Multi-path resource allocation for confidential services based on network coding and fragmentation awareness of EONs
-
摘要: 机密业务在弹性光网络中传输和处理面临窃听攻击风险,论文提出一种网络编码(NC)和碎片感知的机密业务多路径传输资源分配方法。在该方法中,采用NC对机密业务进行加密传输;在路由选择阶段,设计感知窃听概率的路径代价函数和多路径保护方法确定业务传输的可靠性;在资源分配阶段,为机密业务设计满足NC约束的碎片感知频谱分配策略。仿真结果表明,与其他采用NC的路由算法相比,所提算法有效降低了业务阻塞率,提高了频谱利用率。Abstract:
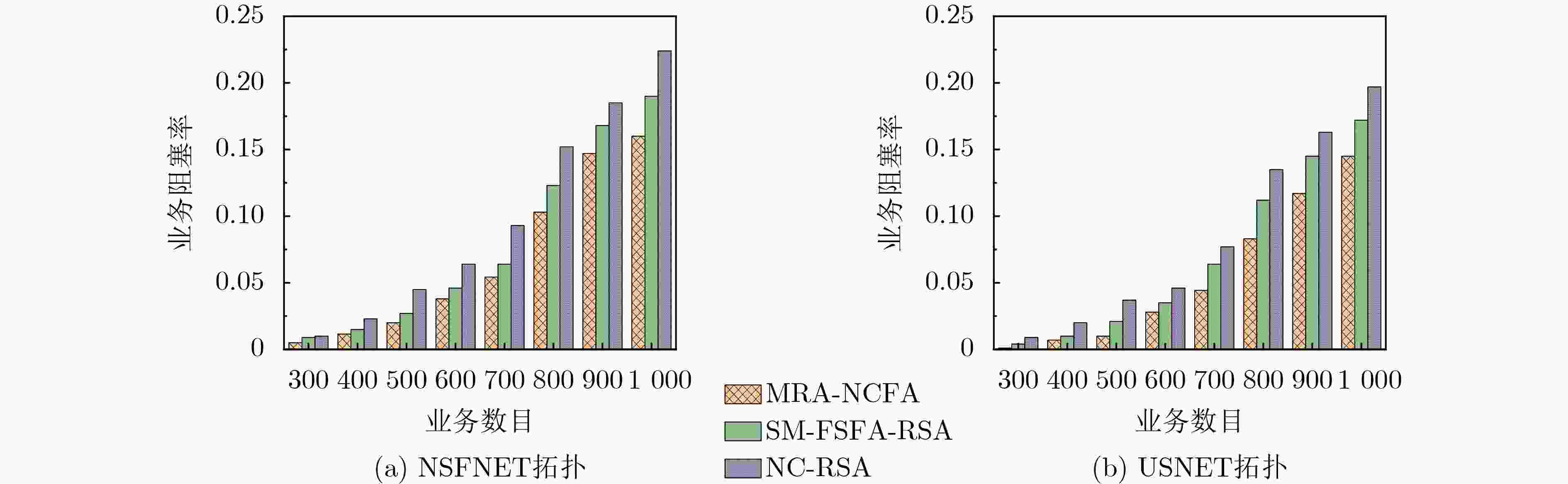
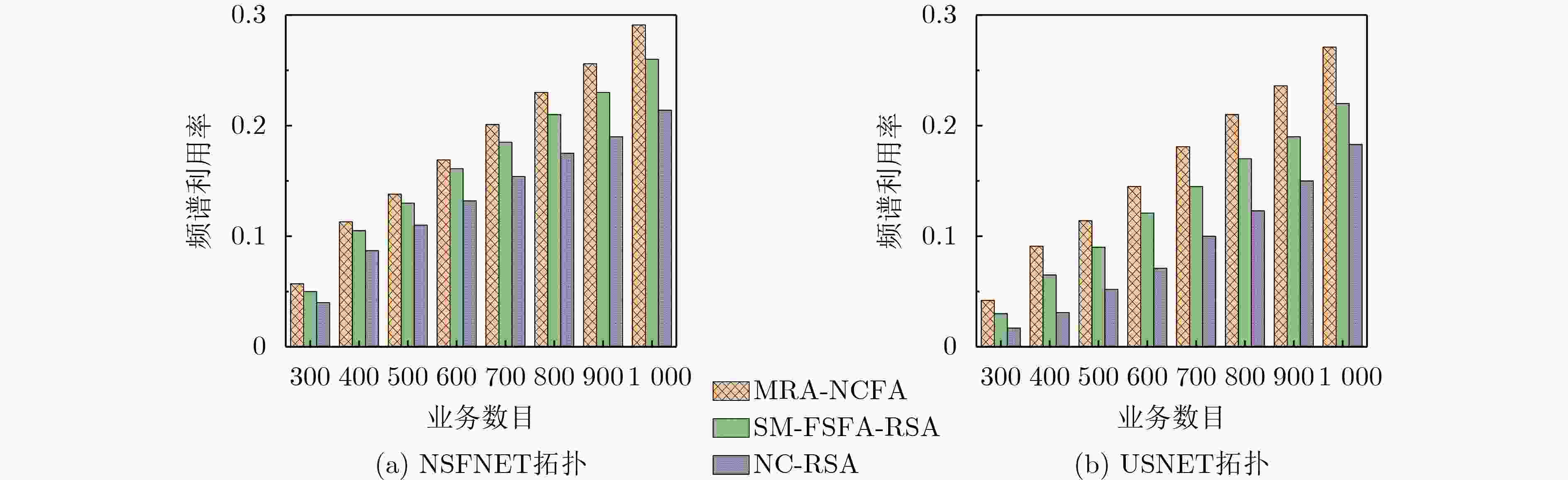
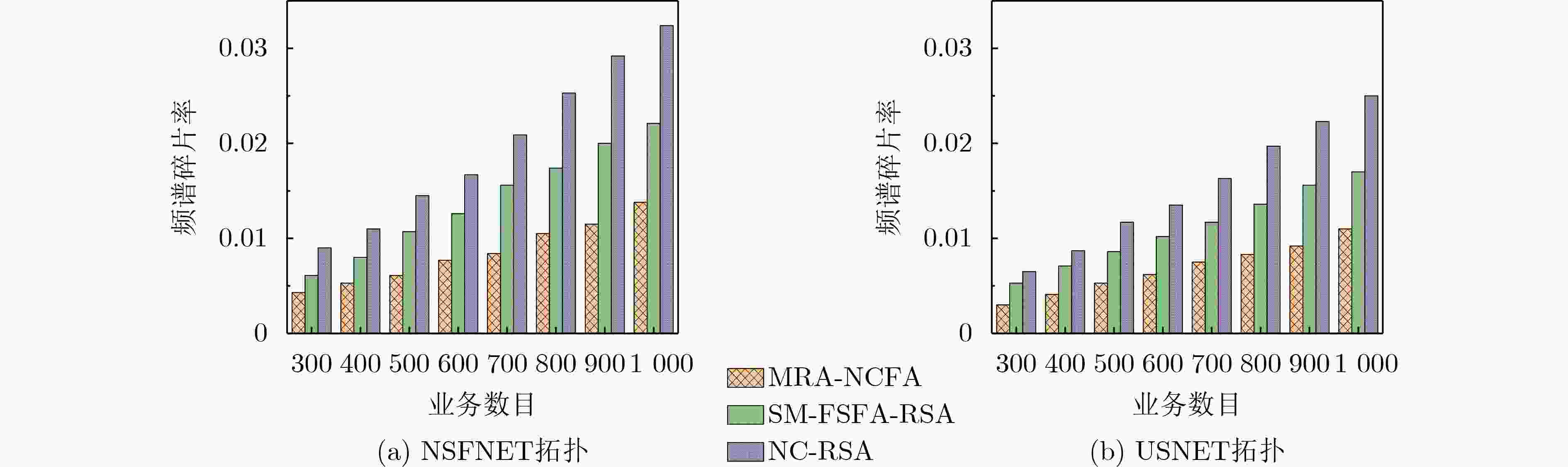
Objective Each fiber in Elastic Optical Networks (EONs) provides enormous bandwidth capacity and carries a large amount of services and data. Even if one of elements in EONs is eavesdropped or attacked in a short period of time, it will cause a large amount of data leakage or loss, resulting in a significant decrease in network performance. At the same time, more and more confidential are more sensitive to data leakage or loss on the path, and network attacks will damage the date of a large number of confidential services. Network Coding (NC) combines data from different services through XOR operation and transmits them over EONs. Then, it performs decoding operation at the receiving end to recover the original data information, opening up a new idea to avoid data eavesdropping on the path. However, the condition for NC is that there are encryption constraints in the EONs where the routing and Frequency Slot (FS) allocation of other services overlap with the routing and FS of the confidential service to be encrypted. Therefore, the routing and spectrum allocation of confidential services need to consider network coding constraints and the efficiency of routing and spectrum resource allocation. Methods A Multi-Path Resource Allocation based on Network Coding and Fragmentation Aware (MRA-NCFA) method is proposed to address the security and reliable transmission for confidential services in response to eavesdropping attacks. Firstly, the MRA-NCFA method uses network coding for data encryption in terms of services security, and employs the multi-path protection method for reliable services transmission. Secondly, in the routing stage, for non-confidential services, the focus is on balancing network payload and improving network resource utilization. So, a path weight function for non-confidential services is mainly designed based on path payload. And a path weight function includes the path hop, maximum idle spectrum block on the path, and the required FS of the service. The path corresponding to the maximum value of this function is selected as the transmission path for non-confidential services. For confidential services, in the routing selection stage, emphasis should be placed on whether information has been leaked, while also considering the availability of path resources. Therefore, a path cost function based on eavesdropping probability and a routing strategy considering eavesdropping probability have been designed. Finally, in the resource allocation stage, the purpose of non-confidential services is to maximize network spectrum efficiency. And it is necessary to avoid the generation of spectrum fragments as much as possible and maintain the continuity and consistency of resources. To this end, we have designed a fragment-sensing spectrum allocation strategy for non-confidential services. Through the designed fragment measurement formula, we measure the impact of service resource allocation on link resources. For confidential services, considering the constraints of encrypted transmission and FS matching, a spectrum allocation strategy based on FS and fragment sensing functions has been designed. This FS and fragment sensing function not only consider the impact of resource fragments, but also the impact of established services resources, providing high security for confidential services. Results and Discussions The proposed MRA-NCFA algorithm can get the lowest service blocking probability ( Figure 2 ) because both confidential and non-confidential services consider the impact of path resources in routing selection, and the impact of fragmentation is also taken into account in resource allocation, which can leave idle resources for subsequent services as much as possible. In addition, confidential services also adopt multi-path transmission methods, which can divide larger services into multiple sub services, which is conducive to the utilization of spectrum resources. With the increase of services, the spectrum utilization of MRA-NCFA algorithm has significantly improved. This is because the algorithm adopts multi-path transmission method, which can divide large services into small services and effectively utilize some small spectrum fragments. In addition, confidential and non-confidential services not only consider the number of resources in the path in routing selection, but also choose the path with less spectrum consumption. When allocating resources, both services consider the impact of fragments, avoiding the generation of fragments on the path and thus improving spectrum utilization (Figure 3 ). As the number of services increases, compared to other two algorithms, the proposed MRA-NCFA algorithm has the slowest and smallest increase in spectrum fragmentation ratio. This is because the MRA-NCFA algorithm adopts multi-path transmission method and fragment-sensing resource allocation method, which can improve the utilization of small-sized spectrum resource fragments and reduce the spectrum fragmentation ratio in EONs. Moreover, both confidential and non-confidential services consider the impact of fragmentation in resource allocation and take measures to reduce fragmentation rates. Therefore, its performance is better than that of compared Survivable Multipath Fragmentation-Sensitive Fragmentation-Aware Routing and Spectrum Assignment (SM-FSFA-RSA) and (Network Coding based Routing and Spectrum Allocation, NC-RSA) algorithms (Figure 4 ).Conclusions The resource allocation of protecting services against eavesdropping attacks in elastic optical networks is studied to guarantee the requirements of confidential services and reduce spectrum fragmentation. The MRA-NCFA is proposed. The MRA-NCFA algorithm employs network coding to encrypt confidential services and adopts multi-path protection to safeguard confidential services. For non-confidential services, a path weight function based on path resources is designed to select routes, and spectrum fragment metric values based on fragment aware are used to allocate resources. For confidential services, a path cost function considering path resources and eavesdropping probability is designed to select routes, a bandwidth segmentation function based on eavesdropping probability is used for multi-path transmission, and a frequency slot and fragment sensing function based on encryption constraints is used to allocate spectrum resources to ensure the reliability and security for confidential services. With the growth of security services in the Internet, the proposed MRA-NCFA can effectively reduce the traffic blocking probability and improve spectrum resource utilization. -
策略1依据路径权重函数值的非机密业务路由选择策略 输入:G(V, E, F),非机密业务r(s, d, B, 0) ,M集合,设置K值; 输出:非机密业务传输路径及其所需FS数。 S1:非机密业务r(s, d, B, 0)到达网络,初始化路径权重函数集合$ W=\varnothing $,转S2; S2:根据EONs拓扑、业务的源节点s、业务的目的节点d,执行最短路径算法,为业务找到K条最短候选路径; S3:根据式(9),计算每条候选路径的路径权重函数值,将其降序存入集合W中; S4:若W为空集,返回业务路由选择失败信息,否则,选择W中第一个路径权重函数对应的路径,作为非机密业务的传输路径; S5:从M中选择路径长度限制的最高调制等级m,由式(8)计算传输业务在该路径上所需FS数$ {N}_{r} $; S6:若传输路径上不存在满足$ {N}_{r} $的可用频谱块,从W中删除该路径,转S4;否则,标志该路径为非机密业务传输路径; S7:输出该非机密业务的传输路径及其所需FS数。 策略2 根据路径代价函数值的机密业务两路径选择策略 输入:G(V, E, F),各链路被窃听的概率值,机密业务r(s, d, B, 1),设置α1值,K值,Np=2; 输出:机密业务传输路径集$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $及其各路径所需FS数。 S1:机密业务r(s, d, B, 1)到达网络,初始化该业务的候选传输路径集$ {P}_{\text{cr}}=\varnothing $、路径代价函数集$ {F}_{C}=\varnothing $; S2:执行最短路径算法,为该业务找到K条最短的候选路径; S3:由式(11),计算机密业务每条候选路径的路径代价函数,将其升序存入集合FC中; S4:选择FC中前两条路径代价函数所对应的路径,标记为$ {p}_{1} $和$ {p}_{2} $,组成机密业务的传输路径集$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $; S5:由式(12),分别计算业务分割在$ {p}_{1} $和$ {p}_{2} $上的带宽值; S6:由式(8),选择路径长度限制的最高调制等级,分别计算业务分割带宽在$ {p}_{1} $和$ {p}_{2} $所需FS数; S7:若$ {p}_{1} $和$ {p}_{2} $上不存在满足机密业务FS需求的频谱块,从$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $中删除不满足业务带宽需求的路径,转S8,否则,转S9; S8:若$ {F}_{C} $所有候选路径的两两组合都不满足机密业务FS要求,结束策略2,执行策略3;否则,将$ {F}_{C} $中下一条候选路径加入$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $中,转S5; S9:输出机密业务的两条传输路径集$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $及在该各子路径上所需FS数。 策略3根据路径代价函数的机密业务三路径选择策略 输入:G(V, E, F),各链路被窃听的概率值,机密业务r(s, d, B, 1),设置α1和K值,Np=3; 输出:机密业务传输路径集$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $及其各路径所需FS数。 S1:业务r(s, d, B, 1)到达网络,初始化业务传输路径集$ {P}_{\text{cr}}=\varnothing $、路径代价函数集$ {F}_{C}=\varnothing $; S2:执行最短路径算法,为业务找到K条最短候选路径; S3:由式(11),计算机密业务在每条候选路径的路径代价函数,将其升序存入集合FC中; S4:选择FC中前三个路径代价函数所对应的路径,标记为$ {p}_{1} $、$ {p}_{2} $和$ {p}_{3} $,组成机密业务的传输路径集$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $; S5:由式(12),分别计算业务分割在$ {p}_{1} $、$ {p}_{2} $和$ {p}_{3} $上的带宽值; S6:由式(8),采用路径长度限制的最高调制等级,分别计算业务分割带宽在$ {p}_{1} $、$ {p}_{2} $和$ {p}_{3} $所需FS数; S7:若$ {p}_{1} $、$ {p}_{2} $和$ {p}_{3} $上不存在满足机密业务FS需求的频谱块,从$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $中删除不满足需求的路径,转S8;否则,转S9; S8:若枚举$ {F}_{C} $中所有候选路径组合,均不满足机密业务FS要求,返回路径选择失败信息;否则,将$ {F}_{C} $中下一条候选路径加入$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $中,
转S5;S9:输出机密业务的三条传输路径集$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $及在各子路径所需FS数。 策略4机密和非机密业务的资源分配策略 输入:G(V, E, F),业务r(s, d, B, δ),非机密业务的传输路径及其所需FS数,机密业务传输路径集$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $每条路径$ {p}_{k} $及其所需FS数,
EONs中已建立的其他业务的路径集合$ {P}_{\text{ed}} $和资源使用状态;输出:业务的频谱资源分配结果。 S1:初始化频谱碎片度量值集$ {\text{FR}}^{\text{SW}}=\varnothing $、候选加密路径集$ {P}_{\text{CC}}=\varnothing $、频隙与碎片感知函数值集$ {\Theta }^{\text{SW}}=\varnothing $; S2:若δ=0,执行策略1;由式(13),计算非机密业务在传输路径上分配每个可用频谱窗后路径的频谱碎片度量值,将其升序存入集合
$ {\text{FR}}^{\text{SW}} $中;S3:选择$ {\text{FR}}^{\text{SW}} $中最小值对应的频谱窗为非机密业务分配资源,输出非机密业务资源分配结果,结束算法。 S4:若δ=1,执行策略2,确定$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $和各子路径所需FS数目,从$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $中取出第1条路径$ {p}_{1} $,令$ {p}_{1}={p}_{0} $; S5:检查网络中已建立业务的路径集合$ {P}_{\text{ed}} $,找到与机密业务所选传输路径$ {p}_{0} $至少有2个公共节点的路径,存入候选加密路径集$ {P}_{\text{CC}} $中; S6:若$ {P}_{\text{CC}} $中路径满足$ {p}_{0} $的NC约束条件,则将该路径存入$ {P}_{\text{CC}} $中,若$ {P}_{\text{CC}} $不为空,转S7;否则,标记$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $中路径资源分配失败,转S9; S7:由式(14),为路径$ {p}_{0} $计算分配每个可用频谱窗后路径的频隙与碎片感知函数值,将其升序存入$ {\Theta }^{\text{SW}} $中,若$ {\Theta }^{\text{SW}} $为空,转S9;否则,
转S8;S8:选择$ {\Theta }^{\text{SW}} $中最小值对应的频谱窗分配给$ {p}_{0} $,若$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $中每条路径资源分配都成功,则转S9;否则,选择$ {P}_{\text{cr}} $中下一条路径,记为$ {p}_{0} $,转
S5;S9:若机密业务传输路径资源分配成功,输出机密业务资源分配成功结果;否则,输出机密业务资源分配失败结果,阻塞该机密业务请求。 -
[1] 徐勇军, 李晶, 骆东鑫, 等. 近场通信物理层安全技术综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(11): 4129–4143. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250336.XU Yongjun, LI Jing, LUO Dongxin, et al. A survey on physical layer security in near-field communication[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(11): 4129–4143. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250336. [2] 黄蔚亮, 李锦煊, 余志文, 等. 确定性网络: 架构、关键技术和应用[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报: 自然科学版, 2025, 37(1): 1–16. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.202409020229.HUANG Weiliang, LI Jinxuan, YU Zhiwen, et al. Deterministic networks: Standards, architectures and applications[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications: Natural Science Edition, 2025, 37(1): 1–16. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.202409020229. [3] 刘焕淋, 张建剑, 陈勇, 等. 弹性光网络中基于频谱窗滑动的时变业务共享保护方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(10): 3694–3701. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221406.LIU Huanlin, ZHANG Jianjian, CHEN Yong, et al. A time-varying traffic sharing protection based on spectrum window sliding in elastic optical networks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(10): 3694–3701. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221406. [4] 刘焕淋, 谭明明, 任杰, 等. 基于频谱切片的弹性光网络中可调度请求资源分配算法[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 35(2): 286–293. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.202201050007.LIU Huanlin, TAN Mingming, REN Jie, et al. Resource allocation algorithm for scheduled lightpath demands in elastic optical networks based on spectrum slicing[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications: Natural Science Edition, 2023, 35(2): 286–293. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.202201050007. [5] SAVVA G, MANOUSAKIS K, and ELLINAS G. Confidentiality meets protection in elastic optical networks[J]. Optical Switching and Networking, 2021, 42: 100620. doi: 10.1016/j.osn.2021.100620. [6] ZOU Yucong, CAI Xiaofeng, ZHU Min, et al. Nonlinear impairment-aware RMSA under the sliding scheduled traffic model for EONs based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2023, 41(22): 6854–6864. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2023.3299272. [7] SAVVA G, MANOUSAKIS K, and ELLINAS G. A network coding optimization approach for physical layer security in elastic optical networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2025, 22(2): 1145–1159. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2024.3498108. [8] LIU Huanlin, TANG Chang, CHEN Yong, et al. A survivable multipath resource allocation strategy based on fragmentation-sensitive fragmentation-aware in space division multiplexing elastic optical networks[J]. Computer Communications, 2023, 204: 78–88. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2023.03.025. [9] XU He, WANG Hongxiang, and JI Yuefeng. Secure and efficient resource allocation for anti-eavesdropping in MCF-based SDM-EONs[C]. Proceedings of 2021 Asia Communications and Photonics Conference, Shanghai, China, 2021: 1–3. [10] 赵夙, 王伟, 朱晓荣, 等. 基于自适应网络编码的异构无线链路并发传输控制方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(8): 2777–2784. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210520.ZHAO Su, WANG Wei, ZHU Xiaorong, et al. Research on concurrent transmission control of heterogeneous wireless links based on adaptive network coding[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(8): 2777–2784. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210520. [11] ARABUL E, OLIVEIRA R D, EMAMI A, et al. 100 Gbps quantum-secured and O-RAN-enabled programmable optical transport network for 5G fronthaul[J]. Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 2023, 15(8): C223–C231. doi: 10.1364/JOCN.483644. [12] HAI D T. On routing, wavelength, network coding assignment, and protection configuration problem in optical-processing-enabled networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2023, 20(3): 2504–2514. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2023.3283880. [13] HU Liyazhou, WANG Wei, PAN Yuanyuan, et al. Security enhanced routing and spectrum allocation against crosstalk attacks for confidential lightpath in elastic optical networks[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(5): 7254–7275. doi: 10.1364/OE.511055. [14] 刘焕淋, 邓棣, 陈勇, 等. 基于网络编码的机密业务多路径光传输方法[J]. 电子学报, 2024, 52(9): 3272–3277. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20230856.LIU Huanlin, DENG Di, CHEN Yong, et al. A network coding-based multipath optical transmission method for secret traffic[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2024, 52(9): 3272–3277. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20230856. [15] LIU Huanlin, HUO Xingji, CHEN Yong, et al. Shared protection survivable multipath-based VONE in EONs integrated with QKD[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2024, 42(17): 5800–5807. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2024.3406349. [16] YU Mingxuan, JIANG Jing, SHANG T, et al. A load balancing and time-frequency fragmentation-aware algorithm for elastic optical network[C]. Proceedings of 2023 Asia Communications and Photonics Conference/2023 International Photonics and Optoelectronics Meetings, Wuhan, China, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ACP/POEM59049.2023.10369171. [17] SRIVASTAVA R and SINGH Y N. A novel fragmentation metric and fragmentation-aware adaptive routing and spectrum allocation algorithm in elastic optical network[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2025, 94: 104318. doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2025.104318. [18] 张盛峰, 陈会丹, 彭樱. SDM-EON中基于串扰避免的多纤芯分配算法[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 35(1): 23–30. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.202109190334.ZHANG Shengfeng, CHEN Huidan, and PENG Ying. Multi-core assignment algorithm based on crosstalk-avoiding in space division multiplexing elastic optical networks[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications: Natural Science Edition, 2023, 35(1): 23–30. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.202109190334. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
