对线性层,该文设计出深度为15的量子电路新方案,相较已有方案在深度方面优化11.7%,为目前该组件最优in-place量子实现。该文通过Grover密钥搜索攻击模型对ARIA系列算法进行了抗量子攻击安全性评估。结果表明,ARIA系列算法在新方案下的实现效率均有提升,ARIA-128/192/256在电路总深度$ \times $总门数($ D \times G $)和T门深度×电路宽度($ {\mathrm{Td}} \times M $)指标上分别优化21.8/12.8/4.5%和11.7/6.6/16.4%。特别地,ARIA-192的抗量子攻击安全性指标甚至已低于NIST的抗量子安全等级3,存在被量子攻击攻破的风险。Abstract:
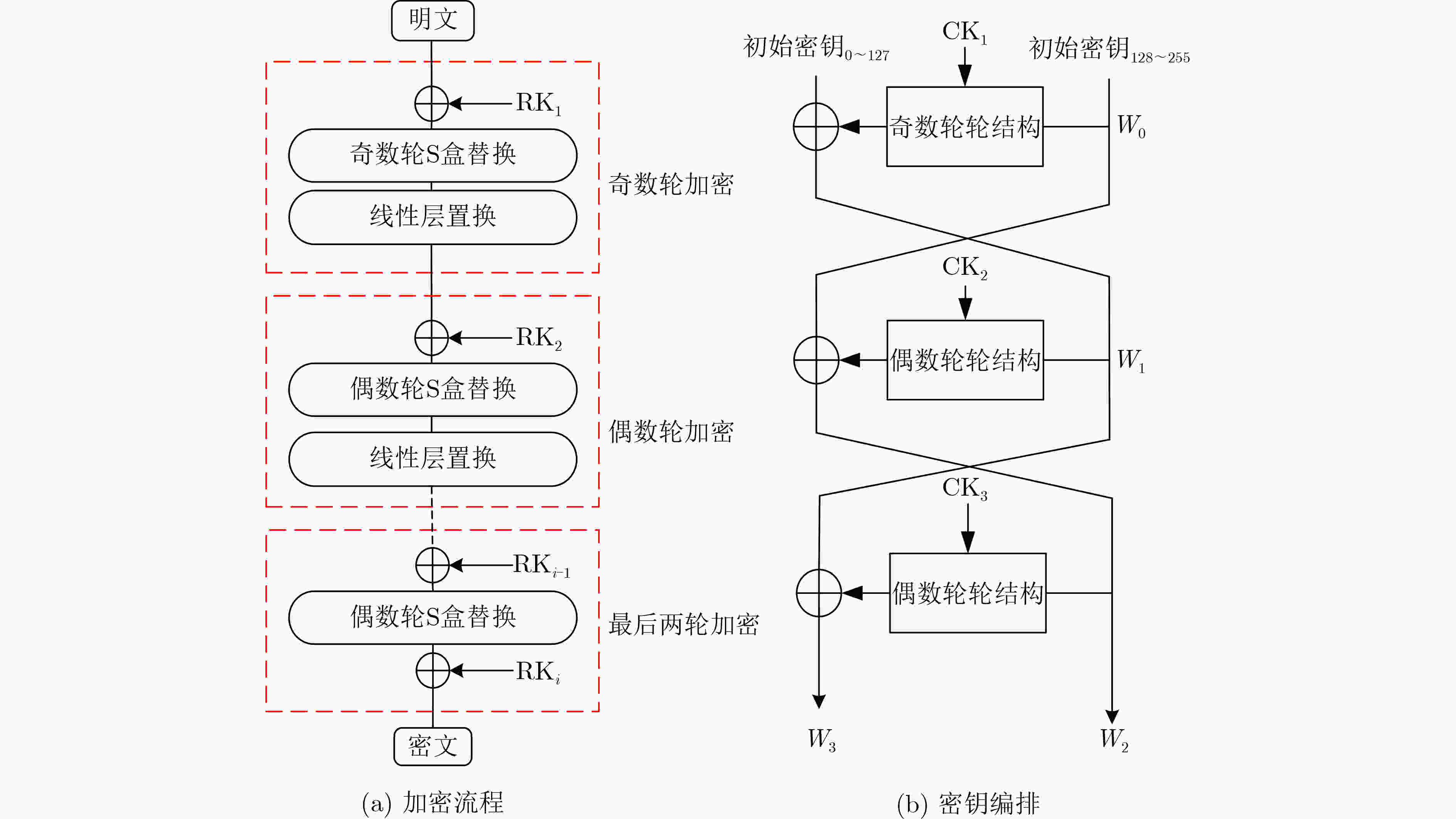
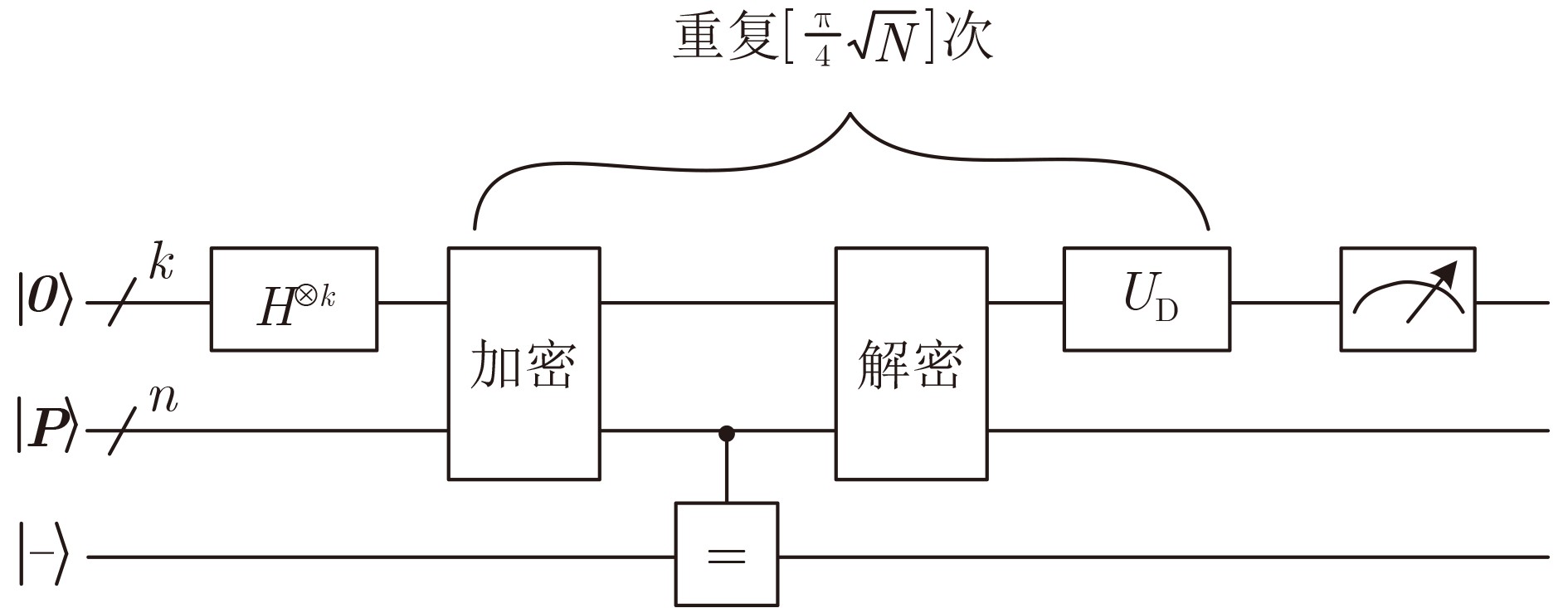
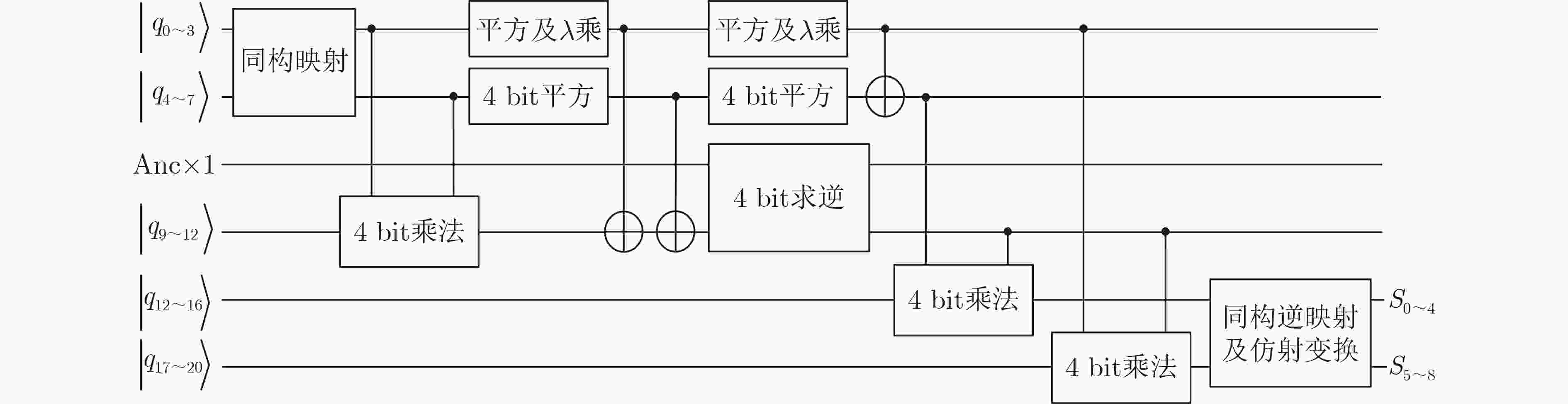
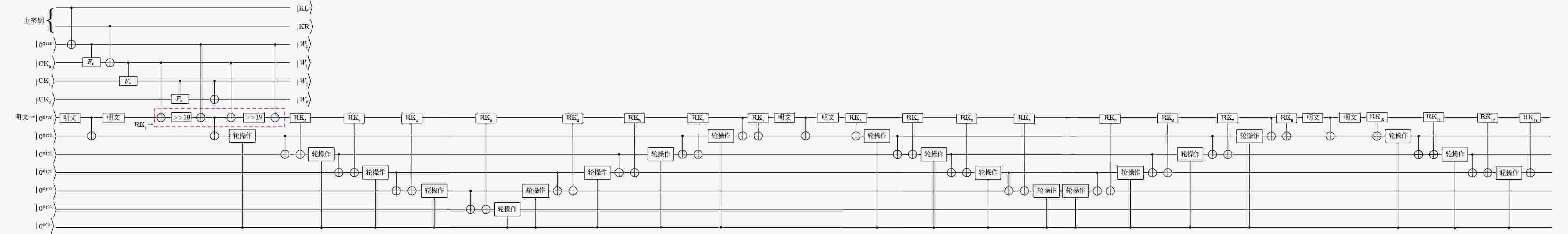
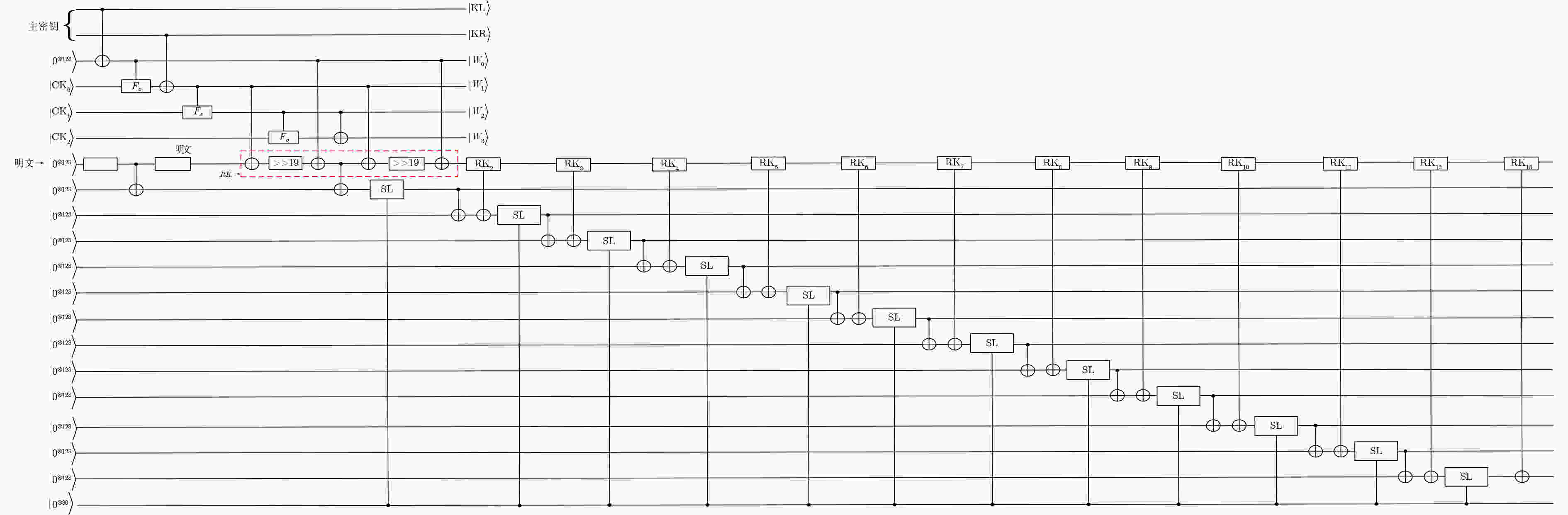
Objective ARIA is established as the Korean national Standard block cipher (KS X 1213) in 2003 to meet the demand for robust cryptographic solutions across government, industrial, and commercial sectors in South Korea. Designed by a consortium of Korean cryptographers, the algorithm adopts a hardware-efficient architecture that supports 128-, 192-, and 256-bit key lengths, providing a balance between computational performance and cryptographic security. This design allows ARIA to serve as a competitive alternative to the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), with comparable encryption and decryption speeds suitable for deployment in resource-constrained environments, including embedded systems and high-performance applications. The security of ARIA is ensured by its Substitution-Permutation Network (SPN) structure, which incorporates two distinct substitution layers and a diffusion layer to resist classical cryptanalytic methods such as differential, linear, and related-key attacks. This robustness has promoted its adoption in secure communication protocols and financial systems within South Korea and internationally. With the emergence of quantum computing, challenges to classical ciphers arise. Quantum algorithms such as Grover’s algorithm reduce the effective key strength of symmetric ciphers, necessitating reassessment of their post-quantum security. In this study, ARIA’s quantum circuit implementation is optimized through tower-field decomposition and in-place circuit optimization, enabling a comprehensive evaluation of its resilience against quantum adversaries. Methods The quantum resistance of ARIA is evaluated by estimating the resources required for exhaustive key search attacks under Grover’s algorithm. Grover’s quantum search algorithm achieves quadratic speedup, effectively reducing the security strength of a 128-bit key to the classical equivalent of 64 bit. To ensure accurate assessment, the quantum circuits for ARIA’s encryption and decryption processes are optimized within Grover’s framework, thereby reducing the required quantum resources. The core technique employed is tower-field decomposition, which transforms high-order finite field operations into equivalent lower-order operations, yielding compact computational representations. Specifically, the S-box and linear layer circuits are optimized using automated search tools to identify efficient combinations of low-order field operations. The resulting quantum circuits are then applied to estimate Grover-attack resource requirements, and the results are compared against the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) post-quantum security standards. Results and Discussions Optimized quantum circuits for all four ARIA S-boxes are constructed using tower-field decomposition and automated circuit search tools ( Fig. 7 ,Table 2 ). By integrating these with the linear layer, a complete quantum encryption circuit is implemented, and Grover-attack resource requirements are re-evaluated (Tables 5 and6 ). Detailed implementation data are provided in the Clifford+T gate set. The experimental results show that ARIA-192 does not meet the NIST Level 3 post-quantum security standard, indicating vulnerabilities to quantum adversaries. In contrast, ARIA-128 and ARIA-256 comply with Level 1 and Level 3 requirements, respectively. Further optimization is theoretically feasible through methods such as pseudo-key techniques. Future research may focus on developing automated circuit search tools to extend this framework, enabling systematic post-quantum security evaluations of ARIA and comparable symmetric ciphers (e.g., AES, SM4) within a generalized assessment model.Conclusions This study investigates the quantum resistance of classical cryptographic algorithms in the context of quantum computing, with a particular focus on the Korean block cipher ARIA. By leveraging the distinct algebraic structures of ARIA’s four S-boxes, tower-field decomposition is applied to design optimized quantum circuits for all S-boxes. Additionally, the circuit depth of the ARIA linear layer is optimized through an in-place quantum circuit implementation, resulting in a more efficient realization of the ARIA algorithm in the quantum setting. A complete quantum encryption circuit is constructed by integrating these optimization components, and the security of the ARIA family of algorithms is evaluated against quantum adversaries using Grover’s key search attack model. The results demonstrate improved implementation efficiency under the newly designed quantum scheme. However, ARIA-192 exhibits resistance below the NIST Level 3 quantum security threshold, indicating a potential vulnerability to quantum attacks. -
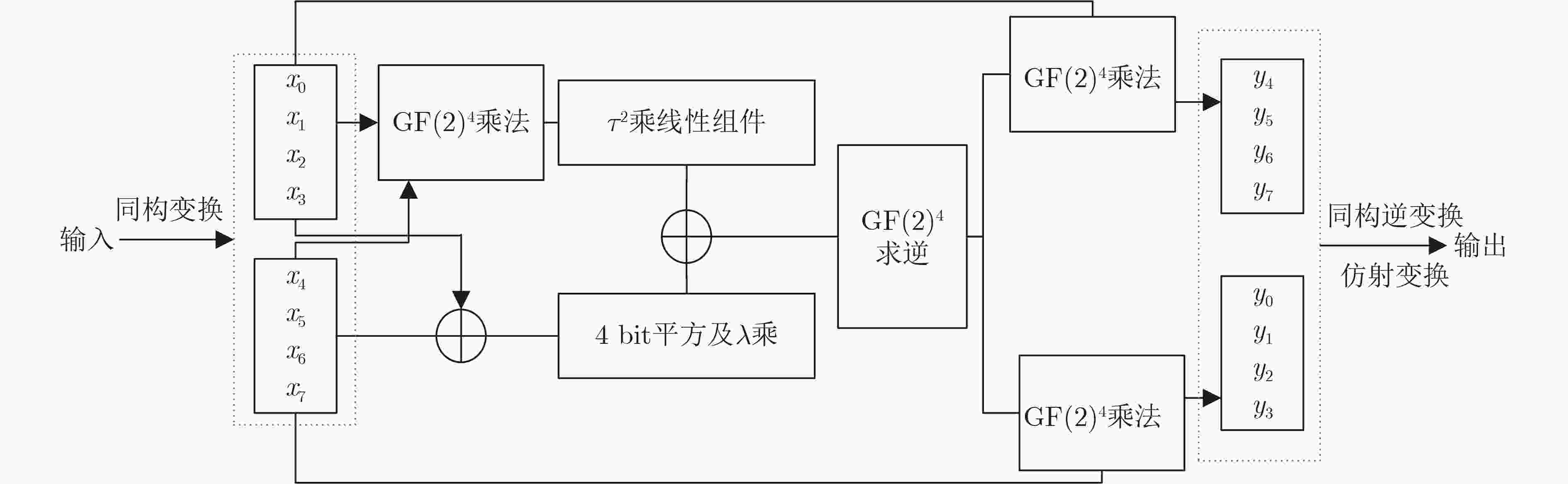
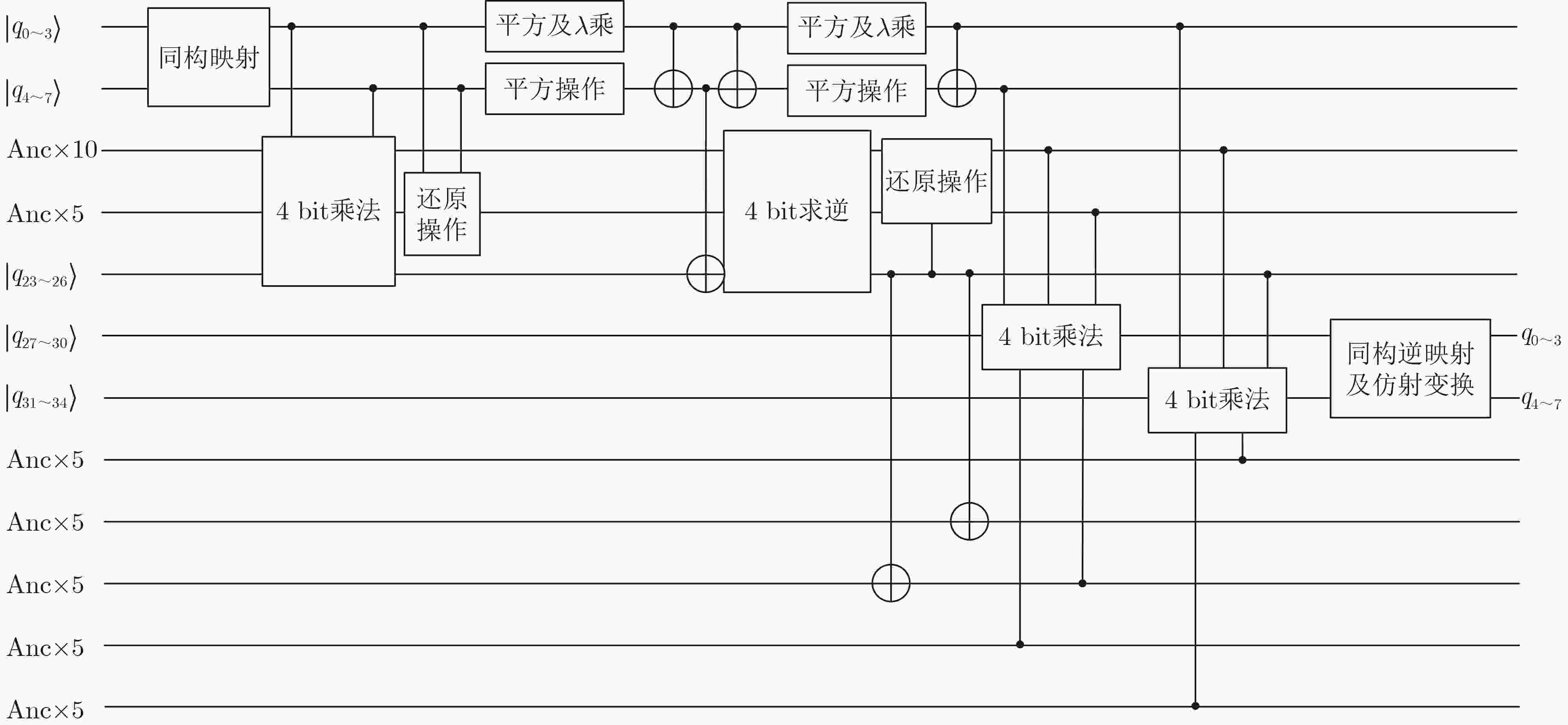
表 1 不可约多项式为$ {x^4} + {x^3} + 1 $的$ {\text{GF(}}{{\text{2}}^{\text{4}}}{\text{)}} $求逆4 bit S盒
输入x3,x2,x1,x0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 输出y3,y2,y1,y0 0 1 12 8 6 15 4 14 3 13 11 10 2 9 7 5 表 2 S盒的NCT结构量子电路实现资源消耗对比
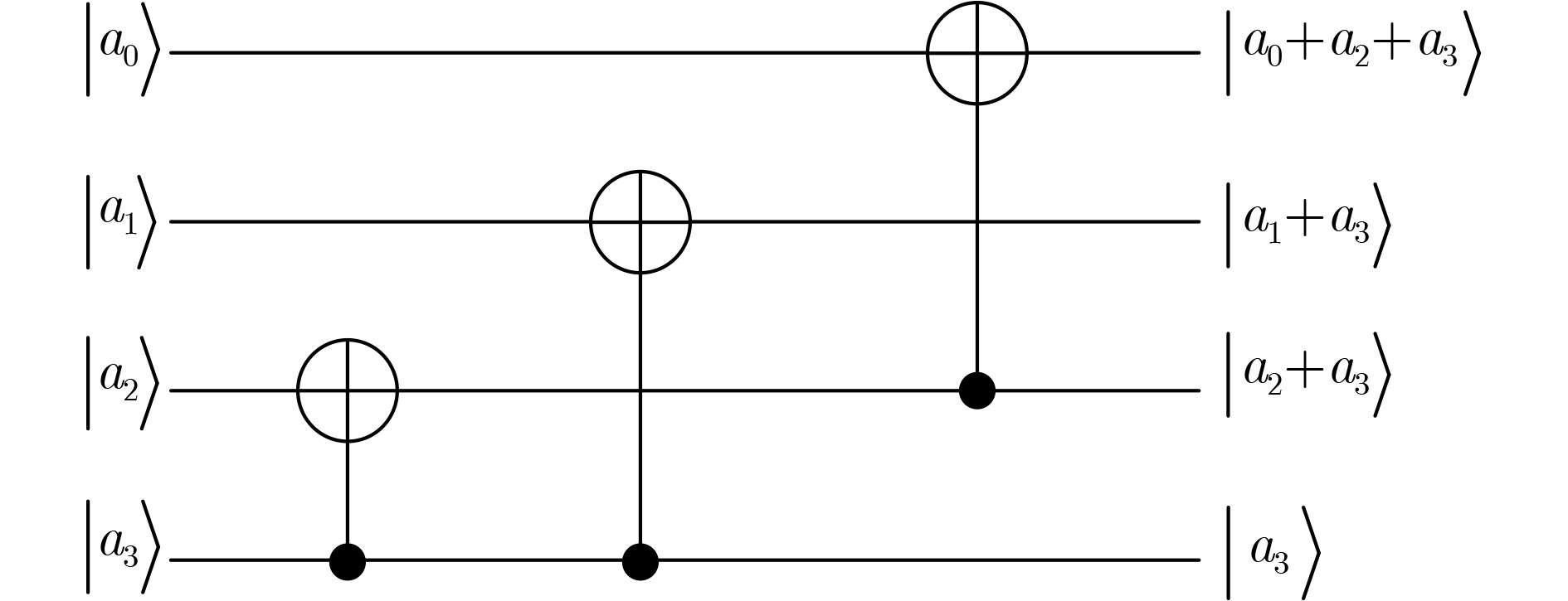
参考文献 辅助比特m #CNOT #X #Toffoli Toffoli深度 总深度D $ D \times m $ Itoh-Tsujii [25] 40 569 4 448 196 391 15 760 [26] 162 1 114 4 108 4 151 24 462 [27] 170 1 106 4 108 4 137 23 290 塔域分解 [29]* 84 162 4 35 4 $ \ge 66 $ $ \ge 5\;544 $ $ \mathrm{本}\mathrm{文} $ 5 225 8 50 35 317 1 585 $ {\mathrm{本}\mathrm{文}}^{†} $ 46 247 4 63 11 114 5 244 注: *文献给出的S1总深度(33)未充分考虑量子电路与经典电路深度统计差异且未设置还原操作,所设计量子电路实际深度可能超过2倍;
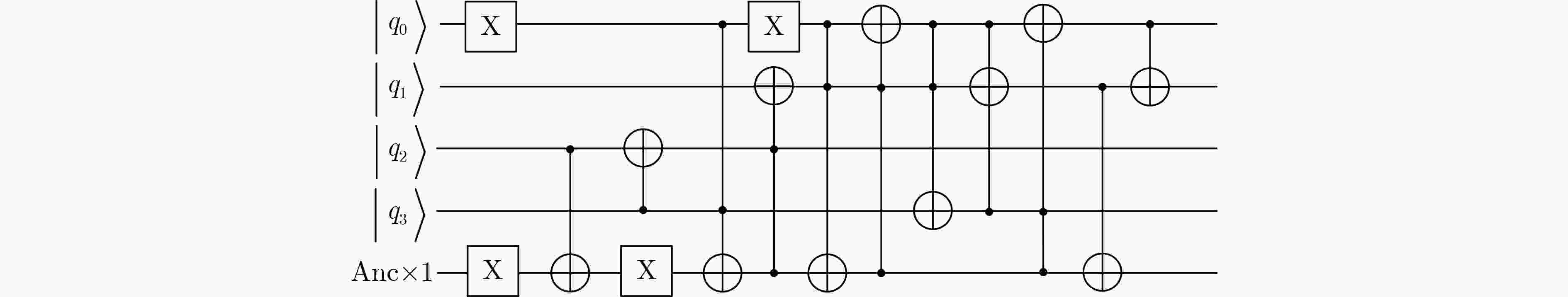
$ † $标注方案是权衡深度指标设计的S盒,参考附录图A2。表 3 ARIA算法4种类型S盒的NCT结构量子电路资源统计
量子比特数M #CNOT #X #Toffoli Toffoli深度 总深度D $ D \times M $ S1 21 225 8 50 35 317 6 657 S2 21 225 8 50 35 329 6 909 S3 21 224 8 50 35 317 6 657 S4 21 224 8 50 35 328 6 888 表 4 ARIA-128的轮结构量子电路实现资源统计
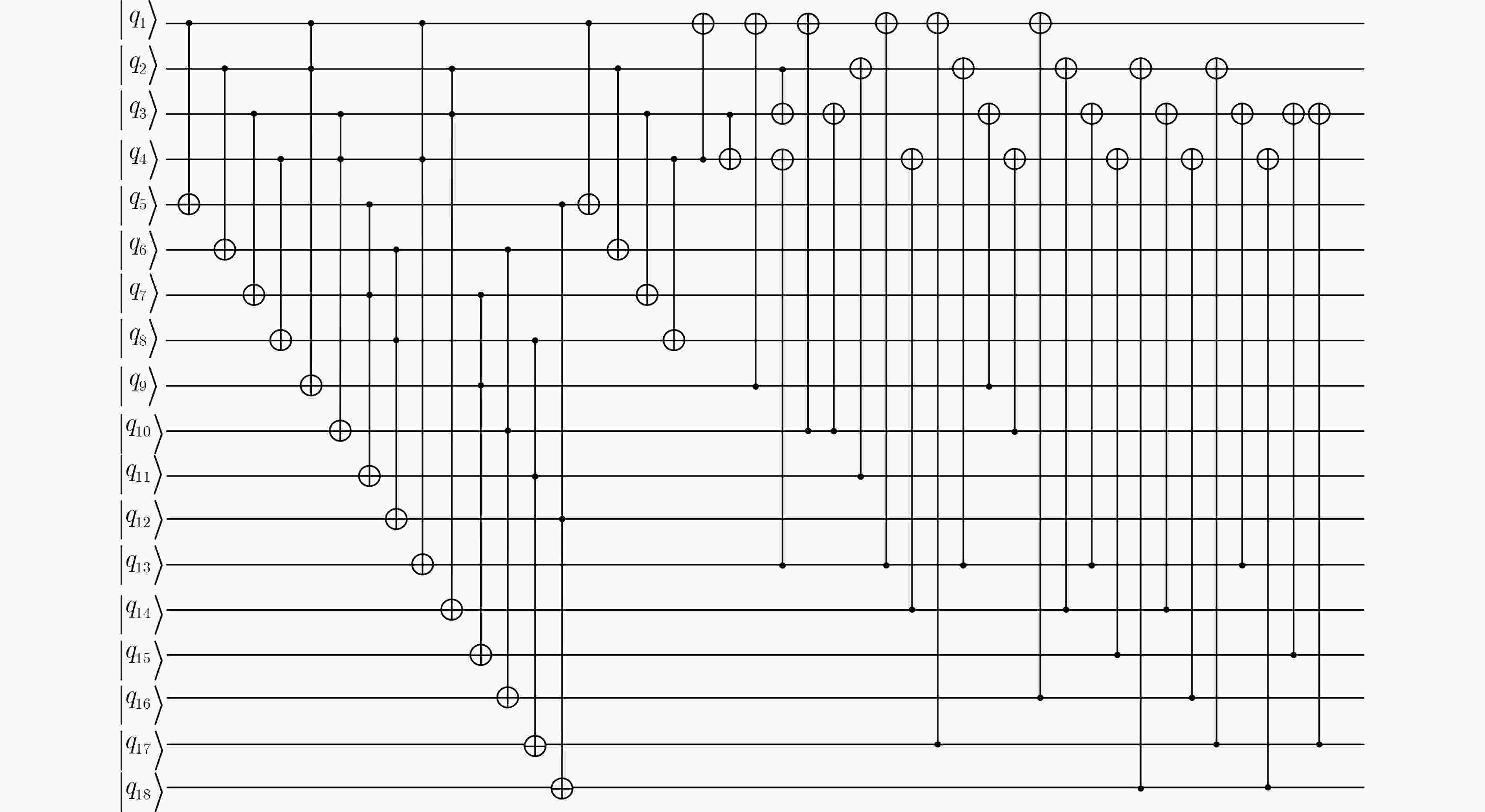
量子比特数M #CNOT #X #Toffoli 总深度D $ D \times M $ 本文 336 4 096 4 192 344 115 584 $ {\mathrm{本}\mathrm{文}}^{†} $ 992 3 992 4 64 130 128 960 [25] 640 19 052 4 64 417 266 880 [26] 2 848 17 832 8 64 164 467 072 [27] 2 976 11 576 4 64 146 434 496 [29]* 1 728 3 964 544 64 $ \ge 73 $ $ \ge 126\;144 $ 注: *文献中总深度数据,根据表2所示修正的S盒深度获得;$ † $标注轮结构方案采用权衡深度指标设计的S盒,见附录图A2。 表 5 ARIA-128算法在NCT门集下量子电路资源统计
#CNOT #X #Toffoli Toffoli深度TD 量子比特数M 总深度D $ D \times M $ $ {\text{TD}} \times M $ 本文 95 872 4 411 17 600 770 1 616 7 353 $ 1.42 \times {2^{23}} $ $ 1.19 \times {2^{20}} $ $ {\mathrm{本}\mathrm{文}}^{†} $ 96 016 1 595 22 176 242 2 400 2 953 $ 1.69 \times {2^{22}} $ $ 1.11 \times {2^{19}} $ $ {\mathrm{本}\mathrm{文}}^{‡} $ 65 516 3 569 12 000 525 2 464 5 160 $ 1.52 \times {2^{23}} $ $ 1.23 \times {2^{20}} $ $ {\mathrm{本}\mathrm{文}}^{†‡} $ 61 088 957 15 120 165 3 040 1 952 $ 1.41 \times {2^{22}} $ $ 1.91 \times {2^{18}} $ [25] 231 124 1 595 157 696 4 312 1 560 9 260 $ 1.72 \times {2^{23}} $ $ 1.60 \times {2^{22}} $ [26] 285 784 1 408 25 920 60 29 216 3 500 $ 1.52 \times {2^{27}} $ $ 1.67 \times {2^{20}} $ [27] 173 652 1 408 17 040 60 26 864 2 187 $ 1.75 \times {2^{25}} $ $ 1.54 \times {2^{20}} $ [29]* 97 748 1 408 14 816 60 9 536 $ \ge 1\;528 $ $ \ge 1.37 \times {2^{23}} $ $ 1.09 \times {2^{19}} $ 注: *文献中总深度数据,基于表2所示修正后的S盒深度数据得到;$ † $方案遵循低深度S盒设计并搭配Zig-zag架构实现,见附录图B1;$ ‡ $方案遵循少量子比特S盒设计及Pipeline架构实现;$ †‡ $方案用低深度S盒设计并搭配Pipeline架构实现,见附录图B2。 表 6 ARIA算法在Clifford+T门集下的Grover密钥攻击量子资源统计
算法 文献 总门数G T深度Td 总深度D 量子比特数M $ {\text{Td}} \times M $ $ D \times G $ NIST标准 128 $ {\mathrm{本}\mathrm{文}}^{†‡} $ $ 1.76 \times {2^{82}} $ $ 1.01 \times {2^{74}} $ $ 1.47 \times {2^{75}} $ 3041 $ 1.50 \times {2^{85}} $ $ 1.29 \times {2^{158}} $ 2157 [25] $ 1.99 \times {2^{85}} $ $ 1.65 \times {2^{78}} $ $ 1.82 \times {2^{79}} $ 1561 $ 1.25 \times {2^{89}} $ $ 1.81 \times {2^{165}} $ [26] $ 1.12 \times {2^{84}} $ $ 1.47 \times {2^{72}} $ $ 1.78 \times {2^{76}} $ 29217 $ 1.31 \times {2^{87}} $ $ 1.99 \times {2^{160}} $ [27] $ 1.03 \times {2^{83}} $ $ 1.47 \times {2^{72}} $ $ 1.13 \times {2^{76}} $ 26865 $ 1.21 \times {2^{87}} $ $ 1.47 \times {2^{159}} $ [29]* $ 1.87 \times {2^{82}} $ $ 1.47 \times {2^{72}} $ $ 1.77 \times {2^{74}} $ 9537 $ 1.70 \times {2^{85}} $ $ \ge 1.65 \times {2^{158}} $ ARIA 192 $ {\mathrm{本}\mathrm{文}}^{†‡} $ $ 1.05 \times {2^{116}} $ $ 1.15 \times {2^{106}} $ $ 1.78 \times {2^{107}} $ 6849 $ 1.92 \times {2^{118}} $ $ 1.87 \times {2^{223}} $ 2224 [25] $ 1.15 \times {2^{119}} $ $ 1.95 \times {2^{110}} $ $ 1.07 \times {2^{112}} $ 3121 $ 1.48 \times {2^{122}} $ $ 1.23 \times {2^{231}} $ [26] $ 1.20 \times {2^{117}} $ $ 1.67 \times {2^{104}} $ $ 1.01 \times {2^{109}} $ 65857 $ 1.67 \times {2^{120}} $ $ 1.22 \times {2^{226}} $ [27] $ 1.47 \times {2^{116}} $ $ 1.67 \times {2^{104}} $ $ 1.28 \times {2^{108}} $ 60499 $ 1.54 \times {2^{120}} $ $ 1.89 \times {2^{224}} $ [29]* $ 1.06 \times {2^{116}} $ $ 1.67 \times {2^{104}} $ $ 1.00 \times {2^{107}} $ 20865 $ 1.06 \times {2^{119}} $ $ \ge 1.07 \times {2^{224}} $ 256 $ {\mathrm{本}\mathrm{文}}^{†‡} $ $ 1.23 \times {2^{148}} $ $ 1.15 \times {2^{138}} $ $ 1.04 \times {2^{140}} $ 7617 $ 1.07 \times {2^{151}} $ $ 1.28 \times {2^{288}} $ 2285 [25] $ 1.38 \times {2^{151}} $ $ 1.17 \times {2^{143}} $ $ 1.24 \times {2^{144}} $ 3377 $ 1.93 \times {2^{154}} $ $ 1.71 \times {2^{295}} $ [26] $ 1.34 \times {2^{149}} $ $ 1.86 \times {2^{136}} $ $ 1.14 \times {2^{141}} $ 72081 $ 1.02 \times {2^{153}} $ $ 1.52 \times {2^{290}} $ [27] $ 1.64 \times {2^{148}} $ $ 1.86 \times {2^{136}} $ $ 1.44 \times {2^{140}} $ 67553 $ 1.92 \times {2^{152}} $ $ 1.18 \times {2^{289}} $ [29]* $ 1.20 \times {2^{148}} $ $ 1.86 \times {2^{136}} $ $ 1.12 \times {2^{139}} $ 22657 $ 1.28 \times {2^{151}} $ $ \ge 1.34 \times {2^{288}} $ AES 128 [7] $ 1.03 \times {2^{85}} $ $ 1.06 \times {2^{80}} $ $ 1.16 \times {2^{81}} $ 984 $ 1.02 \times {2^{90}} $ $ 1.83 \times {2^{166}} $ 2157 192 $ 1.83 \times {2^{118}} $ $ 1.21 \times {2^{112}} $ $ 1.33 \times {2^{113}} $ 2224 $ 1.31 \times {2^{123}} $ $ 1.38 \times {2^{232}} $ 2224 256 $ 1.59 \times {2^{150}} $ $ 1.44 \times {2^{144}} $ $ 1.57 \times {2^{145}} $ 2762 $ 1.92 \times {2^{155}} $ $ 1.02 \times {2^{296}} $ 2285 SM4 [22] $ - $ $ 1.72 \times {2^{78}} $ $ - $ 737 $ 1.24 \times {2^{88}} $ $ - $ 2157 注: *文献中总深度数据,基于表2所示修正后的S盒深度数据得到;$ †‡ $方案是低深度S盒搭配Pipeline架构实现,见附录图B2。 -
[1] SHOR P W. Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer[J]. SIAM Review, 1999, 41(2): 303–332. doi: 10.1137/S0036144598347011. [2] SIMON D R. On the power of quantum computation[J]. SIAM Journal on Computing, 1997, 26(5): 1474–1483. doi: 10.1137/S0097539796298637. [3] GROVER L K. A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search[C]. The Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Philadelphia, USA, 1996: 212–219. doi: 10.1145/237814.237866. [4] ALAGIC G, APON D, COOPER D, et al. Status report on the third round of the NIST post-quantum cryptography standardization process[R]. NIST IR 8413, 2022. doi: 10.6028/nist.ir.8413-upd1. [5] DAEMEN J, RIJMEN V. AES proposal: Rijndael[R]. 1999. [6] AUMASSON J P, HENZEN L, MEIER W, et al. SHA-3 proposal BLAKE[R]. Submission to NIST, 2008: 194. [7] GRASSL M, LANGENBERG B, ROETTELER M, et al. Applying Grover’s algorithm to AES: Quantum resource estimates[C]. The 7th International Workshop on Post-Quantum Cryptography, Fukuoka, Japan, 2016: 29–43. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-29360-8_3. [8] AMENTO B, RÖTTELER M, STEINWANDT R. Efficient quantum circuits for binary elliptic curve arithmetic: Reducing T-gate complexity[J]. Quantum Information & Computation, 2013, 13(7/8): 631–644. [9] ALMAZROOIE M, SAMSUDIN A, ABDULLAH R, et al. Quantum reversible circuit of AES-128[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2018, 17(5): 112. doi: 10.1007/s11128-018-1864-3. [10] LANGENBERG B, PHAM H, and STEINWANDT R. Reducing the cost of implementing the advanced encryption standard as a quantum circuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Quantum Engineering, 2020, 1: 2500112. doi: 10.1109/tqe.2020.2965697. [11] ZOU Jian, WEI Zihao, SUN Siwei, et al. Quantum circuit implementations of AES with fewer qubits[C]. The 26th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security on Advances in Cryptology, Daejeon, South Korea, 2020: 697–726. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-64834-3_24. [12] LI Zhenqiang, CAI Binbin, SUN Hongwei, et al. Novel quantum circuit implementation of advanced encryption standard with low costs[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2022, 65(9): 290311. doi: 10.1007/s11433-022-1921-y. [13] HUANG Zhenyu and SUN Siwei. Synthesizing quantum circuits of AES with lower T-depth and less qubits[C]. The 28th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security on Advances in Cryptology, Taipei, China, 2022: 614–644. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-22969-5_21. [14] JAQUES S, NAEHRIG M, ROETTELER M, et al. Implementing Grover oracles for quantum key search on AES and LowMC[C]. The 39th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques on Advances in Cryptology, Zagreb, Croatia, 2020: 280–310. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-45724-2_10. [15] LIN Da, XIANG Zejun, XU Runqing, et al. Optimized quantum implementation of AES[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2023, 22(9): 352. doi: 10.1007/s11128-023-04043-9. [16] S. SW. GM/T 0002-2012 SM4 block cipher algorithm[S]. State Cryptography Administration, Chinese Commercial Cryptography Standard, 2012. [17] BAI Xuefei, XU Yanhua, and GUO Li. Securing SMS4 cipher against differential power analysis and its VLSI implementation[C]. 2008 11th IEEE Singapore International Conference on Communication Systems, Guangzhou, China, 2008: 167–172. doi: 10.1109/iccs.2008.4737165. [18] PAAR C. Efficient VLSI architectures for bit-parallel computation in Galois fields[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Duisburg-Essen, 1994. [19] ABBASI I and AFZAL M. A compact S-box design for SMS4 block cipher[M]. PARK J J, ARABNIA H, CHANG H B, et al. IT Convergence and Services. Dordrecht: Springer, 2011: 641–658. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-2598-0_69. [20] MARTÍNEZ-HERRERA A F, MEX-PERERA C, and NOLAZCO-FLORES J. Merging the camellia, SMS4 and AES s-boxes in a single s-box with composite bases[C]. The 16th International Conference on Information Security, Dallas, United States, 2013: 209–217. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-27659-5_15. [21] WEI Zihao, SUN Siwei, HU Lei, et al. Searching the space of tower field implementations of the $ \mathbb{F}_{2} 8 $ inverter-with applications to AES, Camellia and SM4[J]. International Journal of Information and Computer Security, 2023, 20(1/2): 1–26. doi: 10.1504/ijics.2023.127999. [22] 林达, 向泽军, 张若琳, 等. SM4算法的量子实现[J]. 密码学报, 2021, 8(6): 999–1018. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000493.LIN Da, XIANG Zejun, ZHANG Ruolin, et al. Quantum implementation of SM4[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2021, 8(6): 999–1018. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000493. [23] LUO Qingbin, LI Qiang, LI Xiaoyu, et al. Quantum circuit implementations of SM4 block cipher optimizing the number of qubits[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2024, 23(5): 177. doi: 10.1007/s11128-024-04394-x. [24] KWON D, KIM J, PARK S, et al. New block cipher: ARIA[C]. The 6th International Conference on Information Security and Cryptology, Seoul, Korea, 2003: 432–445. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-24691-6_32. [25] CHAUHAN A K and SANADHYA S K. Quantum resource estimates of Grover’s key search on ARIA[C]. The 10th International Conference on Security, Privacy, and Applied Cryptography Engineering, Kolkata, India, 2020: 238–258. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-66626-2_13. [26] YANG Yujin, JANG K, OH Y, et al. Depth-optimized quantum implementation of ARIA[C]. The 26th International Conference on Information Security and Cryptology, Seoul, South Korea, 2023: 79–96. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-1235-9_5. [27] OH Y, JANG K, YANG Yujin, et al. Quantum implementation and analysis of ARIA[C]. 2024 Silicon Valley Cybersecurity Conference (SVCC), Seoul, Korea, 2024: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/svcc61185.2024.10637311. [28] BOYAR J and PERALTA R. A new combinational logic minimization technique with applications to cryptology[C]. Tthe 9th International Symposium on Experimental Algorithms, Naples, Italy, 2010: 178–189. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-13193-6_16. [29] OH Y, JANG K, SEO H. Improved quantum analysis of ARIA[J]. Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2024. [30] NG W J and TAN C H. Depth–measurement trade-off for quantum search on block ciphers[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2024, 23(4): 151. doi: 10.1007/s11128-024-04359-0. [31] 刘嘉宏, 谭晓青, 李明, 等. SM4算法S盒的高效量子电路实现[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2024, 54(4): 240314. doi: 10.1360/sspma-2023-0386.LIU Jiahong, TAN Xiaoqing, LI Ming, et al. Efficient quantum circuit implementation of the SM4 S-box[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2024, 54(4): 240314. doi: 10.1360/sspma-2023-0386. [32] 陈晨, 郭华, 王闯, 等. 一种基于复合域的国密SM4算法快速软件实现方法[J]. 密码学报, 2023, 10(2): 289–305. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000594.CHEN Chen, GUO Hua, WANG Chuang, et al. A fast software implementation of SM4 based on composite fields[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2023, 10(2): 289–305. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000594. [33] CHEN Jingwen, LIU Qun, FAN Yanhong, et al. New SAT-based model for quantum circuit decision problem: Searching for low-cost quantum implementation[J]. IACR Communications in Cryptology, 2024, 1(1): 31. doi: 10.62056/anmmp-4c2h. [34] JANG K, BAKSI A, KIM H, et al. Quantum analysis of AES[J]. IACR Communications in Cryptology, 2025, 2(1): cc2–1-36. doi: 10.62056/ay11zo-3y. [35] XIANG Zejun, ZENG Xiangyoung, LIN Da, et al. Optimizing implementations of linear layers[J]. IACR Transactions on Symmetric Cryptology, 2020, 2020(2): 120–145. doi: 10.13154/tosc.v2020.i2.120-145. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
