Mamba-YOWO: An Efficient Spatio-Temporal Representation Framework for Action Detection
-
摘要: 针对时空动作检测中现有方法难以统一框架中高效协同建模外观语义与动态运动特征,以及主流框架往往因高计算复杂度和局部感受野限制,难以兼顾长程时序依赖建模与实时推理效率的问题。本文提出一种基于选择性状态空间模型的Mamba-YOWO轻量化时空动作检测框架。首先,引入Mamba模块重构YOWOv3的时序建模骨干,在保持线性计算复杂度的同时建模长程时序依赖。其次,设计高效多尺度时空融合模块,实现多尺度空间特征与动态时间上下文的有效融合,增强判别性表征。最后,在UCF101-24和JHMDB数据集上进行实验。结果表明,本方法较YOWOv3参数量减少7.3%,计算量(FLOPs)降低5.4%,帧级mAP分别达到90.24%和83.2%,显著优于现有实时检测方法。验证了所提方法在实时时空动作检测任务中的精度-效率平衡上的优势。Abstract:
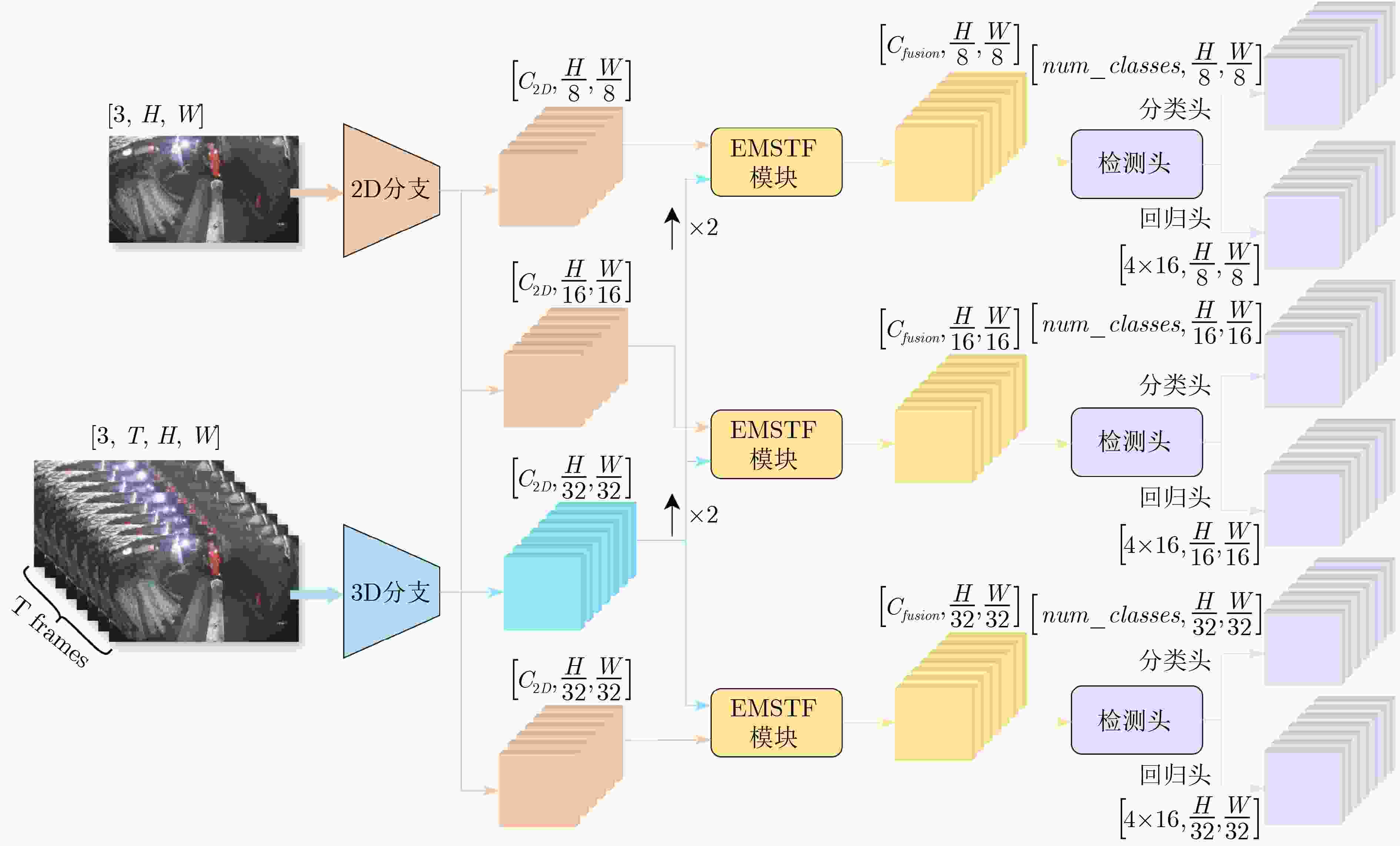
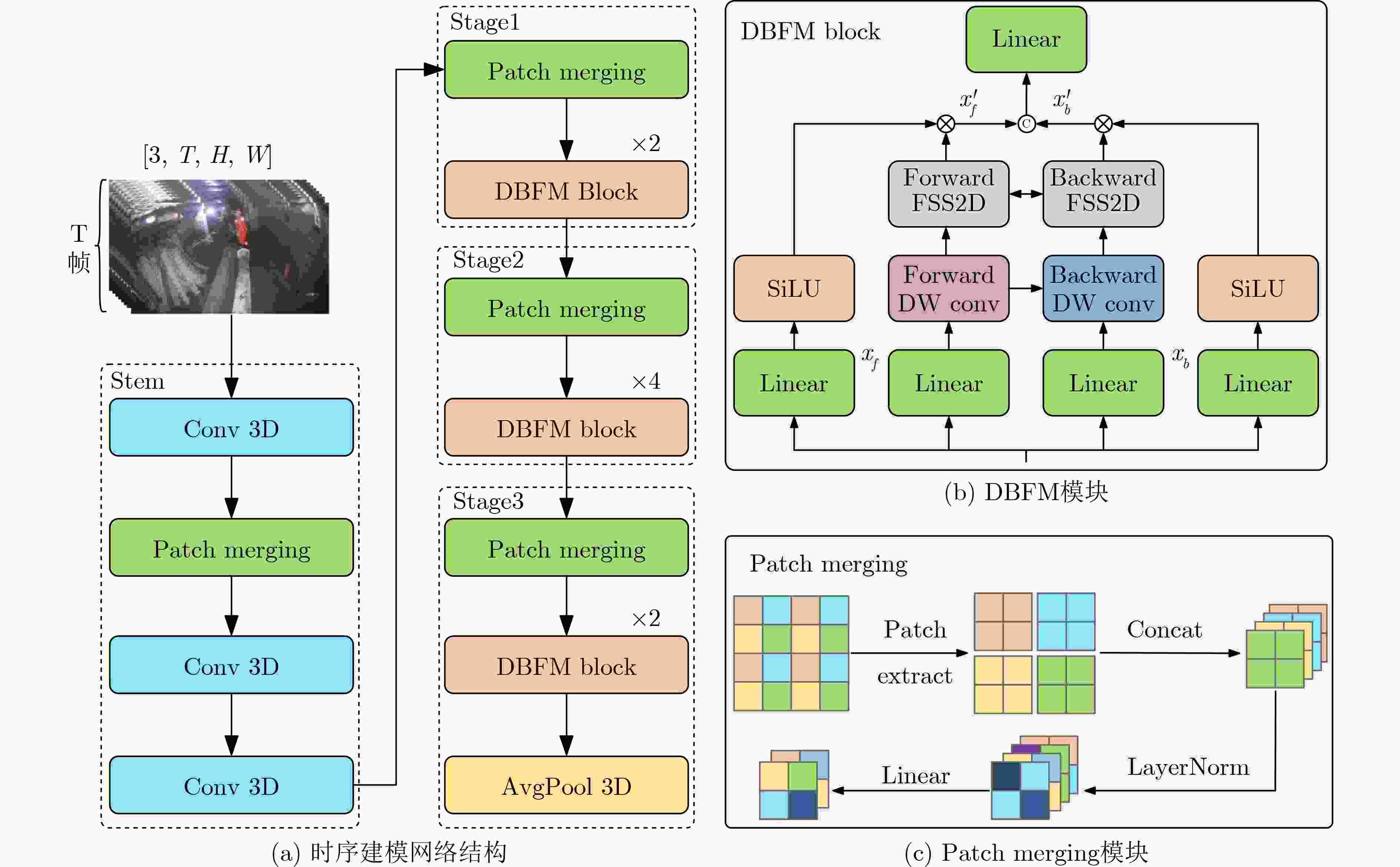
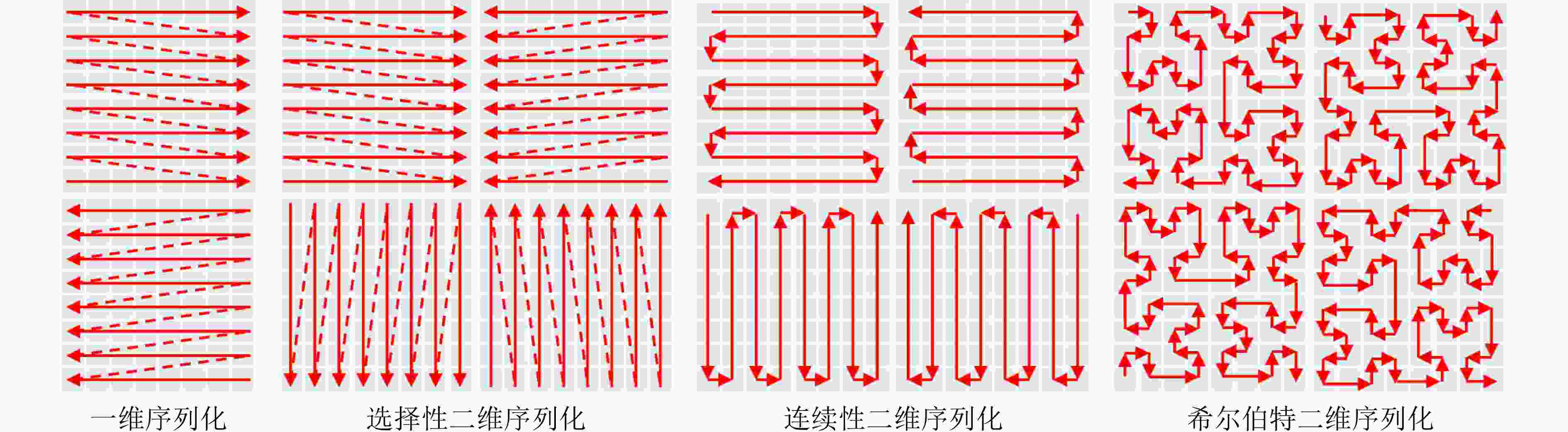
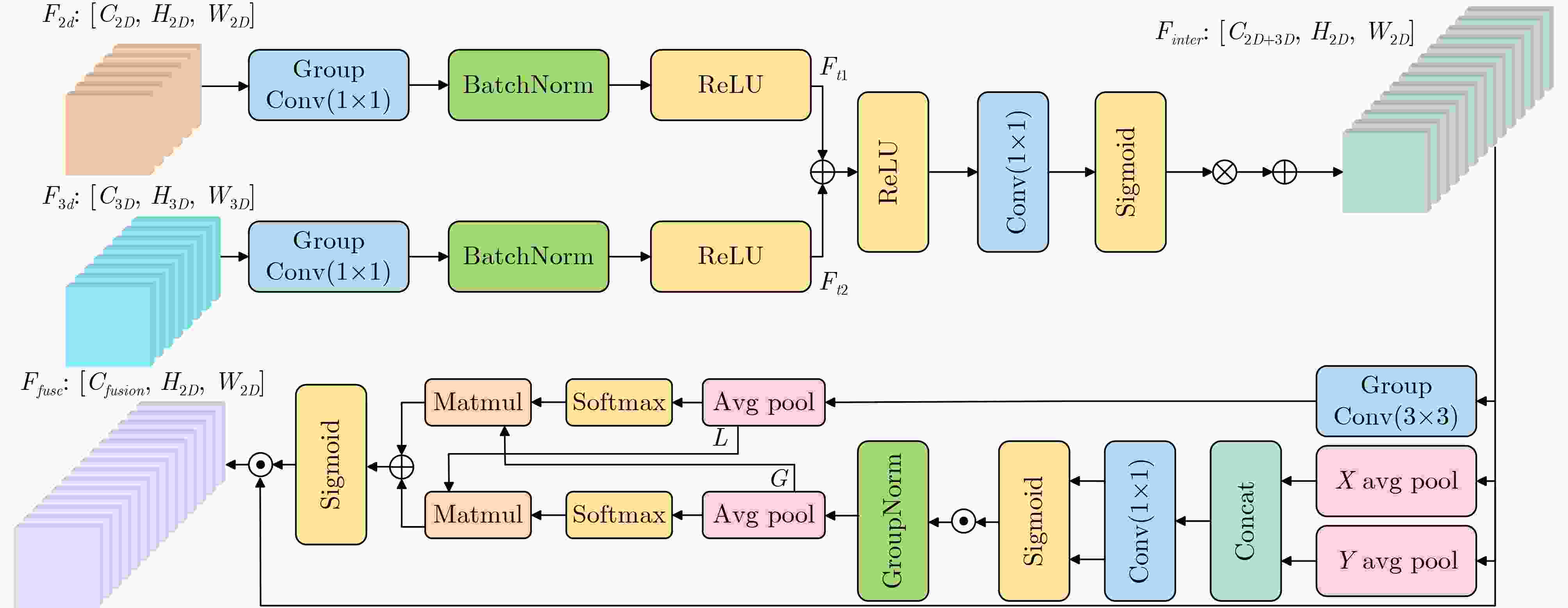
Objective Spatio-temporal action detection aims to localize and recognize action instances in untrimmed videos, which is crucial for applications like intelligent surveillance and human-computer interaction. Existing methods, particularly those based on 3D CNNs or Transformers, often struggle with balancing computational complexity and modeling long-range temporal dependencies effectively. The YOWO series, while efficient, relies on 3D convolutions with limited receptive fields. The recent Mamba architecture, known for its linear computational complexity and selective state space mechanism, shows great potential for long-sequence modeling. This paper explores the integration of Mamba into the YOWO framework to enhance temporal modeling efficiency and capability while reducing computational burden, addressing a significant gap in applying Mamba specifically to spatio-temporal action detection tasks. Methods The proposed Mamba-YOWO framework is built upon the lightweight YOWOv3 architecture. It features a dual-branch heterogeneous design for feature extraction. The 2D branch, based on YOLOv8’s CSPDarknet and PANet, processes keyframes to extract multi-scale spatial features The core innovation lies in the 3D temporal modeling branch, which replaces traditional 3D convolutions with a hierarchical structure composed of a Stem layer and three Stages (Stage1-Stage3). Stage1 and Stage2 utilize Patch Merging for spatial downsampling and stack Decomposed Bidirectionally Fractal Mamba (DBFM) blocks. The DBFM block employs a bidirectional Mamba structure to capture temporal dependencies from both past-to-future and future-to-past contexts. Crucially, a Spatio-Temporal Interleaved Scan (STIS) strategy is introduced within DBFM, which combines bidirectional temporal scanning with spatial Hilbert quad-directional scanning, effectively serializing video data while preserving spatial locality and temporal coherence. Stage3 incorporates a 3D average pooling layer to compress features temporally. An Efficient Multi-scale Spatio-Temporal Fusion (EMSTF) module is designed to integrate features from the 2D and 3D branches. It employs group convolution-guided hierarchical interaction for preliminary fusion and a parallel dual-branch structure for refined fusion, generating an adaptive spatio-temporal attention map. Finally, a lightweight detection head with decoupled classification and regression sub-networks produces the final action tubes. Results and Discussions Extensive experiments were conducted on UCF101-24 and JHMDB datasets. Compared to the YOWOv3/L baseline on UCF101-24, Mamba-YOWO achieved a Frame-mAP of 90.24% and a Video-mAP@0.5 of 60.32%, representing significant improvements of 2.1% and 6.0%, respectively ( Table 1 ). Notably, this performance gain was achieved while reducing parameters by 7.3% and computational load (GFLOPs) by 5.4%. On JHMDB, Mamba-YOWO attained a Frame-mAP of 83.2% and a Video-mAP@0.5 of 86.7% (Table 2 ). Ablation studies confirmed the effectiveness of key components: The optimal number of DBFM blocks in Stage2 was found to be 4, beyond which performance degraded likely due to overfitting (Table 3 ). The proposed STIS scan strategy outperformed 1D-Scan, Selective 2D-Scan, and Continus 2D-Scan, demonstrating the benefit of jointly modeling temporal coherence and spatial structure (Table 4 ). The EMSTF module also proved superior to other fusion methods like CFAM, EAG, and EMA (Table 5 ), highlighting its enhanced capability for cross-modal feature integration. The performance gains are attributed to the efficient long-range temporal dependency modeling by the Mamba-based branch with linear complexity and the effective multi-scale feature fusion facilitated by the EMSTF module.Conclusions This paper presents Mamba-YOWO, an efficient spatio-temporal action detection framework that integrates the Mamba architecture into YOWOv3. By replacing traditional 3D convolutions with a DBFM-based temporal modeling branch featuring the STIS strategy, the model effectively captures long-range dependencies with linear complexity. The designed EMSTF module further enhances discriminative feature fusion through group convolution and dynamic gating. Experimental results on UCF101-24 and JHMDB datasets demonstrate that Mamba-YOWO achieves superior detection accuracy (e.g., 90.24% Frame-mAP on UCF101-24) while simultaneously reducing model parameters and computational costs. Future work will focus on theoretical exploration of Mamba’s temporal mechanisms, extending its capability for long-video sequencing, and enabling lightweight deployment on edge devices. -
表 1 与现有方法在UCF101-24和JHMDB数据集上的性能对比(%)
发表时间
(年)方法 UCF101-24 JHMDB F-mAP V-mAP F-mAP V-mAP @0.2 @0.5 @0.75 0.5:0.95 @0.2 @0.5 @0.75 0.5:0.95 2020 MOC[31] 78.00 82.80 53.80 29.60 28.30 70.80 77.30 77.20 71.70 59.10 2020 Li et al[32] - 71.10 54.00 21.80 - - 76.10 74.30 56.40 - 2021 SAMOC[33] 79.30 80.50 53.50 30.30 28.70 73.10 79.20 78.30 70.50 58.70 2022 TubeR[34] 81.30 85.30 60.20 - 29.70 - 81.80 80.70 - 2023 HIT[35] 84.80 88.80 74.30 - - 83.80 89.70 88.10 - - 2023 EVAD[36] 85.10 - - - - 83.80 - - - - 2023 STMixer[37] 86.70 - - - - 83.70 - - - - 2024 OSTAD[38] 87.20 - 58.30 - - 78.60 - 86.50 - - 2024 YWOM[39] 84.60 - 49.60 - - 73.30 - 83.70 - - - Ours 90.24 87.90 87.90 31.20 30.20 83.20 87.90 86.70 78.52 59.25 表 2 与YOWO系列模型在UCF101-24数据集上的性能对比(%)
发表时间
(年)模型 主干网络 参数量(M) 计算量
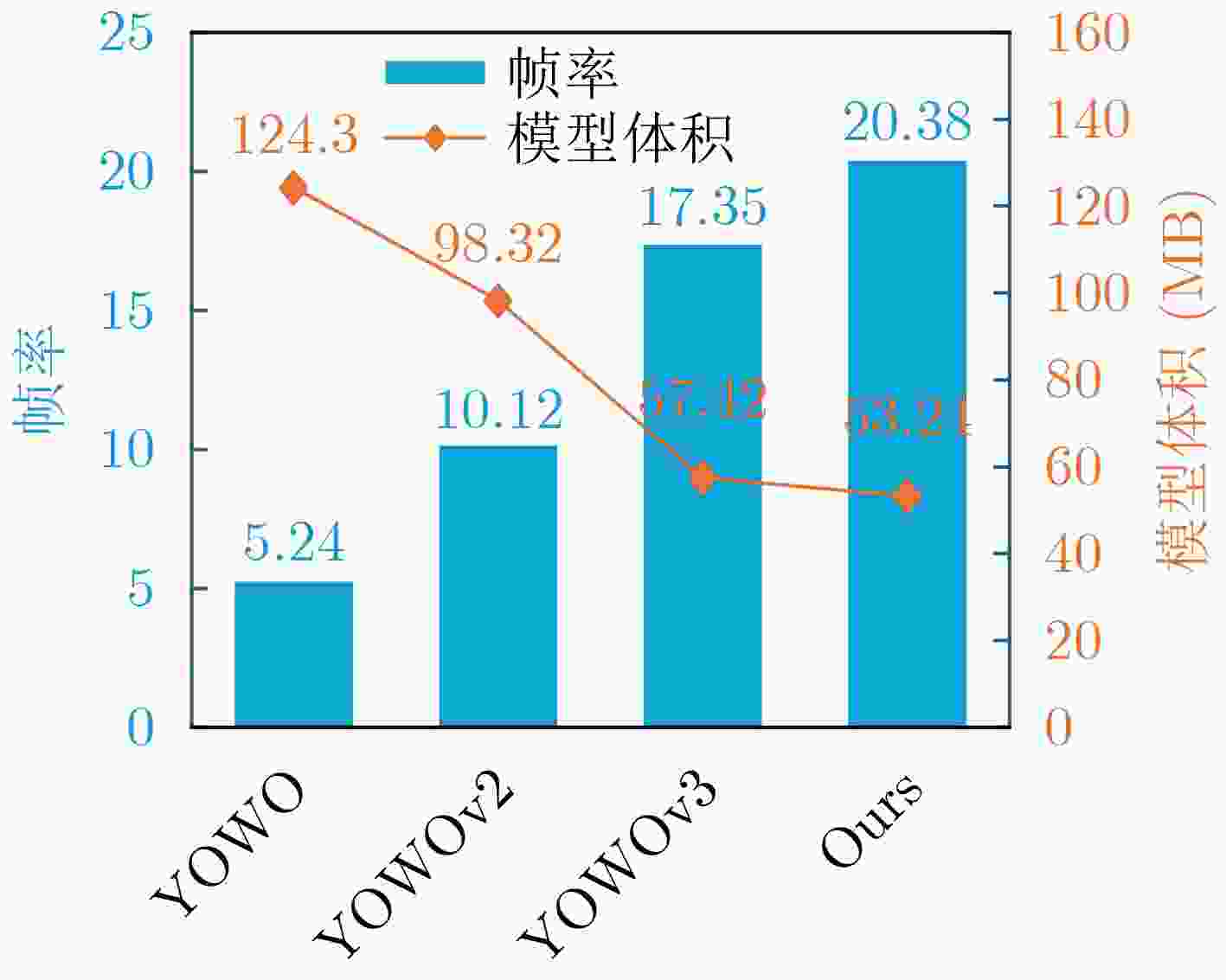
(GFLOPs)UCF101-24 F-mAP V-mAP @0.2 @0.5 @0.75 0.5:0.95 2019 YOWO[23] DarkNet+ShuffleNetV2 78.98 7.10 71.40 - - - - 2019 YOWO[23] DarkNet+ResNext-101 121.40 43.70 80.40 75.80 48.80 - - 2024 YOWOv2/L[24] FreeYolo-L+ResNext-101 109.70 92.00 85.20 80.42 52.00 23.50 24.76 2025 YOWOv3/L[25] Yolov8-M+I3D 59.80 39.80 88.33 85.20 54.32 28.70 27.24 - Ours Yolov8-M+DBFM 55.43 37.65 90.24 87.90 60.32 31.20 30.20 表 3 网络核心模块消融实验(%)
模型配置 3D分支架构 扫描策略 特征融合模块 UCF101-24 JHMDB F-mAP V-mAP@0.5 F-mAP V-mAP@0.5 基线 I3D - CFAM 88.33 54.32 78.62 82.30 变体A DBFM网络(N=4) 1D-Scan CFAM 88.70 58.37 81.30 83.24 变体B DBFM网络(N=4) 1D-Scan EMSTF 89.15 60.54 81.37 85.21 变体C DBFM网络(N=4) STIS CFAM 89.93 75.36 82.47 86.26 完整模型 DBFM网络(N=4) STIS EMSTF 90.24 87.90 83.20 86.70 -
[1] 王彩玲, 闫晶晶, 张智栋. 基于多模态数据的人体行为识别方法研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(9): 1–18. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2310-0090.WANG Cailing, YAN Jingjing, and ZHANG Zhidong. Review on human action recognition methods based on multimodal data[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(9): 1–18. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2310-0090. [2] ZHEN Rui, SONG Wenchao, HE Qiang, et al. Human-computer interaction system: A survey of talking-head generation[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12(1): 218. doi: 10.3390/electronics12010218. [3] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos[C]. Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems - Volume 1, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 568–576. [4] WANG Limin, XIONG Yuanjun, WANG Zhe, et al. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition[C]. Proceedings of 14th European Conference on Computer Vision – ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 20–36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_2. [5] TRAN D, BOURDEV L, FERGUS R, et al. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4489–4497. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.510. [6] CARREIRA J and ZISSERMAN A. Quo Vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4724–4733. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.502. [7] 钱惠敏, 陈实, 皇甫晓瑛. 基于双流-非局部时空残差卷积神经网络的人体行为识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(3): 1100–1108. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230168.QIAN Huimin, CHEN Shi, and HUANGFU Xiaoying. Human activities recognition based on two-stream NonLocal spatial temporal residual convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(3): 1100–1108. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230168. [8] WANG Xiaolong, GIRSHICK R, GUPTA A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7794–7803. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00813. [9] DONAHUE J, ANNE HENDRICKS L, GUADARRAMA S, et al. Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 2625–2634. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298878. [10] 曹毅, 李杰, 叶培涛, 等. 利用可选择多尺度图卷积网络的骨架行为识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(3): 839–849. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240702.CAO Yi, LI Jie, YE Peitao, et al. Skeleton-based action recognition with selective multi-scale graph convolutional network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(3): 839–849. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240702. [11] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Austria, 2021. (查阅网上资料, 未找到出版地信息, 请确认). [12] BERTASIUS G, WANG Heng, and TORRESANI L. Is space-time attention all you need for video understanding?[C]. Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 813–824. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版地信息, 请确认). [13] ZHANG Chenlin, WU Jianxin, and LI Yin. ActionFormer: Localizing moments of actions with transformers[C]. Proceedings of 17th European Conference on Computer Vision – ECCV 2022, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 492–510. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19772-7_29. [14] 韩宗旺, 杨涵, 吴世青, 等. 时空自适应图卷积与Transformer结合的动作识别网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(6): 2587–2595. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230551.HAN Zongwang, YANG Han, WU Shiqing, et al. Action recognition network combining spatio-temporal adaptive graph convolution and Transformer[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(6): 2587–2595. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230551. [15] GU A and DAO T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces[C]. Conference on Language Modeling, Philadelphia, 2024. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认). [16] ZHU Lianghui, LIAO Bencheng, ZHANG Qian, et al. Vision mamba: Efficient visual representation learning with bidirectional state space model[C]. Procedding of Forty-First International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 2024. [17] LIU Yue, TIAN Yunjie, ZHAO Yuzhong, et al. VMamba: Visual state space model[C]. Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2024: 3273. [18] LI Kunchang, LI Xinhao, WANG Yi, et al. VideoMamba: State space model for efficient video understanding[C]. Proceedings of the 18th European Conference on Computer Vision – ECCV 2024, Milan, Italy, 2025: 237–255. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-73347-5_14. [19] LEE S H, SON T, SEO S W, et al. JARViS: Detecting actions in video using unified actor-scene context relation modeling[J]. Neurocomputing, 2024, 610: 128616. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2024.128616. [20] REKA A, BORZA D L, REILLY D, et al. Introducing gating and context into temporal action detection[C]. Proceedings of Computer Vision – ECCV 2024 Workshops, Milan, Italy, 2025: 322–334. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-91581-9_23. [21] KWON D, KIM I, and KWAK S. Boosting semi-supervised video action detection with temporal context[C]. 2025 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Tucson, USA, 2025: 847–858. doi: 10.1109/WACV61041.2025.00092. [22] ZHOU Xuyang, WANG Ye, TAO Fei, et al. Hierarchical chat-based strategies with MLLMs for Spatio-temporal action detection[J]. Information Processing & Management, 2025, 62(4): 104094. doi: 10.1016/j.ipm.2025.104094. [23] Köpüklü O, WEI Xiangyu, and RIGOLL G. You only watch once: A unified CNN architecture for real-time spatiotemporal action localization[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1911.06644, 2019. (查阅网上资料, 不确定本文献类型是否正确, 请确认). [24] JIANG Zhiqiang, YANG Jianhua, JIANG Nan, et al. YOWOv2: A stronger yet efficient multi-level detection framework for real-time spatio-temporal action detection[C]. Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Xi’an, China, 2025: 33–48. doi: 10.1007/978-981-96-0774-7_3. [25] NGUYEN D D M, NHAN B D, WANG J C, et al. YOWOv3: An efficient and generalized framework for spatiotemporal action detection[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2026, 41(1): 75–85. doi: 10.1109/MIS.2025.3581100. [26] VARGHESE R and M S. YOLOv8: A novel object detection algorithm with enhanced performance and robustness[C]. 2024 International Conference on Advances in Data Engineering and Intelligent Computing Systems (ADICS), Chennai, India, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ADICS58448.2024.10533619. [27] LIU Ze, NING Jia, CAO Yue, et al. Video swin transformer[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 3192–3201. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00320. [28] XIAO Haoke, TANG Lv, JIANG Pengtao, et al. Boosting vision state space model with fractal scanning[C]. Proceedings of the 39th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, USA, 2025: 8646–8654. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v39i8.32934. [29] SOOMRO K, ZAMIR A R, and SHAH M. UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1212.0402, 2012. (查阅网上资料, 不确定本文献类型是否正确, 请确认). [30] KUEHNE H, JHUANG H, GARROTE E, et al. HMDB: A large video database for human motion recognition[C]. 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 2556–2563. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126543. [31] LI Yixuan, WANG Zixu, WANG Limin, et al. Actions as moving points[C]. Proceedings of 16th European Conference on Computer Vision – ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 68–84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58517-4_5. [32] LI Yuxi, LIN Weiyao, WANG Tao, et al. Finding action tubes with a sparse-to-dense framework[C]. Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York Hilton Midtown, USA, 2020: 11466–11473. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6811. [33] MA Xurui, LUO Zhigang, ZHANG Xiang, et al. Spatio-temporal action detector with self-attention[C]. 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 2021: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/IJCNN52387.2021.9533300. [34] ZHAO Jiaojiao, ZHANG Yanyi, LI Xinyu, et al. TubeR: Tubelet transformer for video action detection[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 13588–13597. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01323. [35] FAURE G J, CHEN M H, and LAI Shanghong. Holistic interaction transformer network for action detection[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2023: 3329–3339. doi: 10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00334. [36] CHEN Lei, TONG Zhan, SONG Yibing, et al. Efficient video action detection with token dropout and context refinement[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 10354–10365. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00953. [37] WU Tao, CAO Mengqi, GAO Ziteng, et al. STMixer: A one-stage sparse action detector[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 14720–14729. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01414. [38] SU Shaowen and GAN Minggang. Online spatio-temporal action detection with adaptive sampling and hierarchical modulation[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2024, 30(6): 349. doi: 10.1007/s00530-024-01543-1. [39] QIN Yefeng, CHEN Lei, BEN Xianye, et al. You watch once more: A more effective CNN architecture for video spatio-temporal action localization[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2024, 30(1): 53. doi: 10.1007/s00530-023-01254-z. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
