Routing and Resource Scheduling Algorithm Driven by Mixture of Experts in Large-scale Heterogeneous Local Power Communication Network
-
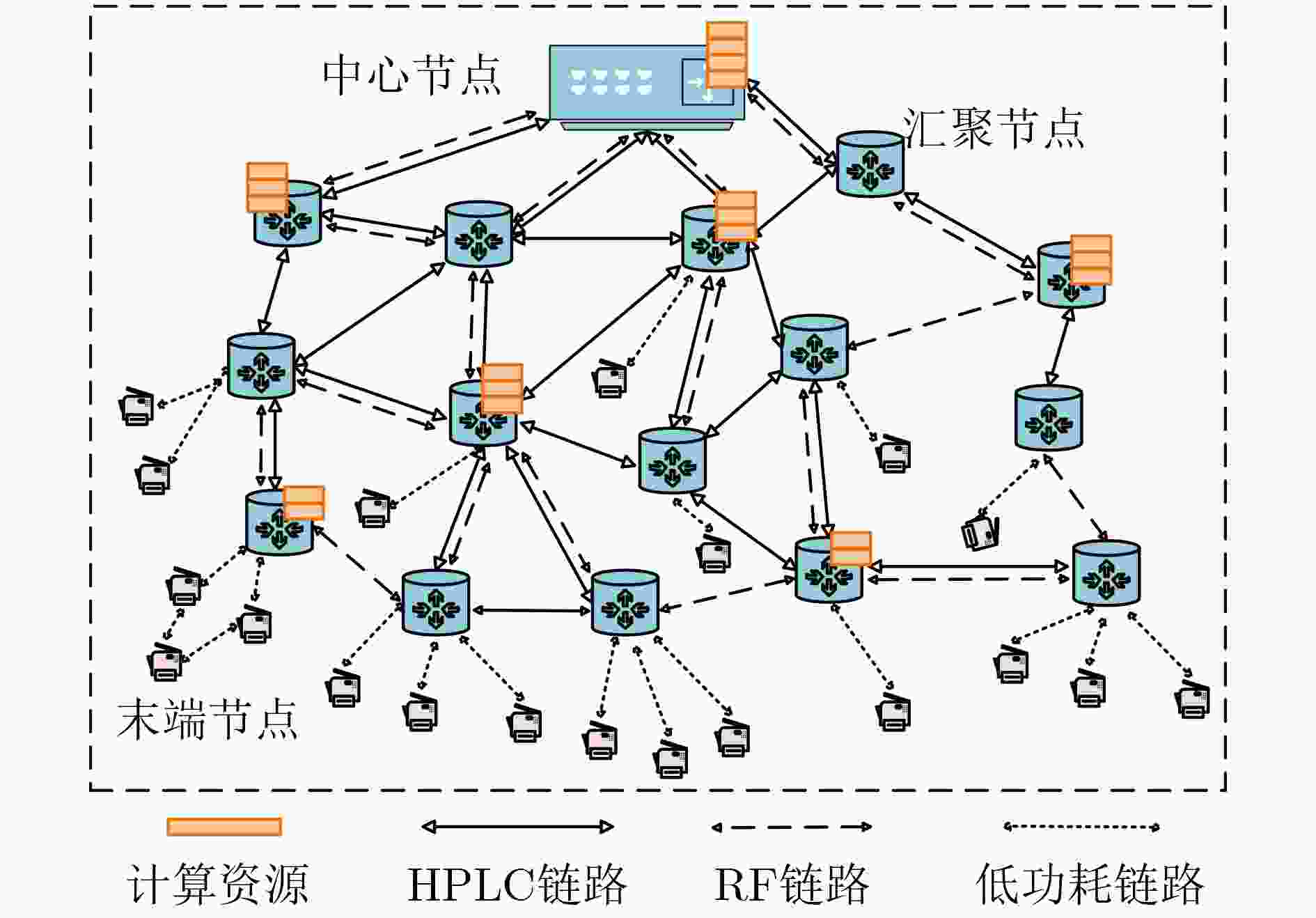
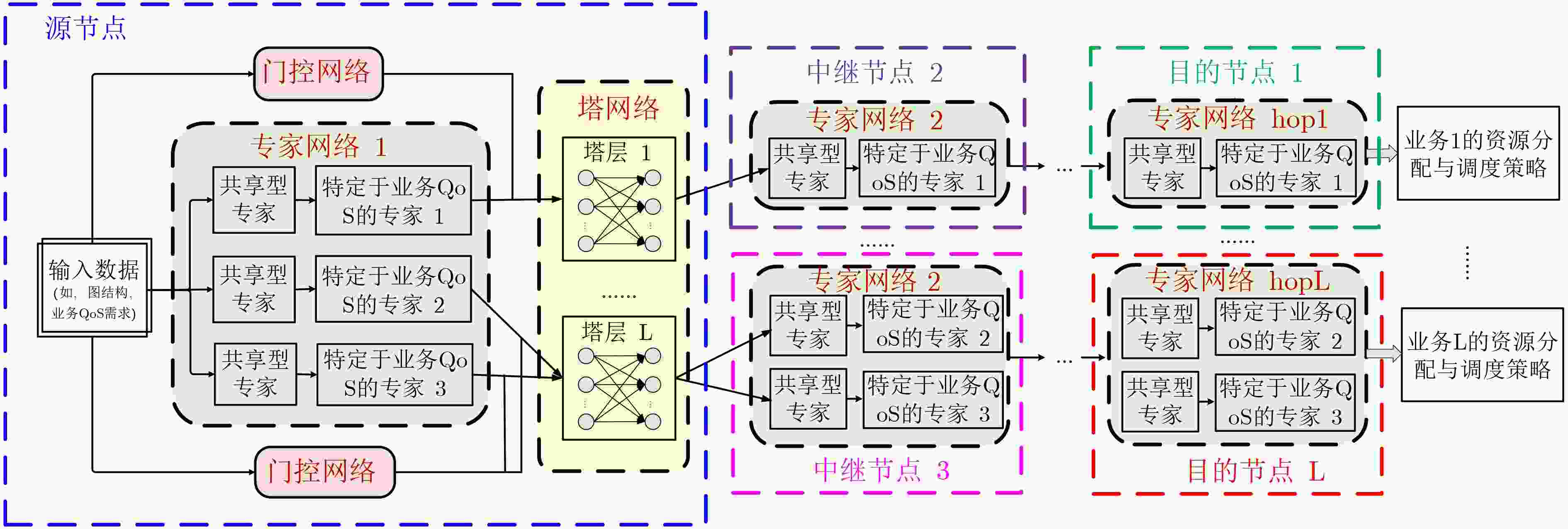
摘要: 为了在资源受限的本地电力通信网中尽可能地满足业务差异化服务质量(QoS)需求,该文提出了一种混合专家驱动的资源分配与调度算法。首先,考虑业务差异化QoS需求、链路类型、信道数量和数据调制方式,建立了大规模异构本地电力通信网资源供需差异最小化问题。接着,为了求解该NP-hard问题,设计了一个包含专家网络和门控网络的混合专家模型,通过不同专家模型专门且并行学习资源分配与调度策略,以满足多样化业务对数据传输速率、时延和可靠性的个性化需求。其中,专家网络由共享型专家和特定于业务QoS的专家组成,用于生成最优下一跳以及节点对间链路、信道和调制方式的有效分配策略。门控网络通过自适应组合和重用多个专家模型来满足已有的和未知的业务QoS需求。最后,仿真结果表明,相较多种对比算法,所提出算法在资源利用率、时延和可靠性方面都有较好的表现。
-
关键词:
- 大规模异构本地电力通信网 /
- 差异化业务QoS /
- 按需服务 /
- 资源分配与调度 /
- 混合专家
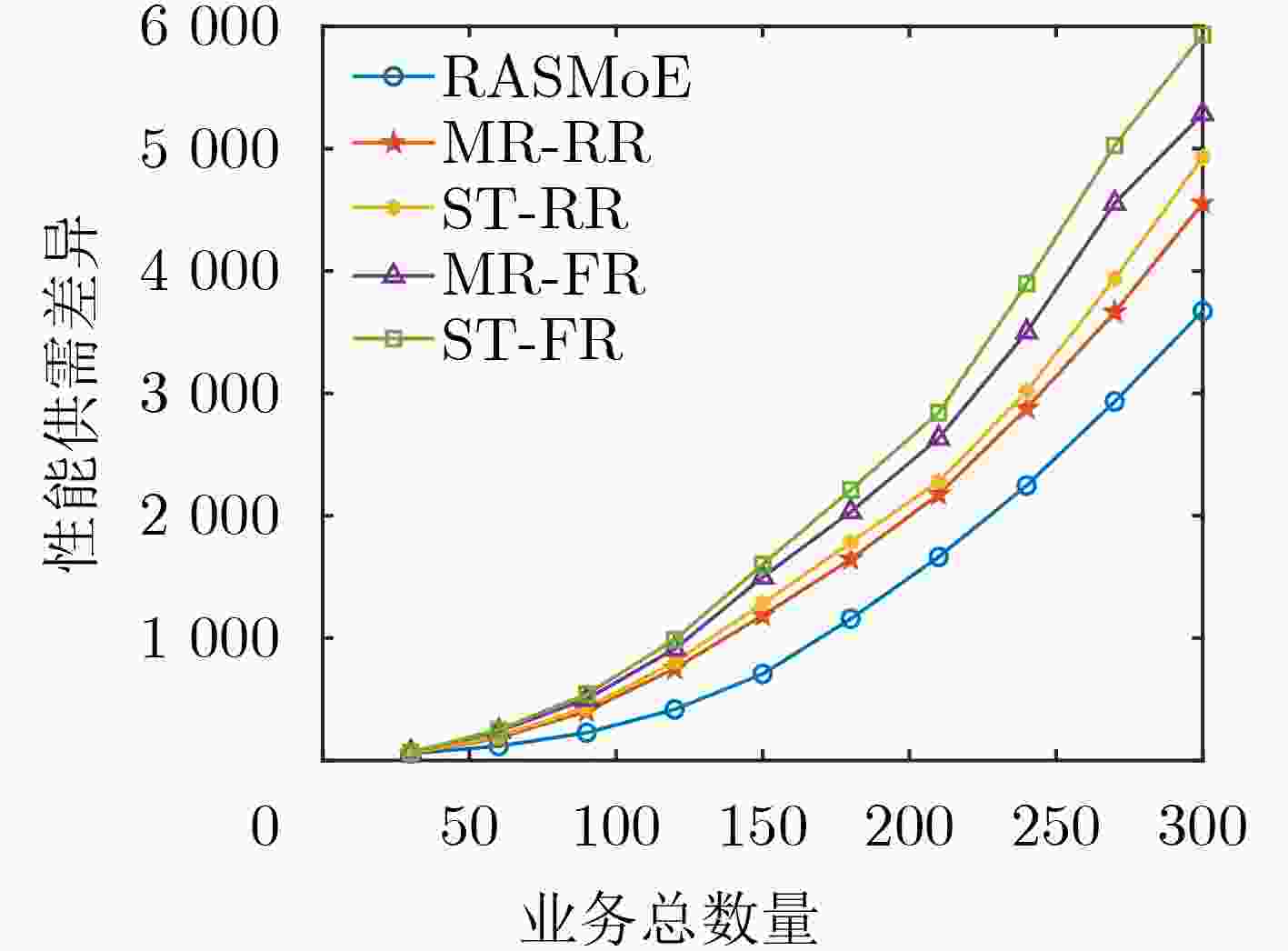
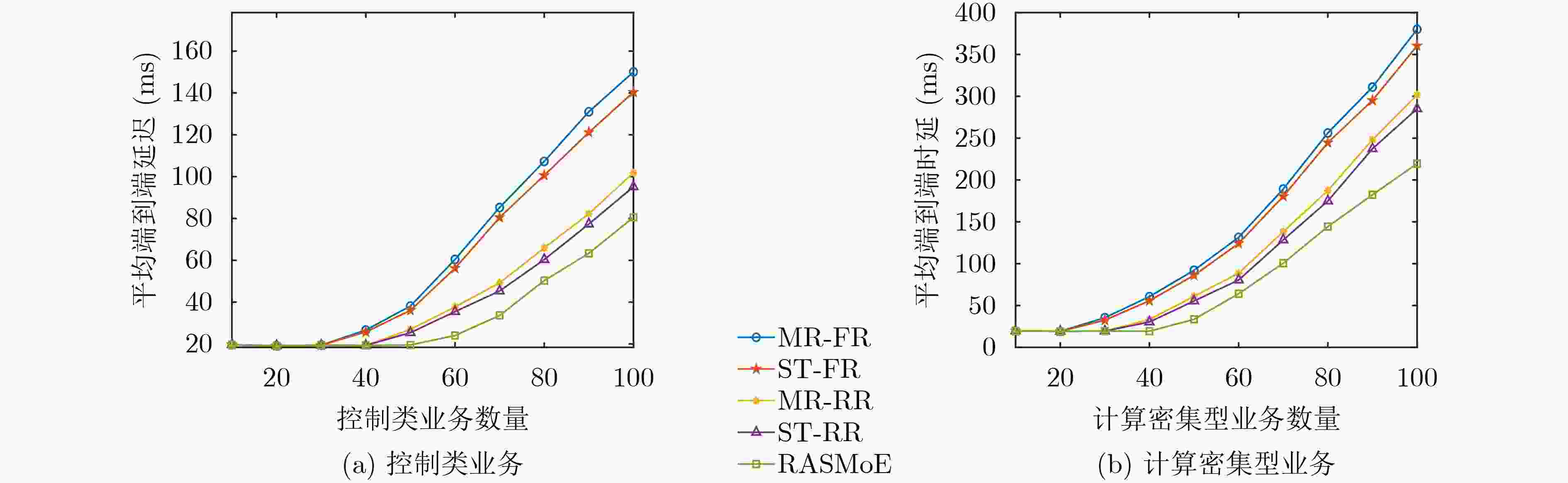
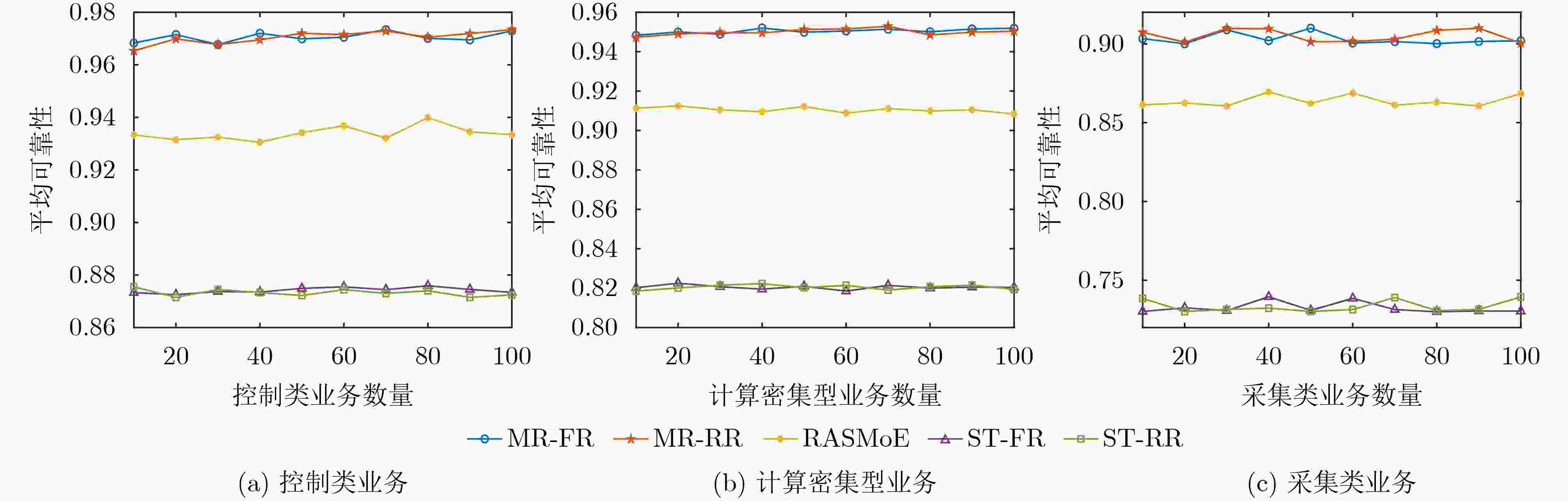
Abstract:Objective Emerging power services, such as distributed energy consumption, impose more stringent requirements on the performance of large-scale heterogeneous local power communication networks (LHLPCNs). Given the limited communication resources and rising service demands, providing on-demand services and enhancing network capacity while guaranteeing Quality of Service (QoS) presents a major challenge for LHLPCNs. Conventional routing and resource scheduling algorithms based on optimization or heuristics depend on precise mathematical models and parameters. As network scales and optimization variables increase, these algorithms become computationally expensive, hindering their effective adaptation to the growing variety of power application scenarios. Recent advances in mixture of experts (MoE) frameworks offer a promising solution, which greatly reduces the need to train individual task-specific model by employing an ensemble of AI models as specialized experts. Motivated by these challenges and the potential of MoE, this paper proposes a MoE-based routing and resource scheduling algorithm (RASMoE) tailored for LHLPCNs integrating High Power Line Carrier (HPLC) and Radio Frequency (RF). RASMoE can efficiently meet the personalized QoS requirements of diverse services and accommodate more power services within limited resources. Methods Firstly, considering the multi-modal links, channels and data modulation methods, the optimization problem of minimizing the difference between QoS supply and demand in LHLPCNs is established, which conforms to a 0-1 integer linear programming model. Then, to solve this NP-hard problem, a novel MOE framework comprising expert networks and gated networks is designed. This framework is capable of meeting the personalized demands of diverse services in terms of data transmission rate, delay and reliability, while achieving faster convergence. The expert networks, which include both shared and QoS-specific experts, are responsible for generating the optimal next hop and computing the efficient allocation strategies of links, channels and data modulation modes between node pairs. Meanwhile, the gated networks dynamically combine and reuse these experts to efficiently accommodate both known and unforeseen service types. Finally, extensive comparative experiments validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. Compared with many baselines, RASMoE shows better performance in terms of resource utilization, delay and Reliability. Results and Discussions The difference between the performance supply and demand of five algorithms under varying service numbers is compared ( Fig. 3 ) . Simulation results show that RASMoE consistently exhibits the smallest performance supply-demand differences across all scenarios. This advantage stems from its gating network, which dynamically combines QoS-specific experts to precisely match resource allocation with service requirements. Given that control and computing-intensive services have strict delay requirements, the average end-to-end (E2E) latency of these two service types under different service numbers is compared (Fig. 4 ) . It can be observed that the proposed algorithm achieves the lowest average E2E latency. This is because its expert networks, enhanced by Graph Attention Networks (GATs), efficiently extract node load states and interact with the network environment in real-time via a Multi-Armed Bandit (MAB) mechanism. This enables RASMoE to learn adaptive resource allocation strategies. Moreover, the average reliability of the E2E paths by the five algorithms for different numbers of control, compute-intensive, and acquisition services is illustrated (Fig. 5 ).Conclusions This paper proposes a MoE-driven routing and resource scheduling algorithm for LHLPCNs. The proposed framework comprises two core components: expert networks and a gating network. The expert networks include shared experts based on GATs and service QoS-specific experts based on MAB. The former are responsible for E2E path selection by analyzing node characteristics, while the latter focuses on adaptively allocating and scheduling links, channels, and modulation schemes according to distinct QoS requirements and link conditions. The gated networks dynamically orchestrate and reuse these expert models to efficiently serve services with single or multiple QoS demands, including previously unseen service types. Theoretical analysis validates that the proposed method enhances resource utilization of LHLCPNs, with its advantages being particularly pronounced in multi-service scenarios characterized by diverse QoS requirements. Future work will explore the integration of the MoE framework with domain-specific models (e.g., for power load forecasting) and predictive analytics, aiming to optimize the integration and utilization of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power. -
[1] CALERO F, CAÑIZARES C A, BHATTACHARYA K, et al. A review of modeling and applications of energy storage systems in power grids[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2023, 111(7): 806–831. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2022.3158607. [2] WU Dan, SEO G S, XU Lie, et al. Grid integration of offshore wind power: Standards, control, power quality and transmission[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Power Electronics, 2024, 5: 583–604. doi: 10.1109/OJPEL.2024.3390417. [3] LI Yuanzheng, YU Chaofan, SHAHIDEHPOUR M, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for smart grid operations: Algorithms, applications, and prospects[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2023, 111(9): 1055–1096. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2023.3303358. [4] LI Jun, SUN Haiyang, DENG Xiumei, et al. Mobility-aware user scheduling in wireless federated learning with contextual multi-armed bandit[J]. China Communications, 2025, 22(11): 256–272. doi: 10.23919/JCC.fa.2023-0427.202511. [5] LI Hongbo and DUAN Lingjie. Competitive multi-armed bandit games for resource sharing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2025, 24(9): 8393–8404. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2025.3555971. [6] SALAH M M, SAAD R S, ZAKI R M, et al. Multi-armed bandits for resource allocation in UAV-assisted LoRa networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Magazine, 2025, 8(2): 40–45. doi: 10.1109/IOTM.001.2400088. [7] GALLI A, MOSCATO V, ROMANO S P, et al. Playing with a multi armed bandit to optimize resource allocation in satellite-enabled 5G networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2024, 21(1): 341–354. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2023.3302064. [8] 朱晓荣, 贺楚闳. 基于强化学习的大规模多模Mesh网络联合路由选择及资源调度算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(7): 2773–2782. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231103.ZHU Xiaorong and HE Chuhong. Joint routing and resource scheduling algorithm for large-scale multi-mode mesh networks based on reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(7): 2773–2782. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231103. [9] LI Guiyi, OUYANG Yuxiang, and LINLONG Siyu. En route congestion prediction method for air route network based on spatiotemporal graph convolution network and attention[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2025, 17(3): 33–57. doi: 10.1109/MITS.2024.3450953. [10] JI Han, WU Xiping, ZENG Zhihong, et al. Graph attention networks-enabled load balancing for 6G heterogeneous networks with parallel transmission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 1–14. Early Access. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2025.3636175. (查阅网上资料,未找到本条文献卷期号,请确认). [11] CHEN Chongpu, CHEN Xinbo, YANG Yi, et al. Sparse attention graph convolution network for vehicle trajectory prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(12): 18294–18306. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3443850. [12] PARK J and LIM S. LEHAN: Link-feature enhanced heterogeneous graph attention network[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 86248–86255. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3198941. [13] LI Chenxu, FENG Lei, LI Wenjing, et al. Long-term traffic flow prediction: A knowledge-driven graph attention spatio-temporal network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2025, 22(5): 4206–4221. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2025.3595919. [14] ZHOU Jingxuan, XIAO Wenhua, ZHANG Dayu, et al. Multi-task model fusion with mixture of experts structure[C]. 2023 9th International Conference on Big Data and Information Analytics (BigDIA), Haikou, China, 2023: 387–391. doi: 10.1109/BigDIA60676.2023.10429752. [15] CHENG Guangran, DONG Lu, CAI Wenzhe, et al. Multi-task reinforcement learning with attention-based mixture of experts[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023, 8(6): 3812–3819. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3271445. [16] YUAN Renteng, ABDEL-ATY M, XIANG Qiaojun, et al. A temporal multi-gate mixture-of-experts approach for vehicle trajectory and driving intention prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024, 9(1): 1204–1216. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3336310. [17] RAMBABU R, VADAKKEPAT P, TAN K C, et al. A mixture-of-experts prediction framework for evolutionary dynamic multiobjective optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(12): 5099–5112. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2909806. [18] DU Hongyang, LIU Guangyuan, LIN Yijing, et al. Mixture of experts for intelligent networks: A large language model-enabled approach[C]. 2024 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC), Ayia Napa, Cyprus, 2024: 531–536. doi: 10.1109/IWCMC61514.2024.10592370. [19] YANG Liang, YAN Xiaoqin, LI Sai, et al. Performance analysis of dual-hop mixed PLC/RF communication systems[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(2): 2867–2878. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2021.3088096. [20] JING Chuanfang, ZHU Xiaorong, and LIU Xu. Data/model jointly driven routing and resource allocation algorithms for large-scale self-organizing networks for new power systems[C]. 2nd Future Industrial Internet (FII 2024), Shenzhen, China, 2024: 55–76. doi: 10.1007/978-981-96-6736-9_5. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
