Communication, Computation, and Caching Resource Collaboration for Heterogeneous AIGC Service Provisioning
-
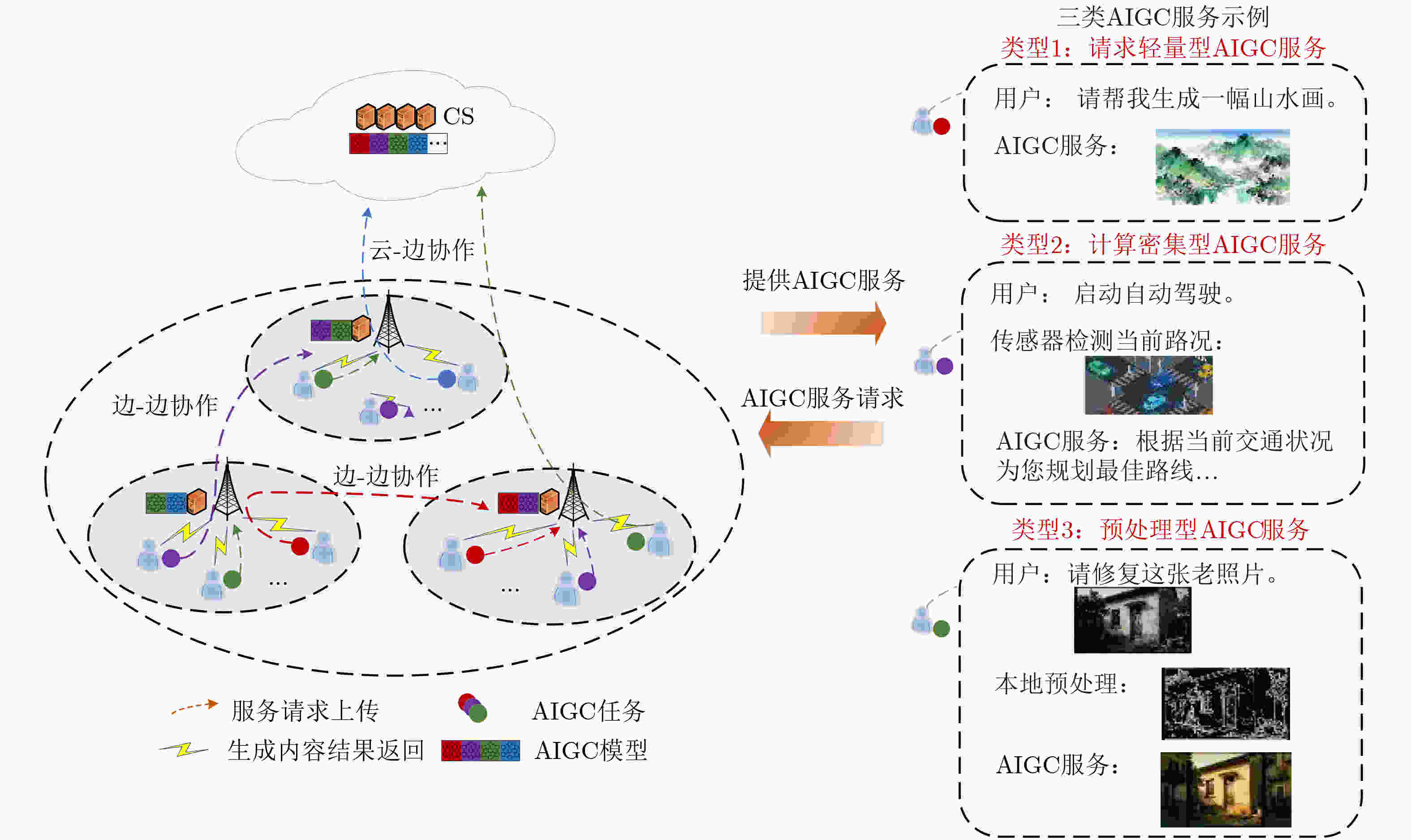
摘要: 在智能物联网(Artificial Intelligence of Things, AIoT)中,边缘服务器可以通过利用存储的人工智能生成内容(AI-Generated Content, AIGC)模型向AIoT设备提供智能服务。然而,边缘服务器的计算能力和模型存储容量有限,难以支撑大规模的模型存储以实现异构AIGC服务。针对此问题,基于AIGC服务的异构性,将AIGC服务划分为请求轻量型、计算密集型以及预处理型三类,并提出了一种云边协同与边边协同相结合的通算存资源优化方案。该方案协同云计算与边缘计算的优势,在考虑边缘服务器计算和存储资源限制的基础上,联合优化AIoT设备和基站的发射功率、计算资源分配、AIGC模型部署及服务请求决策以最小化AIGC服务总时延。由于所构建的优化问题是一个混合整数非线性规划问题,因此设计了一种基于交替优化的算法,该算法将问题分解为三个子问题,并分别采用连续凸逼近方法、卡罗需-库恩-塔克条件和改进的哈里斯鹰算法进行求解。仿真结果表明,所提方案具有较快的收敛速度,并且与基准方案相比能够降低AIGC服务总时延。Abstract:
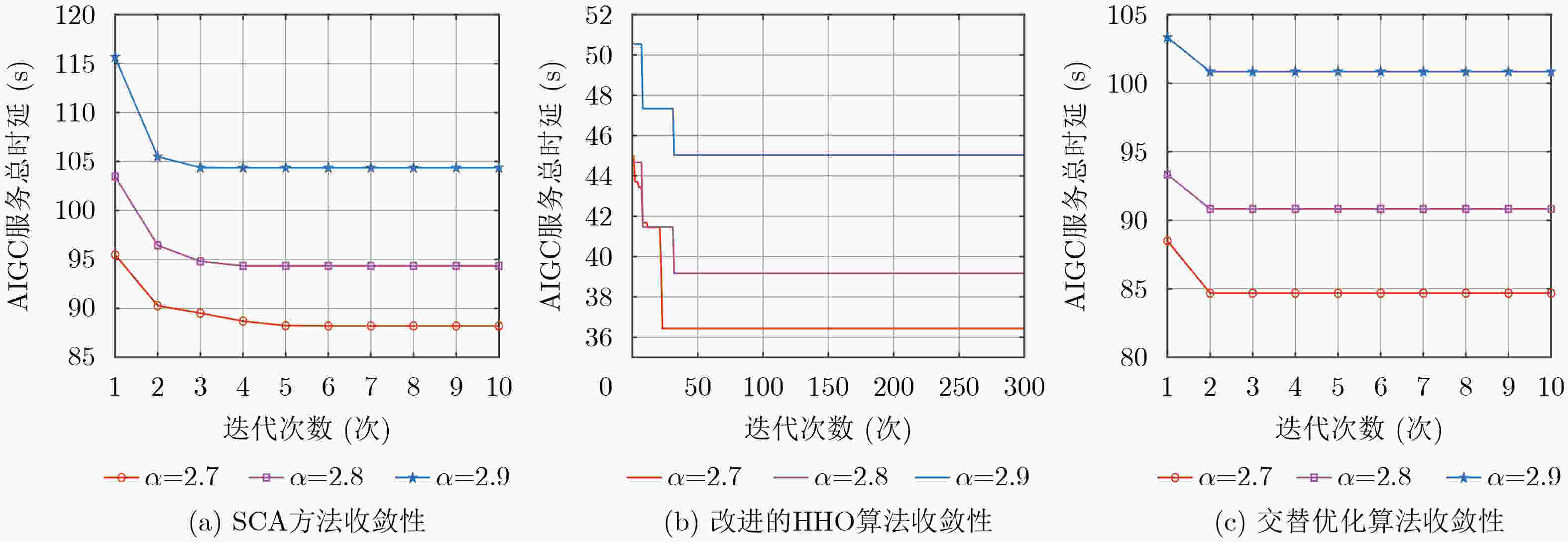
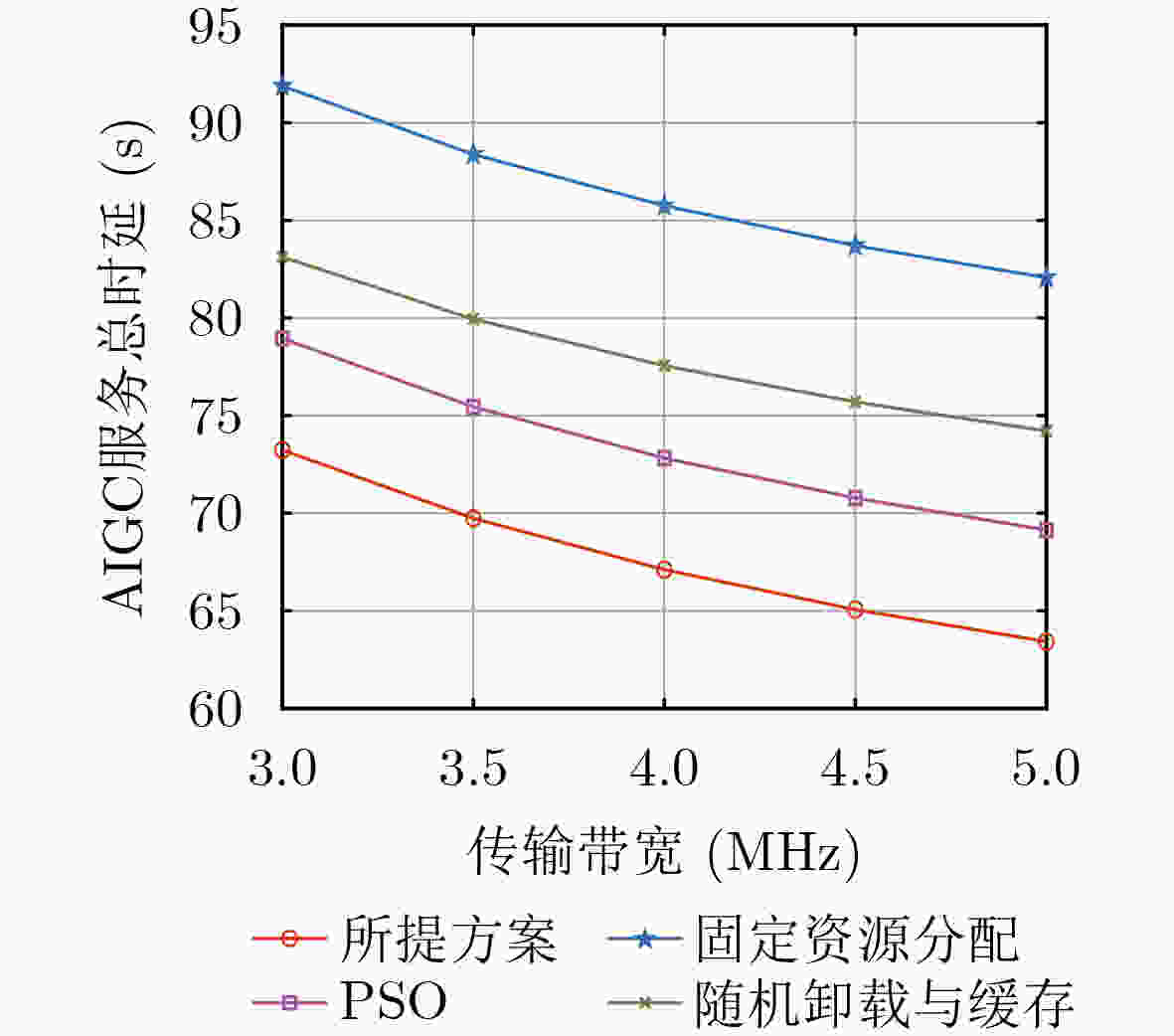
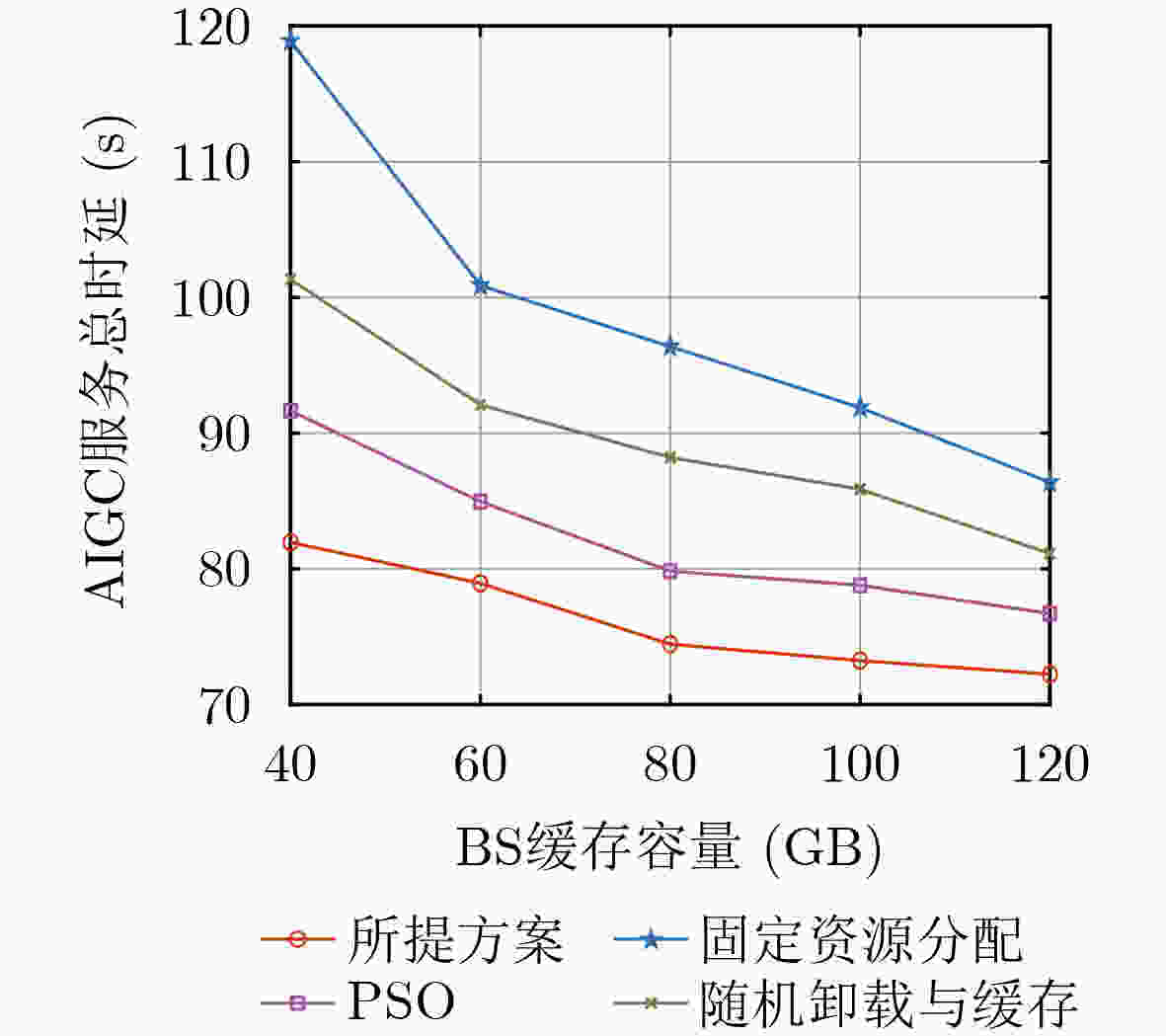
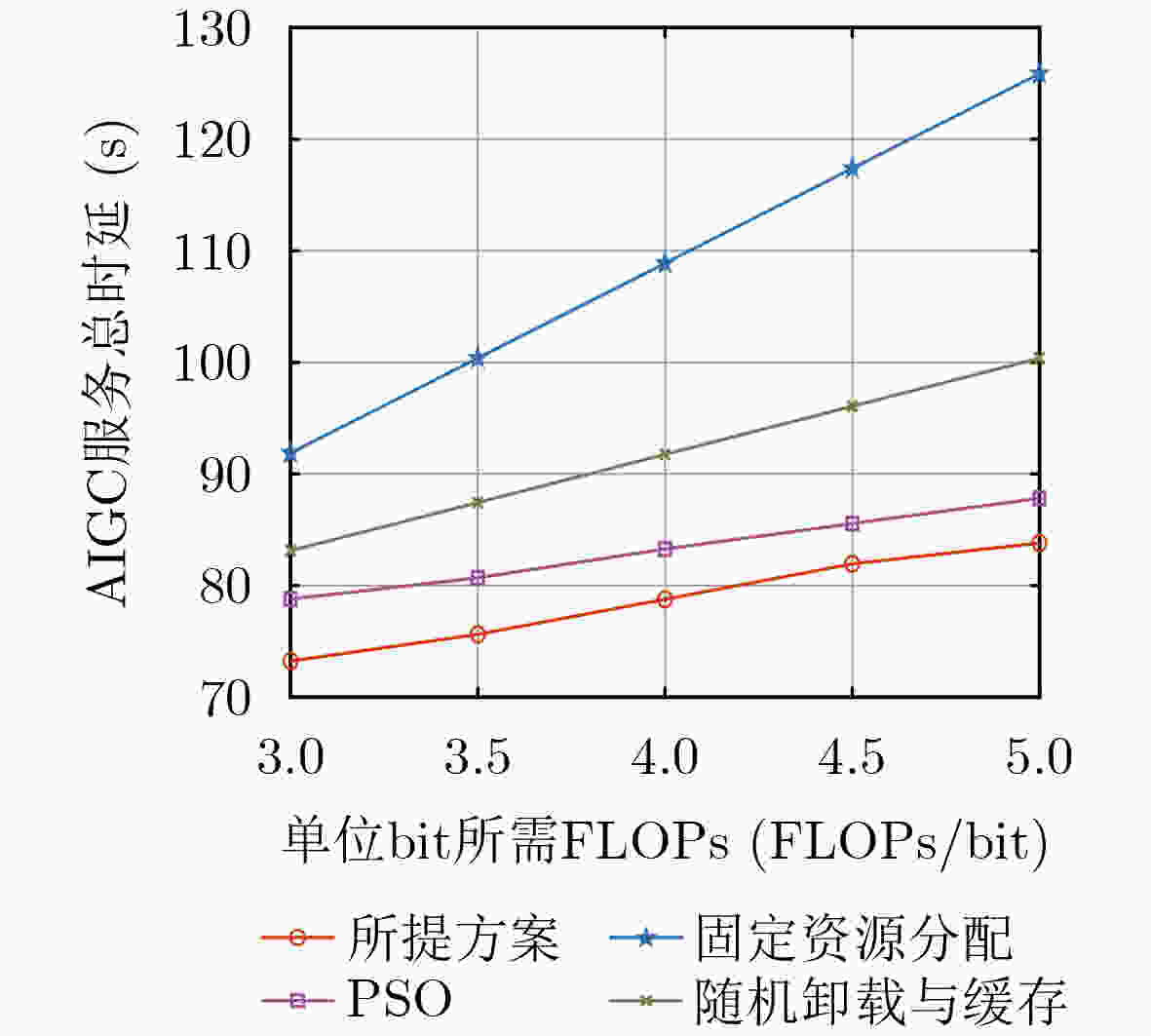
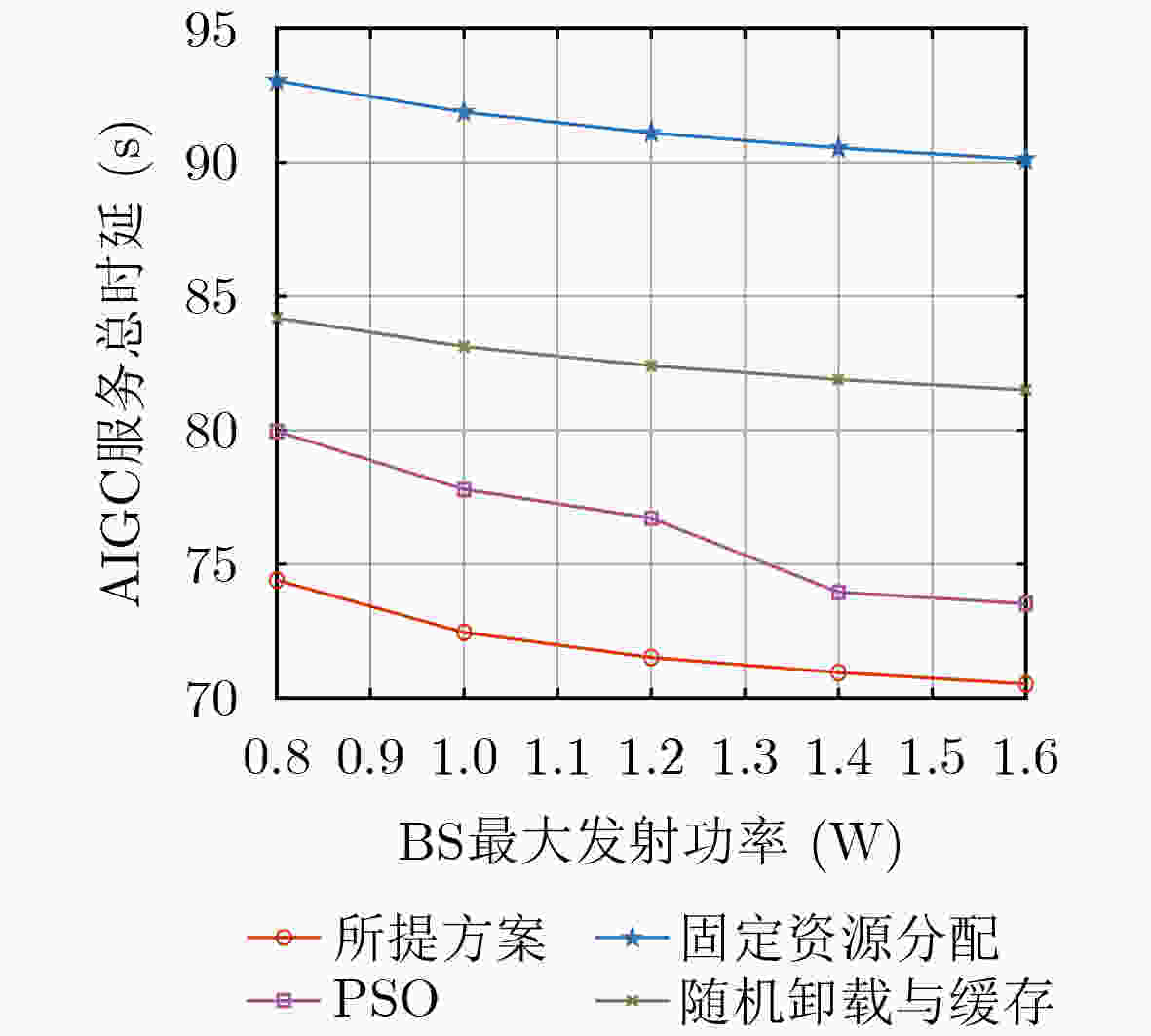
Objective In the artificial intelligence of things (AIoT), edge servers (ESs) can provide intelligent content generation services to AIoT devices by utilizing their cached AI-generated content (AIGC) models. However, the limited computing resources and caching capacity of ESs make it difficult to support the large-scale caching demands of heterogeneous AIGC services. To address this issue, this paper proposes a communication, computation, and caching resource collaboration scheme that leverages a combined cloud-edge and edge-edge collaborative framework. This scheme focuses on three representative AIGC services, including lightweight AIGC services, computation-intensive AIGC services, and preprocessing-based AIGC services. Furthermore, the proposed approach aims to minimize the total AIGC service latency by jointly optimizing transmit power, computing resource allocation, model caching strategies, and offloading decisions. Methods This paper investigates communication, computation, and caching resource collaboration for supporting heterogeneous AIGC services. First, an AIGC service-oriented AIoT system model is proposed to incorporate both cloud-edge and edge-edge collaboration. Subsequently, an optimization problem is formulated with the objective of minimizing the total latency of AIGC services by jointly optimizing transmit power, computing resource allocation, model caching strategies, and offloading decisions. Since the formulated problem is non-convex, an alternating optimization (AO) algorithm is proposed, which decomposes the problem into three subproblems that are solved using the successive convex approximation (SCA) method, Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) conditions, and an improved Harris Hawks Optimization (HHO) algorithm, respectively. Results and Discussions In the simulations, the proposed joint optimization scheme is compared to three baselines, including particle swarm optimization (PSO), fixed resource allocation, and random offloading and caching. First, the convergence of the proposed AO algorithm is verified ( Fig. 2 ). The results demonstrate that the algorithm achieves rapid convergence within a limited number of iterations across different sub-problems. Second, increasing the transmission bandwidth leads to a significant reduction in the total AIGC service latency (Fig. 3 ). This is because each device can occupy more bandwidth resources to send tasks. Similarly, the ES can allocate more bandwidth to send generated content in the downlink. Furthermore, the total AIGC service latency decreases with the ES’s storage capacity for all the schemes (Fig. 4 ). This is because an increase in storage capacity allows the ES to store more AIGC models, thus reducing the transmission delay between the ES and the cloud server. Additionally, as the required floating point operations per bit increase, the total AIGC service latency exhibits a significant upward trend across all schemes (Fig. 5 ). Finally, the total AIGC service latency for all schemes decreases as the BS’s maximum transmit power increases (Fig. 6 ). This trend is attributed to the fact that the improvement of the BS’s maximum transmit power strengthens the downlink signal-to-noise ratio, which improves the downlink transmission rate, thereby leading to a reduction in the total AIGC service latency. However, the proposed scheme mitigates this increase more effectively than the baselines, demonstrating its robustness in handling computationally demanding AIGC tasks. In conclusion, these simulation results confirm that, compared to baselines, the proposed schemes significantly minimize the total AIGC service latency.Conclusions This paper investigates communication, computation, and caching resource collaboration for supporting heterogeneous AIGC services. Our objective is to minimize the total latency of AIGC services by jointly optimizing the transmit power of AIoT devices and base stations, computing resource allocation, AIGC model deployment, and service offloading decisions, subject to computation and caching resource constraints. Since the formulated problem is a mixed-integer non-linear programming problem, an efficient AO algorithm is designed. This algorithm decomposes the original optimization problem into three sub-problems, which are solved via the SCA algorithm, KKT conditions, and the HHO algorithm, respectively. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can reduce the total AIGC service latency compared to baselines. -
1 基于交替优化算法求解$ {\mathcal{P}}_{0} $
初始化参数:$ {\boldsymbol{P}}^{(0)} $,$ {\boldsymbol{F}}^{(0)} $,$ {\boldsymbol{X}}^{(0)} $,$ {\boldsymbol{Y}}^{(0)} $,迭代次数$ l=1 $;定
义最大迭代次数$ {L}_{\max } $(1) While $ l\leq {L}_{\max } $ do (2) 给定$ \boldsymbol{F}={\boldsymbol{F}}^{(l-1)} $, $ \boldsymbol{X}={\boldsymbol{X}}^{(l-1)} $, $ \boldsymbol{Y}={\boldsymbol{Y}}^{(l-1)} $,求解问
题$ {\mathcal{P}}_{1} $获得发射功率$ {\boldsymbol{P}}^{(l)} $;(3) 给定$ \boldsymbol{P}={\boldsymbol{P}}^{(l)} $, $ \boldsymbol{X}={\boldsymbol{X}}^{(l-1)} $, $ \boldsymbol{Y}={\boldsymbol{Y}}^{(l-1)} $求解问题$ {\mathcal{P}}_{2} $
获得计算资源分配$ {\boldsymbol{F}}^{(l)} $;(4) 给定$ \boldsymbol{P}={\boldsymbol{P}}^{(l)} $, $ \boldsymbol{F}={\boldsymbol{F}}^{(l)} $求解问题$ {\mathcal{P}}_{3} $获得AIGC模型部
署决策$ {\boldsymbol{X}}^{(l)} $和服务请求决策$ {\boldsymbol{Y}}^{(l)} $;(5) 更新$ l=l+1 $; (6) End While: 收敛 -
[1] LI Xiaoxiao, XIE Yong, PENG Cong, et al. EPREAR: An efficient attribute-based proxy re-encryption scheme with fast revocation for data sharing in AIoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2025, 24(10): 11005–11018. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2025.3573288. [2] WEN Jinbo, NIE Jiangtian, ZHONG Yue, et al. Diffusion-model-based incentive mechanism with prospect theory for edge AIGC services in 6G IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(21): 34187–34201. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3445171. [3] LIU Yinqiu, DU Hongyang, NIYATO D, et al. ProSecutor: Protecting mobile AIGC services on two-layer blockchain via reputation and contract theoretic approaches[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2024, 23(12): 10966–10983. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2024.3390208. [4] 乔喆. 人工智能生成内容技术在内容安全治理领域的风险和对策[J]. 电信科学, 2023, 39(10): 136–146. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000−0801.2023190.QIAO Zhe. Risks and countermeasures of artificial intelligence generated content technology in content security governance[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2023, 39(10): 136–146. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000−0801.2023190. [5] WU Zijun, ZHANG Haijun, LIU Xiangnan, et al. IRS empowered MEC system with computation offloading, reflecting design, and beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2024, 72(5): 3051–3063. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2024.3354197. [6] 陈健, 马天瑞, 杨龙, 等. 面向移动边缘计算的协作NOMA安全卸载能耗优化[J/OL]. 电子与信息学报, https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.4494.TN.20251209.2144.002, 2025.CHEN Jian, MA Tianrui, YANG Long, et al. Energy consumption optimization of cooperative NOMA secure offload for mobile edge computing[J/OL]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.4494.TN.20251209.2144.002, 2025. [7] WU Mengru, CHEN Weijin, QIAN Liping, et al. Joint service caching and secure computation offloading for reconfigurable-intelligent-surface-assisted edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(19): 30469–30482. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3404972. [8] LIU Jian, XIAO Ming, WEN Jinbo, et al. Optimizing resource allocation for multi-modal semantic communication in mobile AIGC networks: A diffusion-based game approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2025, 11(5): 3346–3360. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2025.3529747. [9] 吴梦如, 孔亚威, 韩会梅, 等. 安全驱动的空地协同边缘计算网络中的服务缓存与计算卸载策略[J]. 通信学报, 2025, 46(7): 132–144. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2025130.WU Mengru, KONG Yawei, HAN Huimei, et al. Security-driven service caching and computation offloading strategy in air-ground collaborative edge computing networks[J]. Journal on Communications, 2025, 46(7): 132–144. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2025130. [10] WU Yinyu, ZHANG Xuhui, REN Jinke, et al. Latency-aware resource allocation for mobile edge generation and computing via deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Networking Letters, 2024, 6(4): 237–241. doi: 10.1109/LNET.2024.3486194. [11] FENG Jie, HUANG Xinqi, LIU Lei, et al. Resource allocation for task-oriented generative artificial intelligence in internet of things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(10): 13233–13247. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2025.3542473. [12] DENG Tao, CHEN Dongyu, JIA Juncheng, et al. Optimizing resource allocation and request routing for AI-generated content (AIGC) services in mobile edge networks with cell coupling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(11): 17911–17916. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3421351. [13] WU Jiaqi, ZHUANG Xinyi, TANG Ming, et al. QoE-aware offloading and resource allocation for MEC-empowered AIGC services[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2025, 24(10): 9664–9682. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2025.3563027. [14] XU Ding, DUAN Lingjie, and ZHU Hongbo. AIGC-enhanced hybrid content caching in wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2025, 24(8): 6780–6796. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2025.3556118. [15] ZHANG Xingxing, LI Shaobo, TANG Jianhang, et al. DRL-enabled computation offloading for AIGC services in IIoT-assisted edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(9): 12829–12844. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3523919. [16] FENG Weijia, ZHANG Ruojia, ZHU Yichen, et al. Exploring collaborative diffusion model inferring for AIGC-enabled edge services[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2025, 11(2): 946–960. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2024.3519320. [17] LI Zhiyang, CHEN Ming, CHEN Jinli, et al. Delay efficient caching enabled hierarchical mobile edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2025, 73(10): 9087–9101. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2025.3562526. [18] 徐勇军, 符加劲, 黄琼, 等. 智能反射面辅助的多天线通信系统鲁棒安全资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(1): 165–174. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221554.XU Yongjun, FU Jiajin, HUANG Qiong, et al. Robust secure resource allocation algorithm for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted multi-antenna communication systems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(1): 165–174. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221554. [19] ALI A, SHAH S A A, AL SHLOUL T, et al. Multiobjective harris hawks optimization-based task scheduling in cloud-fog computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(13): 24334–24352. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3391024. [20] HUANG Xietian, XU Wei, XIE Guo, et al. Learning oriented cross-entropy approach to user association in load-balanced HetNet[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(6): 1014–1017. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2846610. [21] JIANG Feibo, WANG Kezhi, DONG Li, et al. Deep-learning-based joint resource scheduling algorithms for hybrid MEC networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(7): 6252–6265. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2954503. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
