Vision-Guided and Force-Controlled Method for Robotic Screw Assembly
-
摘要: 随着工业自动化与智能制造的发展,机器人在精密装配任务中应用广泛,尤其在螺栓装配等高精度作业环节中发挥着重要作用。然而,在螺栓装配过程中,存在目标物体位姿不确定、微小孔位识别困难以及末端执行器姿态缺乏动态闭环修正等问题。为此,该文提出一种面向机器人螺栓装配的视觉感知与力控协同方法。首先,构建语义增强的6D位姿估计算法,通过融合开放词汇目标检测模块与通用分割模块增强目标感知能力,提升初始位姿精度,并在连续帧跟踪中引入语义约束与平移修正,实现动态环境下稳健跟踪。其次,设计基于改进NanoDet的螺纹孔检测算法,采用轻量级MobileNetV3作为特征提取网络,并增加圆形分支检测头,有效提高微小孔位的识别精度与边界拟合能力,为后续装配提供可靠特征基础。最后,提出分层视觉引导与力控协同的装配策略,通过全局粗定位与局部精定位逐级优化目标位姿,并结合末端力觉反馈进行姿态微调,实现螺栓与螺纹孔的高精度对准与稳定装配。实验结果表明,该文方法在装配精度、鲁棒性及稳定性方面均具有显著优势,具备良好的工程应用前景。Abstract:
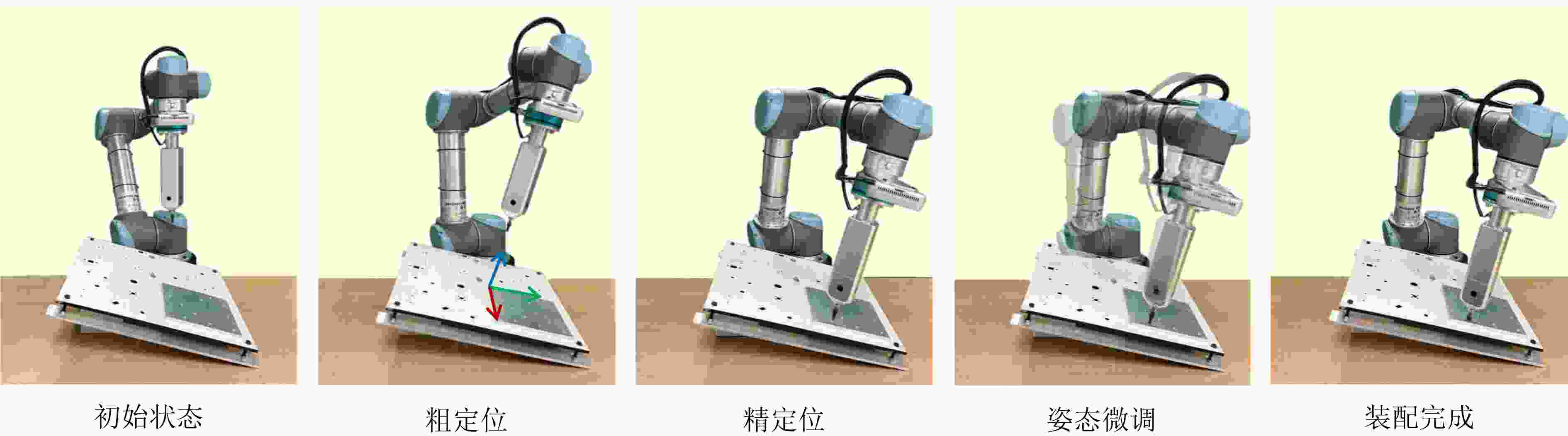
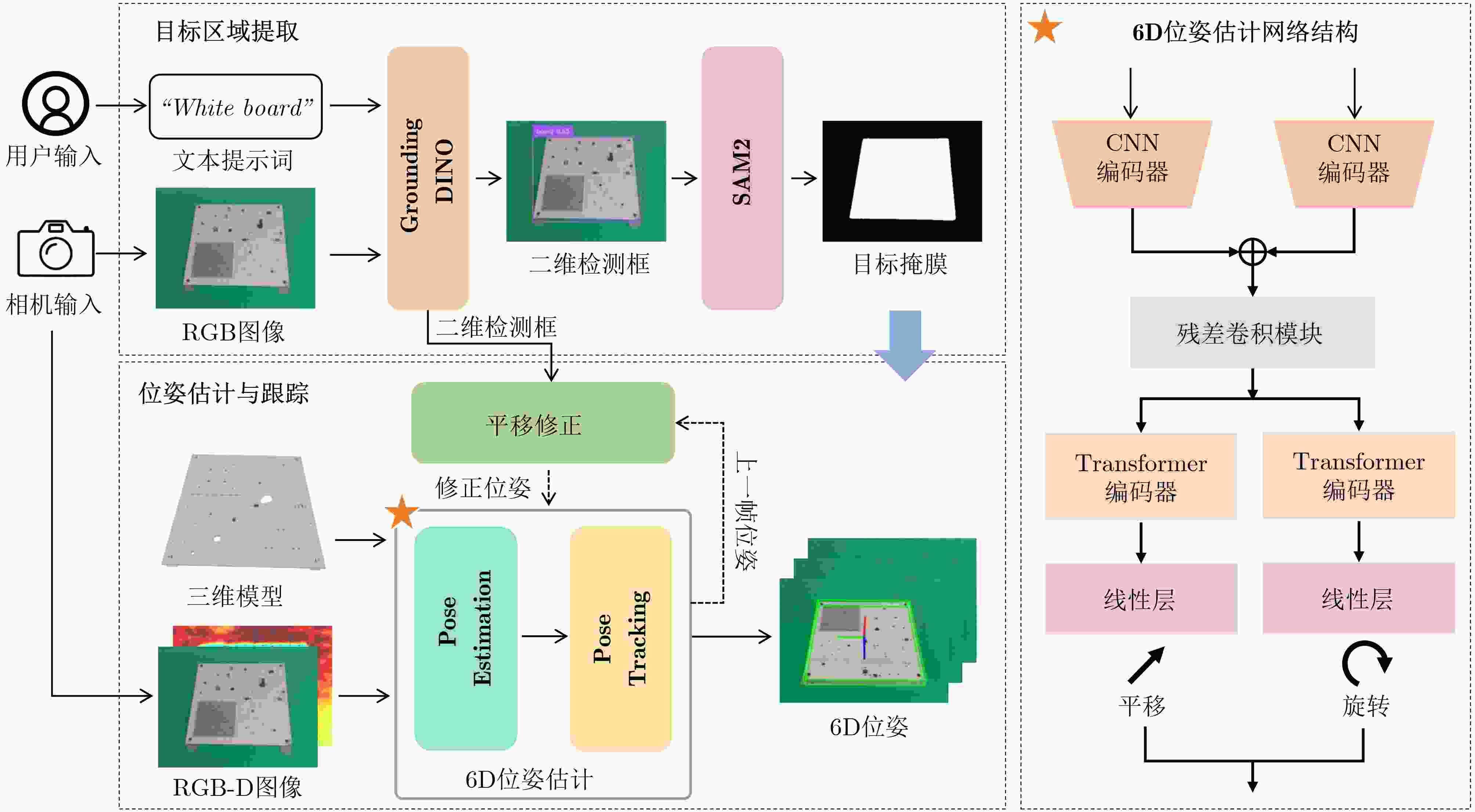
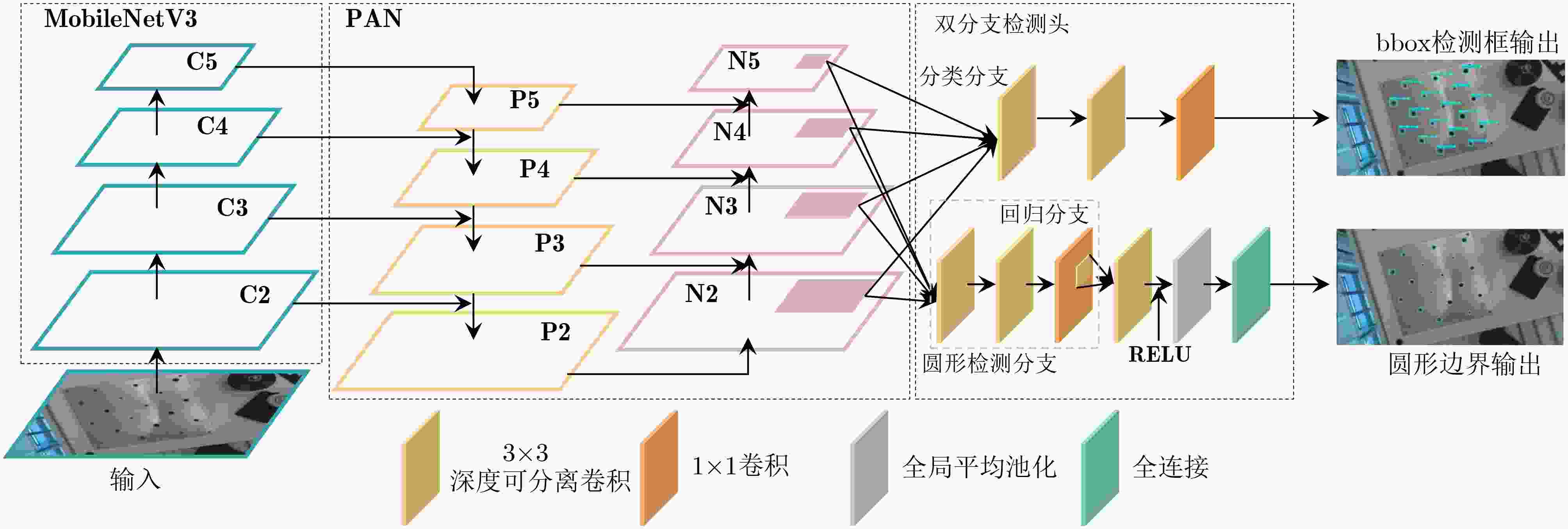
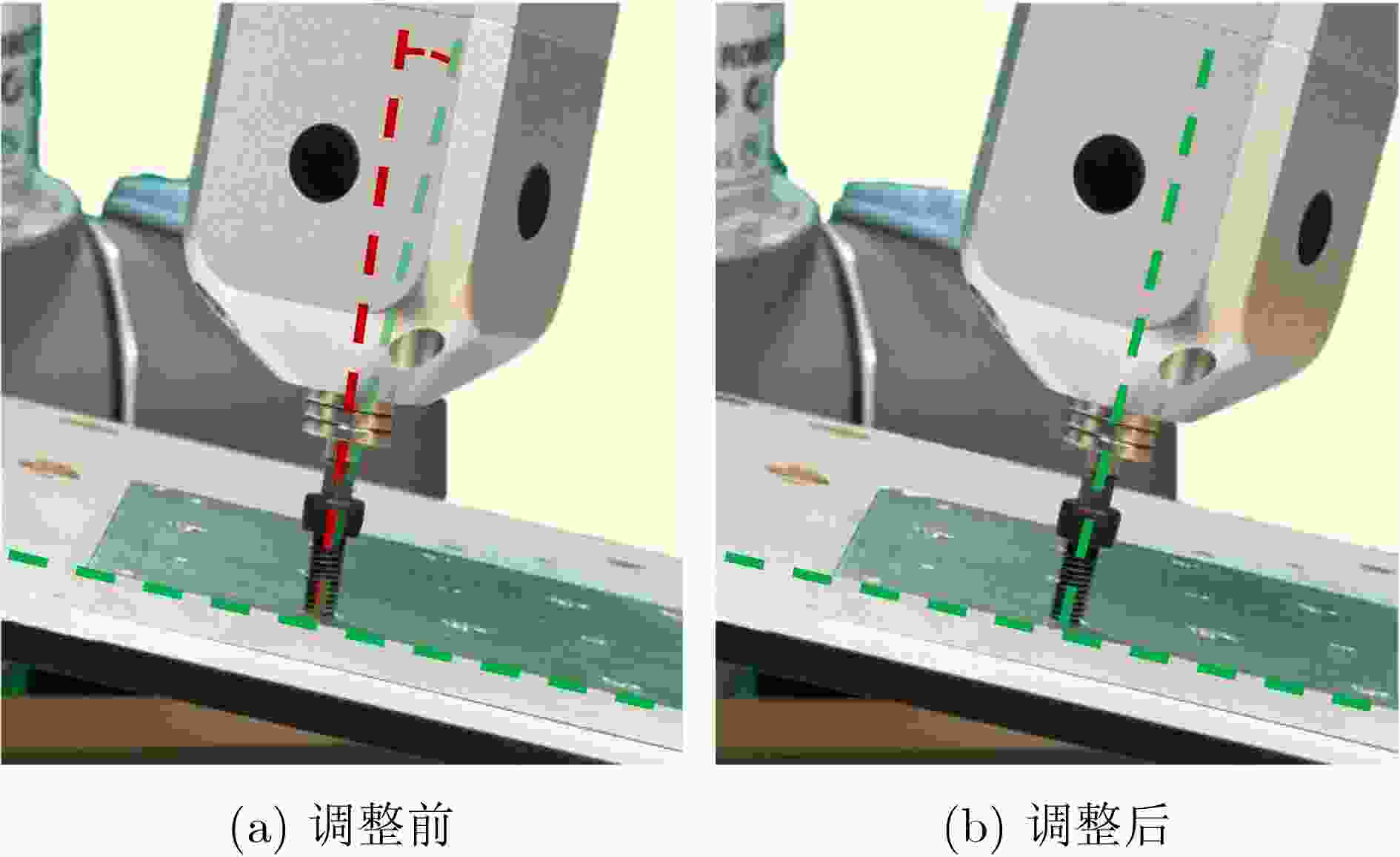
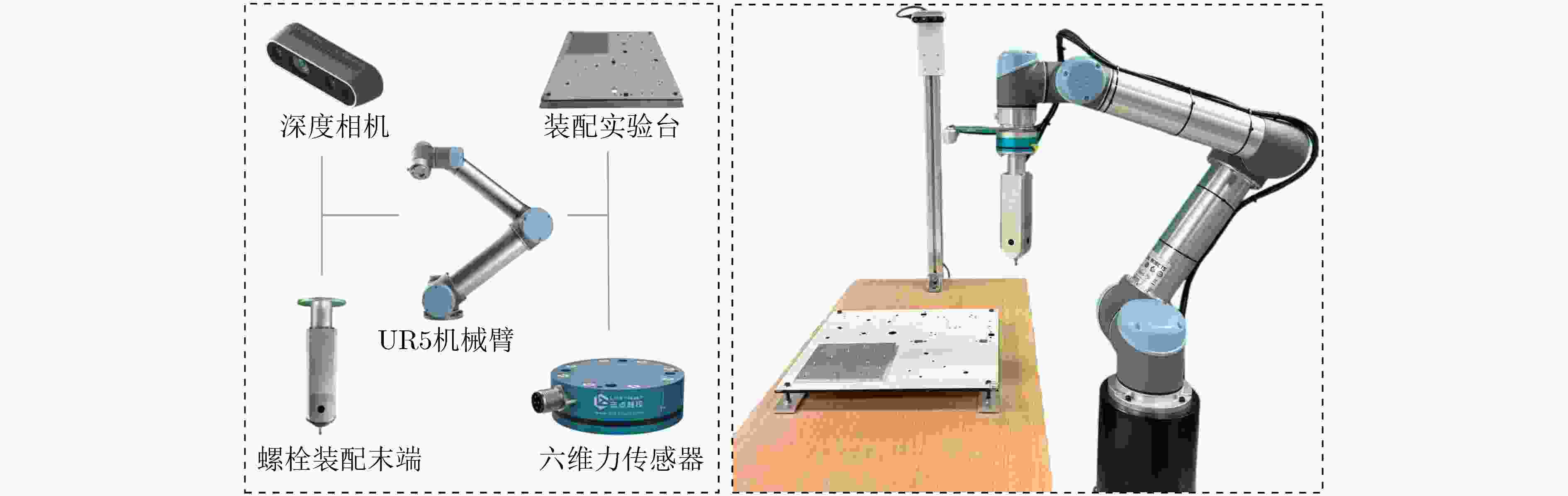
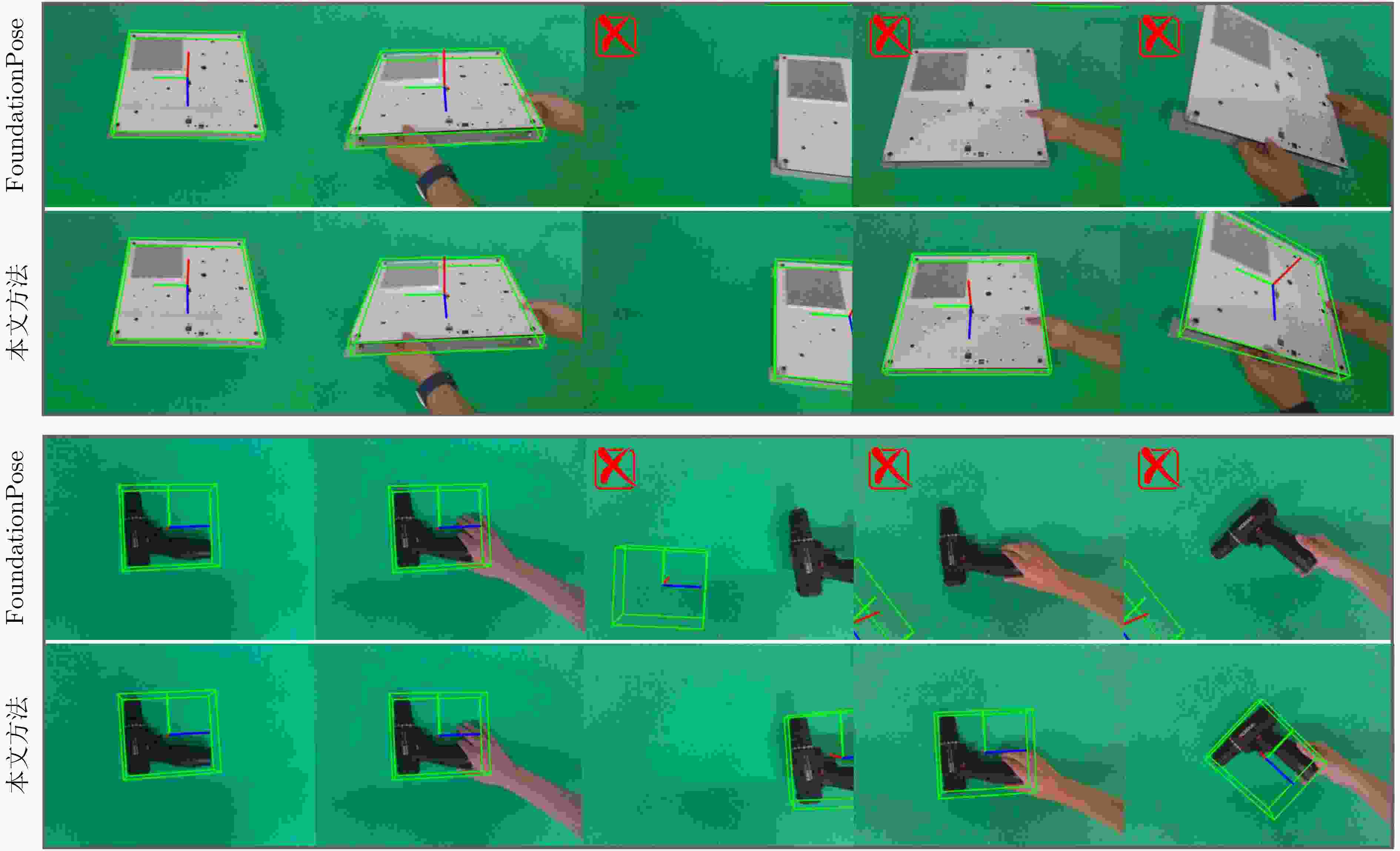
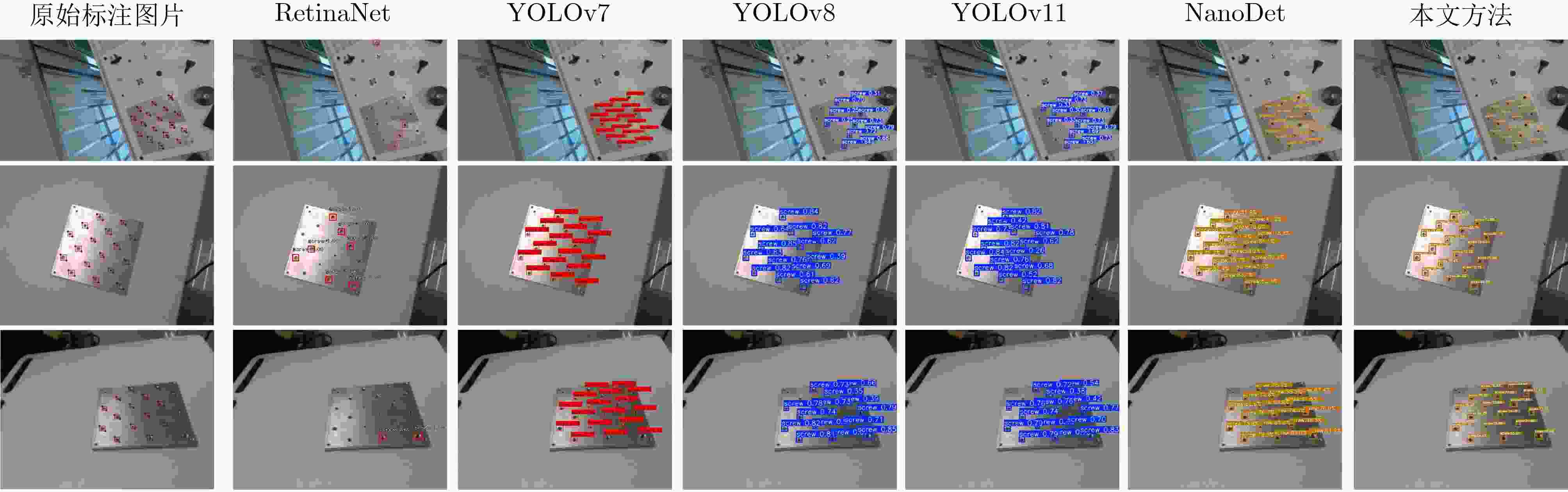
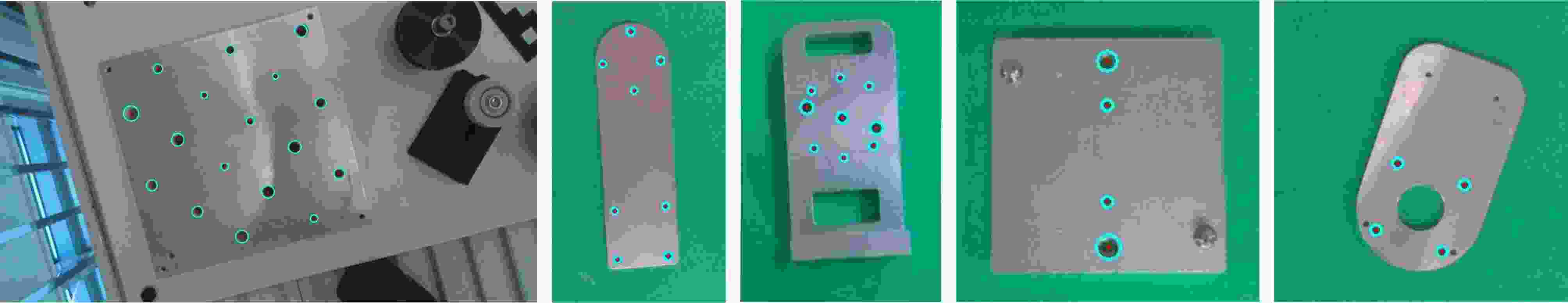
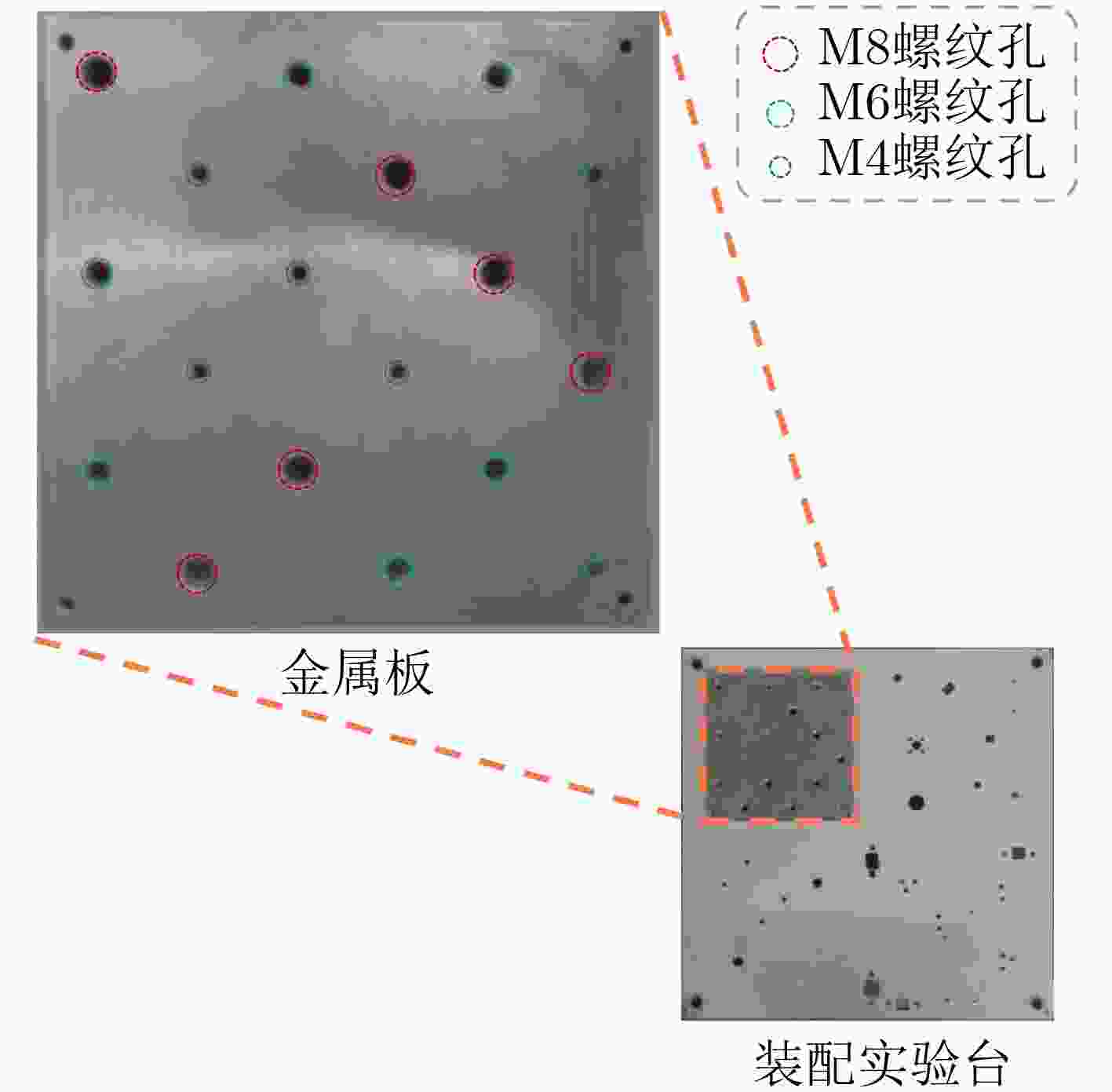
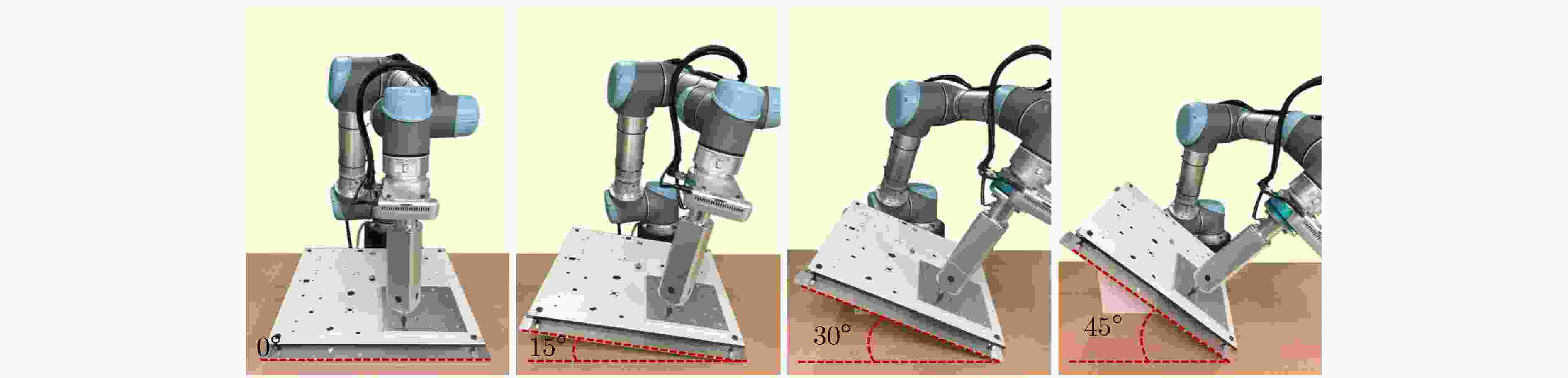
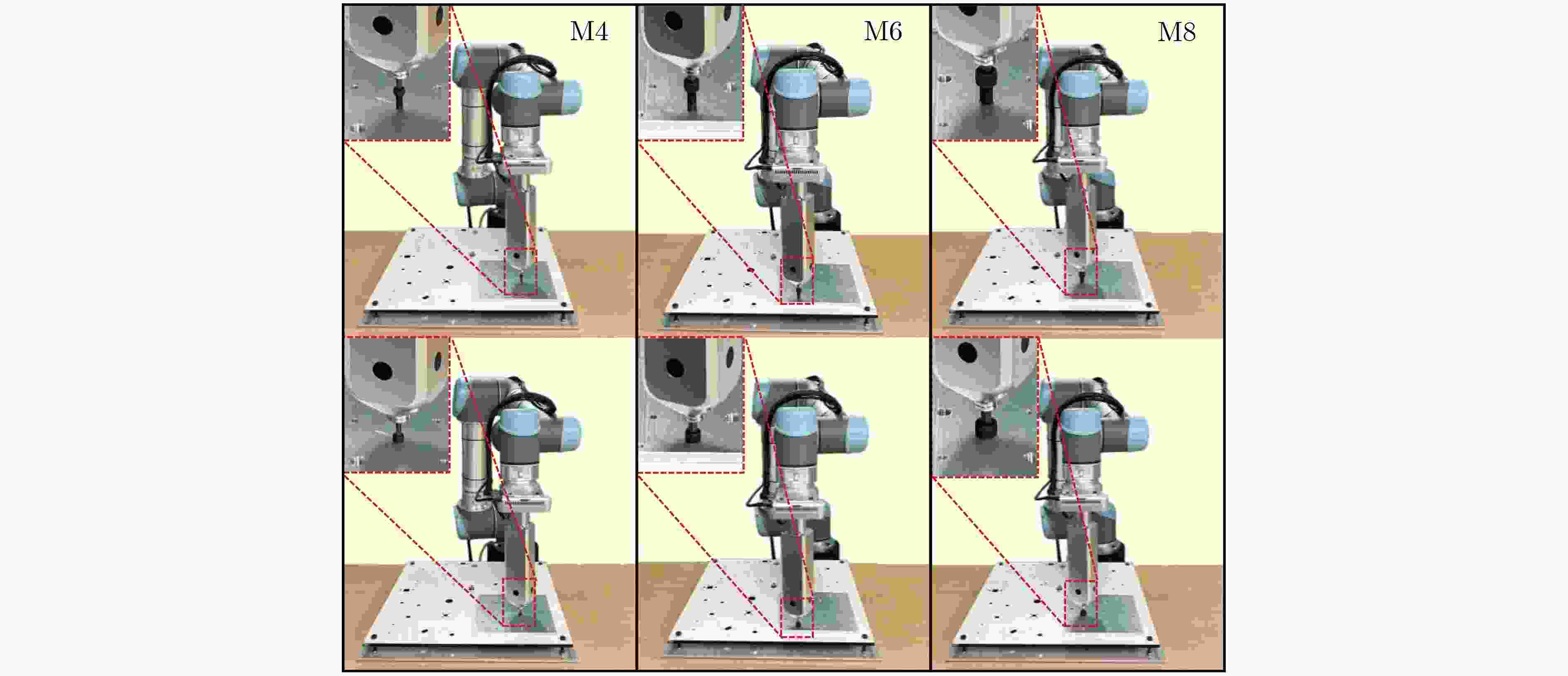
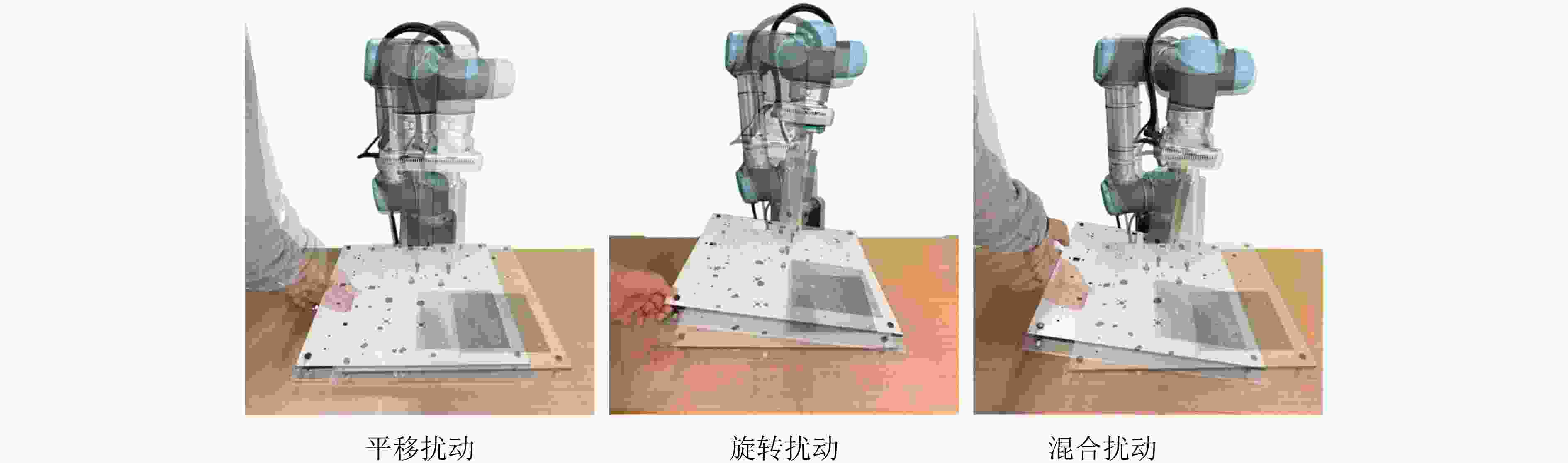
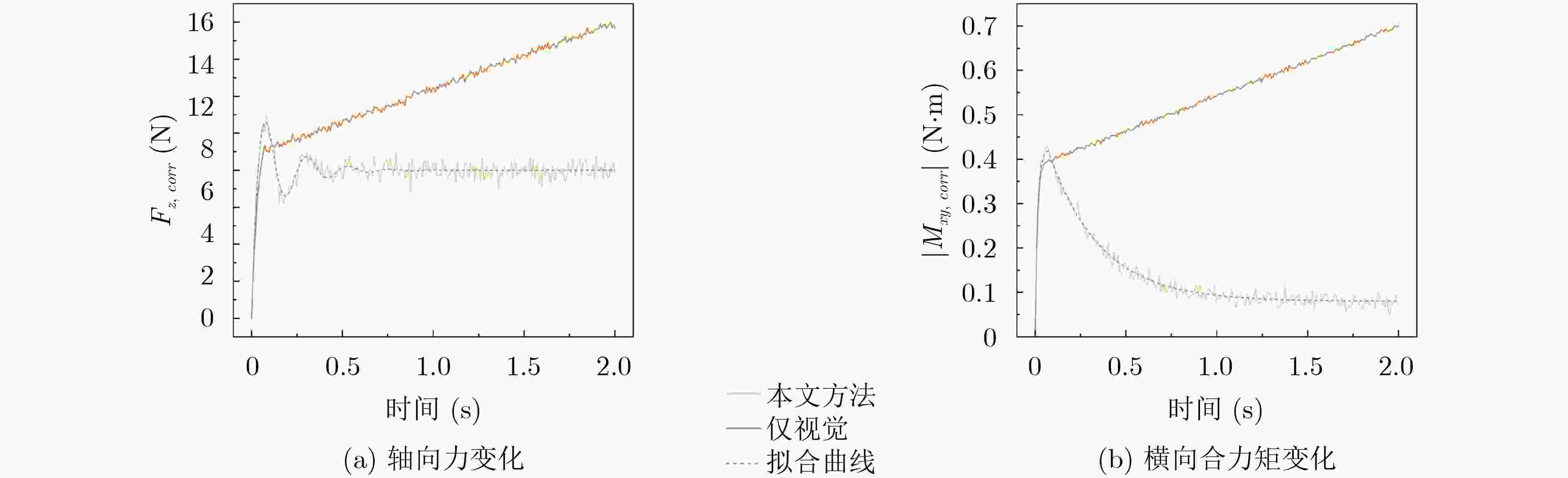
Objective With the rapid development of intelligent manufacturing and industrial automation, robots have been increasingly applied to high-precision assembly tasks, especially in screw assembly. However, existing assembly systems still face multiple challenges. First, the pose of assembly objects is often uncertain, making initial localization difficult. Second, small features such as threaded holes are blurred and hard to identify accurately. Third, traditional vision-based open-loop control may lead to assembly deviation or jamming. To address these issues, this study proposes a vision–force cooperative method for robotic screw assembly. The method builds a closed-loop assembly system that covers both coarse positioning and fine alignment. A semantic-enhanced 6D pose estimation algorithm and a lightweight hole detection model are used to improve perception accuracy. Force feedback control is then applied to adjust the end-effector posture dynamically. The proposed approach improves the accuracy and stability of screw assembly. Methods The proposed screw assembly method is built on a vision–force cooperative strategy, forming a closed-loop process. In the visual perception stage, a semantic-enhanced 6D pose estimation algorithm is applied to handle disturbances and pose uncertainty in complex industrial environments. During initial pose estimation, Grounding DINO and SAM2 jointly generate pixel-level masks to provide semantic priors for the FoundationPose module. In the continuous tracking stage, semantic constraints from Grounding DINO are used for translational correction. For detecting small threaded holes, an improved lightweight hole detection algorithm based on NanoDet is designed. It uses MobileNetV3 as the backbone and adds a CircleRefine module in the detection head to regress the hole center precisely. In the assembly positioning stage, a hierarchical vision-guided strategy is used. The global camera conducts coarse positioning to provide overall guidance. The hand-eye camera then performs local correction based on hole detection results. In the closed-loop assembly stage, force feedback is applied for posture adjustment, achieving precise alignment between the screw and the threaded hole. Results and Discussions The proposed method is experimentally validated in robotic screw assembly scenarios. The improved 6D pose estimation algorithm reduces the average position error by 18% and the orientation error by 11.7% compared with the baseline (Tbl.1). The tracking success rate in dynamic sequences increases from 72% to 85% (Tbl.2). For threaded hole detection, the lightweight algorithm based on the improved NanoDet is evaluated using a dataset collected from assembly scenarios. The algorithm achieves 98.3% precision, 99.2% recall and 98.7% mAP on the test set (Tbl.3). The model size is only 11.7 MB and the computation cost is 2.9 GFLOPS. This remains lower than most benchmark models while maintaining high accuracy. A circular branch is introduced to fit hole edges ( Fig.8 ), providing accurate center for visual guidance. Under various inclination angles (Fig.10 ), the assembly success rate stays above 91.6% (Tbl.4). For screws of different sizes (M4, M6 and M8), the success rate remains higher than 90% (Tbl.5). Under small external disturbances (Fig.12 ), the success rates reach 93.3%, 90% and 83.3% for translational, rotational and mixed disturbances, respectively (Tbl.6). Force-feedback comparison experiments show that the assembly success rate is 66.7% under visual guidance alone. When force feedback is added, the success rate increases to 96.7% (Tbl.7). The system demonstrated stable performance throughout a screw assembly cycle, achieving an average total cycle time of 9.53 seconds (Tbl.8), thereby meeting industrial assembly requirements.Conclusions This study proposes a vision and force control cooperative method to address several challenges in robotic screw assembly. The approach improves target localization accuracy through a semantics-enhanced 6D pose estimation algorithm and a lightweight threaded-hole detection network. By integrating a hierarchical vision-guided strategy with force-feedback control, precise alignment between the screw and the threaded hole is achieved. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method ensures reliable assembly under various conditions, providing a feasible solution for intelligent robotic assembly. Future work will focus on adaptive force control, multimodal perception fusion and intelligent task planning to further enhance the system’s generalization and self-optimization capabilities in complex industrial environments. -
表 1 初始位姿估计对比实验结果
任务 FoundationPose 本文方法 PE/m OE/° PE/m OE/° 1 0.0121 5.083 0.0095 3.974 2 0.0120 5.122 0.0091 4.439 3 0.0101 4.281 0.0083 4.006 4 0.0106 3.462 0.0097 3.158 5 0.0121 4.228 0.0098 3.969 6 0.0120 4.047 0.0083 3.953 7 0.0102 3.796 0.0920 3.411 8 0.0111 4.821 0.0102 3.724 9 0.0106 5.108 0.0088 4.501 10 0.0103 4.656 0.0081 4.204 平均误差 0.0111 4.460 0.0091 3.934 表 2 跟踪性能对比实验结果
算法 总帧数 成功帧数 TSR/% FoundationPose 视频1 641 502 72 视频2 917 698 视频3 695 428 本文方法 视频1 641 576 85 视频2 917 797 视频3 695 548 表 3 不同模型的对比实验结果
模型 mAP@0.5(%) P(%) R(%) Weights/MB GFLOPs RetinaNet 26.3 98.1 26.6 145.7 34.6 YOLOv7 97.4 96.4 97.2 74.8 13.2 YOLOv8 98.1 98.5 91.4 18.9 6.0 YOLOv11 98.1 98.6 92.8 15.6 4.6 NanoDet 97.5 96.7 98.8 7.6 1.9 本文方法 98.7 98.3 99.2 11.7 2.9 表 4 不同倾角装配性能实验结果
倾角 实验次数 成功次数 成功率(%) 0° 30 29 96.7 15° 30 29 96.7 30° 30 27 90 45° 30 25 83.3 表 5 不同螺栓规格装配性能实验结果
螺栓规格 方法(原NanoDet) 本文方法(改进NanoDet) 实验次数 成功次数 成功率(%) 实验次数 成功次数 成功率(%) M8 30 28 93.3 30 30 100 M6 30 27 90 30 29 96.7 M4 30 24 80 30 27 90 表 6 动态扰动装配性能实验结果
扰动类型 实验次数 成功次数 成功率(%) 平移扰动 30 28 93.3 旋转扰动 30 27 90 混合扰动 30 25 83.3 表 7 力觉反馈对比实验结果
实验条件 实验次数 成功次数 成功率(%) 仅视觉 30 20 66.7 本文方法 30 29 96.7 表 8 全流程装配各阶段时间统计结果
装配环节 平均耗时(s) 标准差(s) 初始位姿估计 3.60 0.25 粗定位移动 1.20 0.18 螺纹孔检测 0.086 0.009 精定位移动 0.97 0.08 姿态微调 2.15 0.22 螺栓锁付 1.52 0.10 单次装配总周期时间 9.53 0.42 -
[1] 王耀南, 江一鸣, 姜娇, 等. 机器人感知与控制关键技术及其智能制造应用[J]. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 494–513. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220995.WANG Yaonan, JIANG Yiming, JIANG Jiao, et al. Key technologies of robot perception and control and its intelligent manufacturing applications[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 494–513. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220995. [2] SUN Fuchun, MIAO Shengyi, ZHONG Daming, et al. Manipulation skill representation and knowledge reasoning for 3C assembly[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2025, 30(6): 5387–5397. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2025.3543739. [3] LIU Yang, CHEN Weixing, BAI Yongjie, et al. Aligning cyber space with physical world: A comprehensive survey on embodied AI[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2025, 30(6): 7253–7274. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2025.3574943. [4] WEN Bowen, YANG Wei, KAUTZ J, et al. FoundationPose: Unified 6D pose estimation and tracking of novel objects[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 17868–17879. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.01692. [5] ZHOU Chuangchuang, WU Yifan, STERKENS W, et al. Towards robotic disassembly: A comparison of coarse-to-fine and multimodal fusion screw detection methods[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2024, 74: 633–646. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2024.04.024. [6] HE Yisheng, SUN Wei, HUANG Haibin, et al. PVN3D: A deep point-wise 3D keypoints voting network for 6DoF pose estimation[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 11629–11638. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01165. [7] HE Yisheng, HUANG Haibin, FAN Haoqiang, et al. FFB6D: A full flow bidirectional fusion network for 6D pose estimation[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 3002–3012. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00302. [8] LEE T, TREMBLAY J, BLUKIS V, et al. TTA-COPE: Test-time adaptation for category-level object pose estimation[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 21285–21295. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.02039. [9] ZHANG Ruida, DI Yan, MANHARDT F, et al. SSP-pose: Symmetry-aware shape prior deformation for direct category-level object pose estimation[C]. 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 2022: 7452–7459. doi: 10.1109/IROS47612.2022.9981506. [10] LABBÉ Y, MANUELLI L, MOUSAVIAN A, et al. MegaPose: 6D pose estimation of novel objects via render & compare[C]. Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Robot Learning, Auckland, New Zealand, 2023: 715–725. [11] LI Fu, VUTUKUR S R, YU Hao, et al. NeRF-pose: A first-reconstruct-then-regress approach for weakly-supervised 6D object pose estimation[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Paris, France, 2023: 2115–2125. doi: 10.1109/ICCVW60793.2023.00226. [12] SUN Jiaming, WANG Zihao, ZHANG Siyu, et al. OnePose: One-shot object pose estimation without CAD models[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 6815–6824. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00670. [13] HE Xingyi, SUN Jiaming, WANG Yuang, et al. OnePose++: Keypoint-free one-shot object pose estimation without CAD models[C]. Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 2544. doi: 10.5555/3600270.3602814. [14] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. doi: 10.5555/2999134.2999257. [15] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824. [16] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031. [17] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91. [18] JOCHER G. Ultralytics YOLOv5[EB/OL]. https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5, 2022. [19] JOCHER G, CHAURASIA A, and QIU J. Ultralytics YOLOv8[EB/OL]. https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics, 2023. (查阅网上资料,未能确认网址与文献是否相符). [20] JOCHER G and QIU J. Ultralytics YOLO11[EB/OL]. https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics, 2024. (查阅网上资料,未能确认网址与文献是否相符). [21] JHA D K, ROMERES D, JAIN S, et al. Design of adaptive compliance controllers for safe robotic assembly[C]. 2023 European Control Conference (ECC), Bucharest, Romania, 2023: 1–8. doi: 10.23919/ECC57647.2023.10178229. [22] SPECTOR O, TCHUIEV V, and DI CASTRO D. InsertionNet 2.0: Minimal contact multi-step insertion using multimodal multiview sensory input[C]. 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, USA, 2022: 6330–6336. doi: 10.1109/ICRA46639.2022.9811798. [23] LEE G, LEE J, NOH S, et al. PolyFit: A peg-in-hole assembly framework for unseen polygon shapes via sim-to-real adaptation[C]. 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2024: 533–540. doi: 10.1109/IROS58592.2024.10802554. [24] OTA K, JHA D K, JAIN S, et al. Autonomous robotic assembly: From part singulation to precise assembly[C]. 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2024: 13525–13532. doi: 10.1109/IROS58592.2024.10802423. [25] LIU Shilong, ZENG Zhaoyang, REN Tianhe, et al. Grounding DINO: Marrying DINO with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection[C]. 18th European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 2025: 38–55. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-72970-6_3. [26] RAVI N, GABEUR V, HU Yuanting, et al. SAM 2: Segment anything in images and videos[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2408.00714, 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2408.00714. (查阅网上资料,不确定本条文献类型及格式是否正确,请确认). [27] RANGILYU. NanoDet-plus: Super fast and high accuracy lightweight anchor-free object detection model[EB/OL]. https://github.com/RangiLyu/nanodet, 2021. [28] HOWARD A, SANDLER M, CHEN Bo, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 1314–1324. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00140. [29] 张立建, 胡瑞钦, 易旺民. 基于六维力传感器的工业机器人末端负载受力感知研究[J]. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(3): 439–447. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150753.ZHANG Lijian, HU Ruiqin, and YI Wangmin. Research on force sensing for the end-load of industrial robot based on a 6-axis force/torque sensor[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 439–447. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150753. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
