Genetic-Algorithm-Optimized All-Metal Metasurface for Cross-Band Stealth via Low-cost CNC Fabrication
-
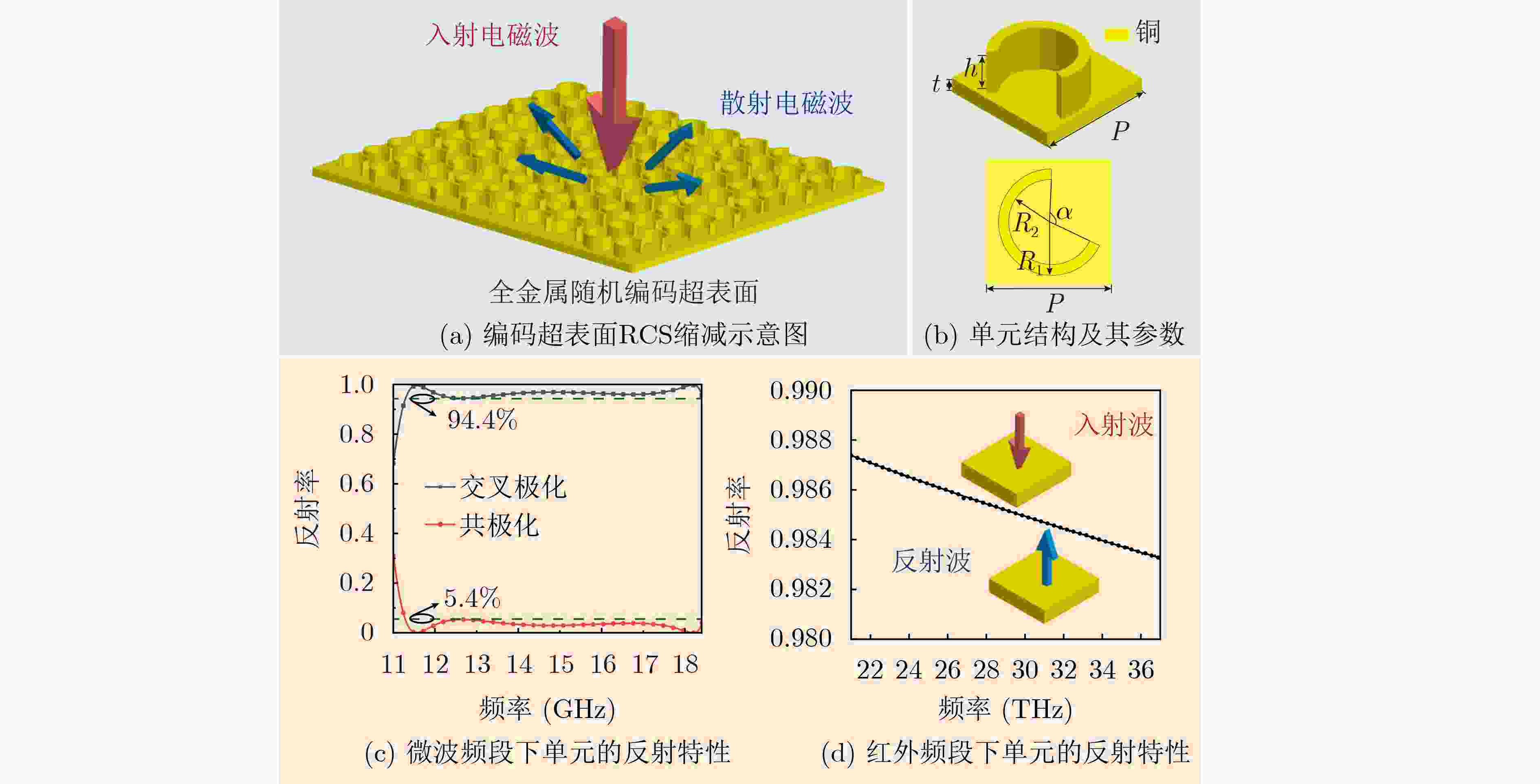
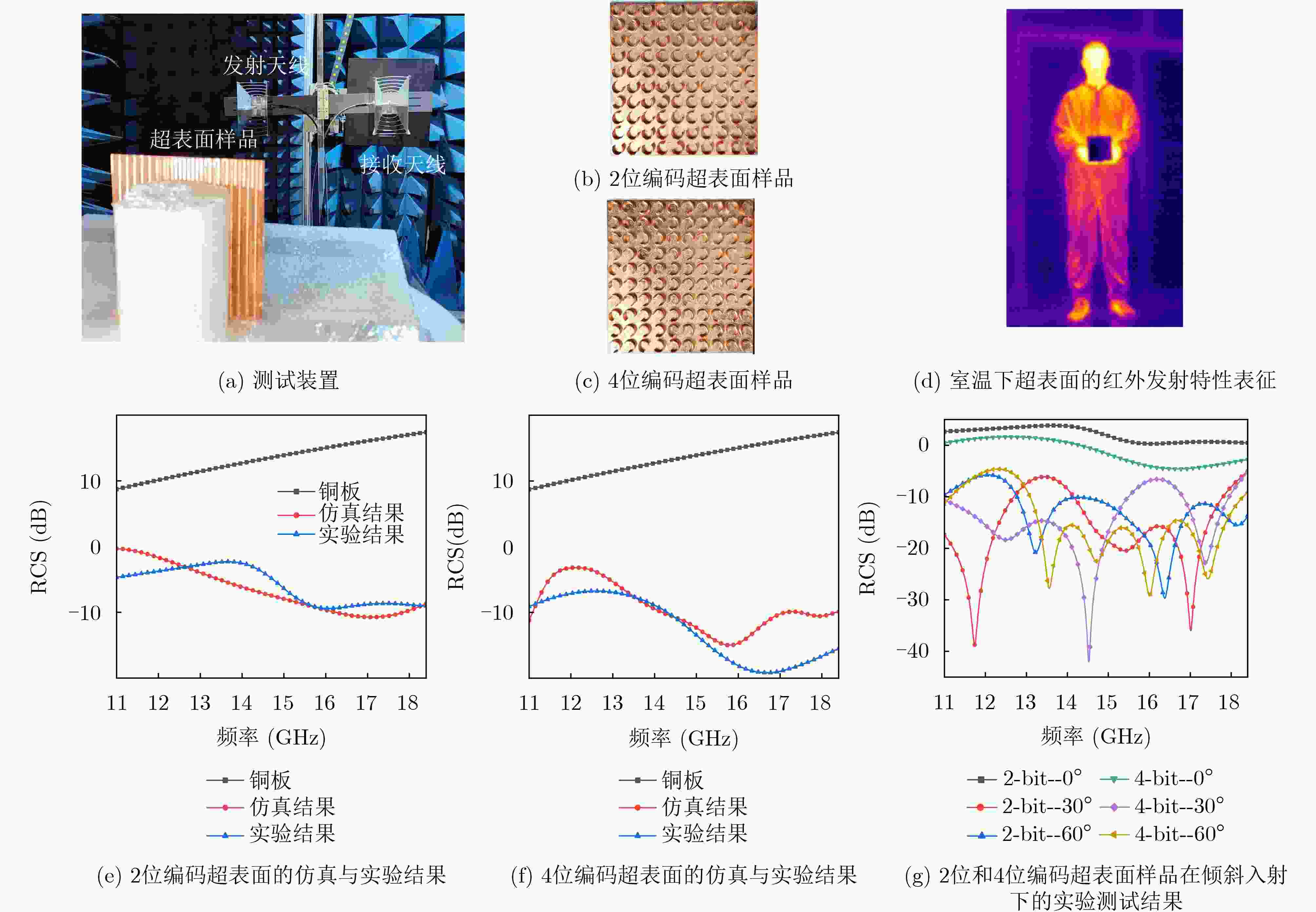
摘要: 本文通过单一材料平台集成宽带微波散射(7.4 GHz带宽)与被动红外抑制,为跨波段隐身提供了一种解决方案,克服了传统隐身材料同时兼顾微波吸收与热管理之间的设计挑战。本文提出了一种新型全金属随机编码超表面,实现了跨波段隐身功能,兼具微波频段雷达散射截面(radar cross-section, RCS)缩减和红外隐身效果。该超表面整体采用铜结构,通过计算机数控加工制造,相比传统复合材料设计,消除了界面脱层的风险。同时,其单一材料构造使其能够同时调控微波散射特性和红外辐射特性。该结构通过遗传算法优化相位分布后,在11–18.4 GHz频段(73%带宽)内实现了超过10 dB的RCS缩减,在14.7 GHz频点处的最大抑制效果超过15 dB,相关结果已通过仿真和微波暗室测试验证。该全金属结构在8–14 μm红外波段展现出超过99.9%的红外反射率,且通过商业红外成像仪热成像实验证实其被动红外隐身能力,显示出在多光谱隐身应用中的潜力。所制造的CNC原型结构尺寸为150×150 mm2,包含10×10的单元阵列,在最大达60°的线极化斜入射角下仍保持良好的结构稳定性,验证了其在贴合式应用中推广的可行性。Abstract:
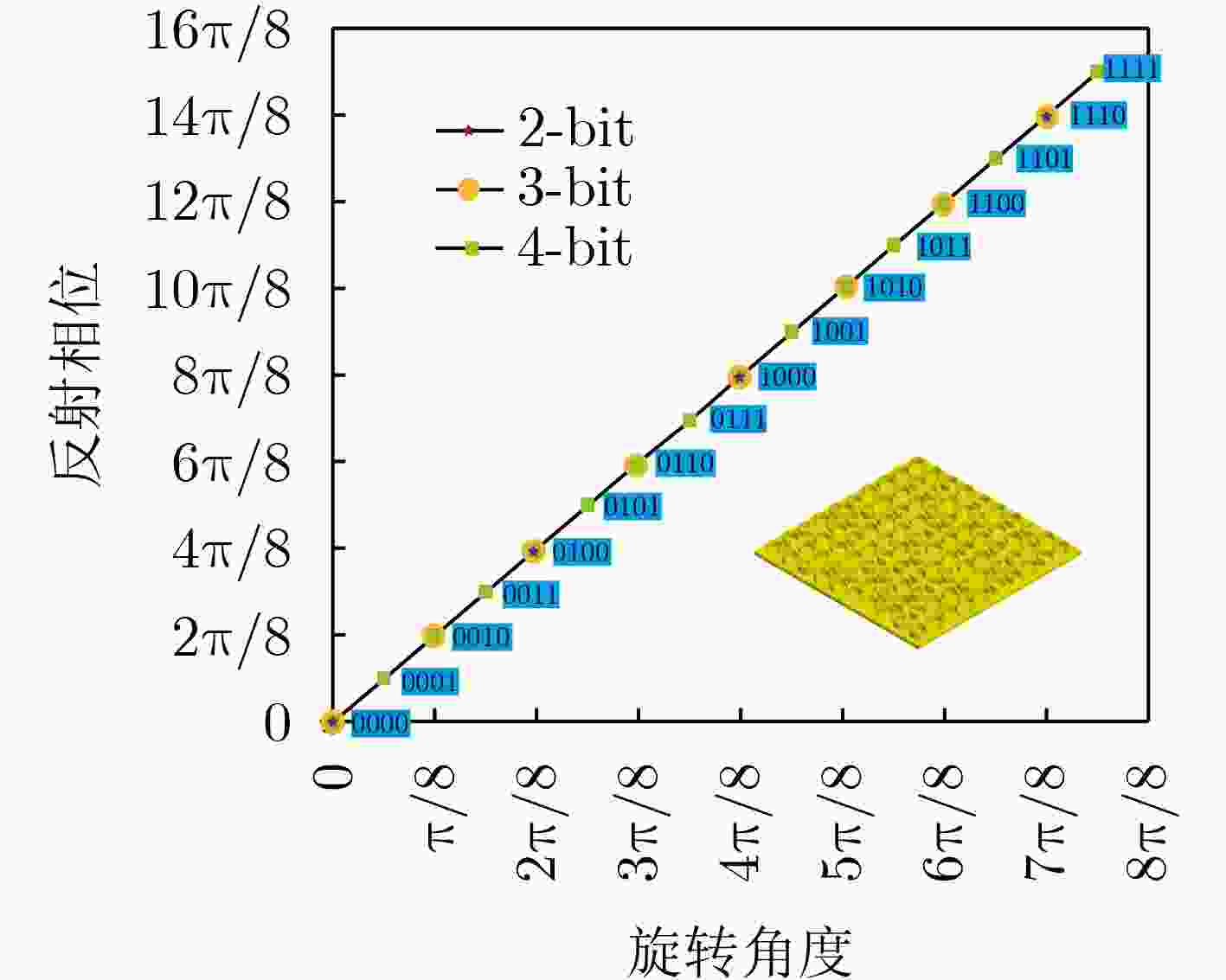
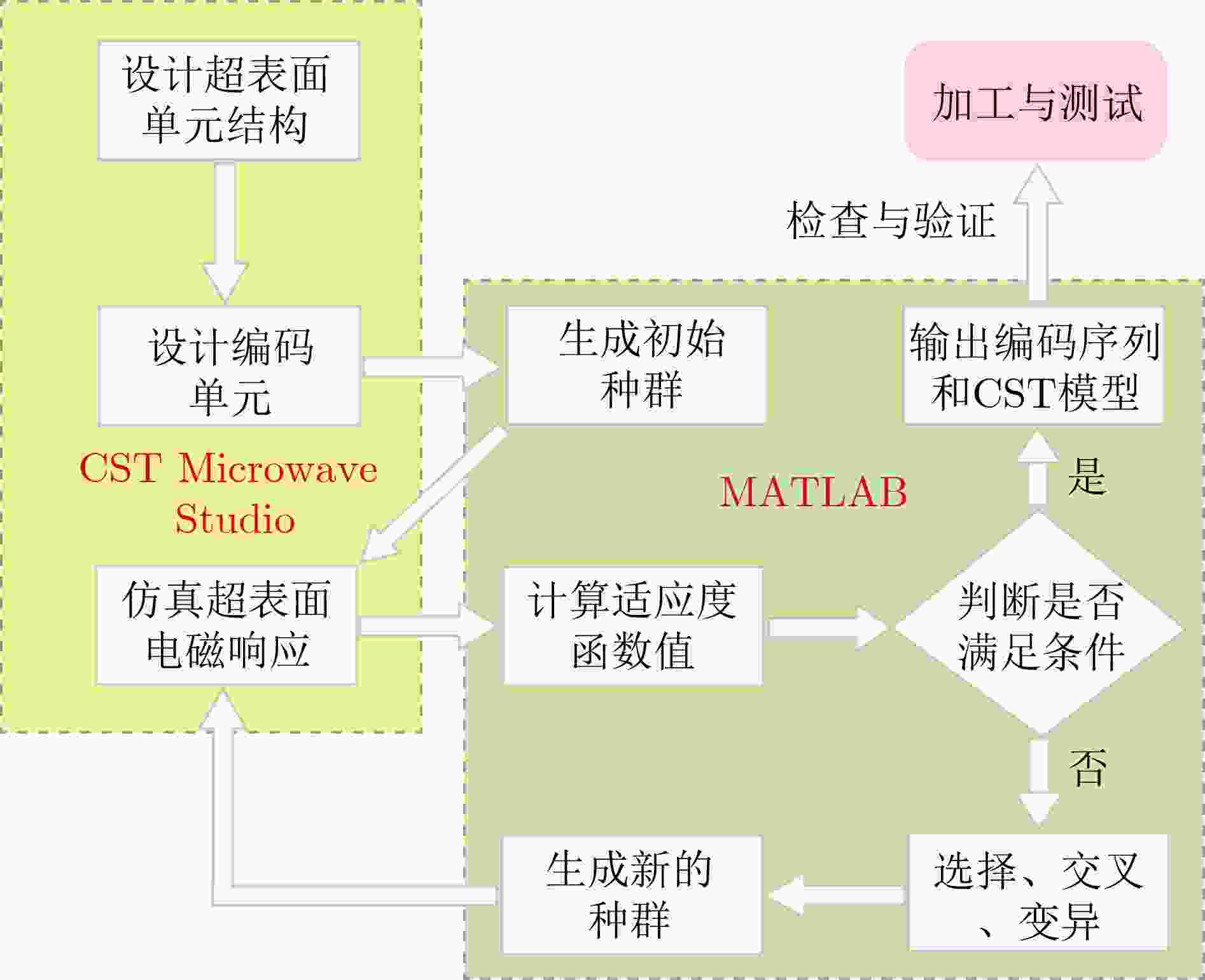
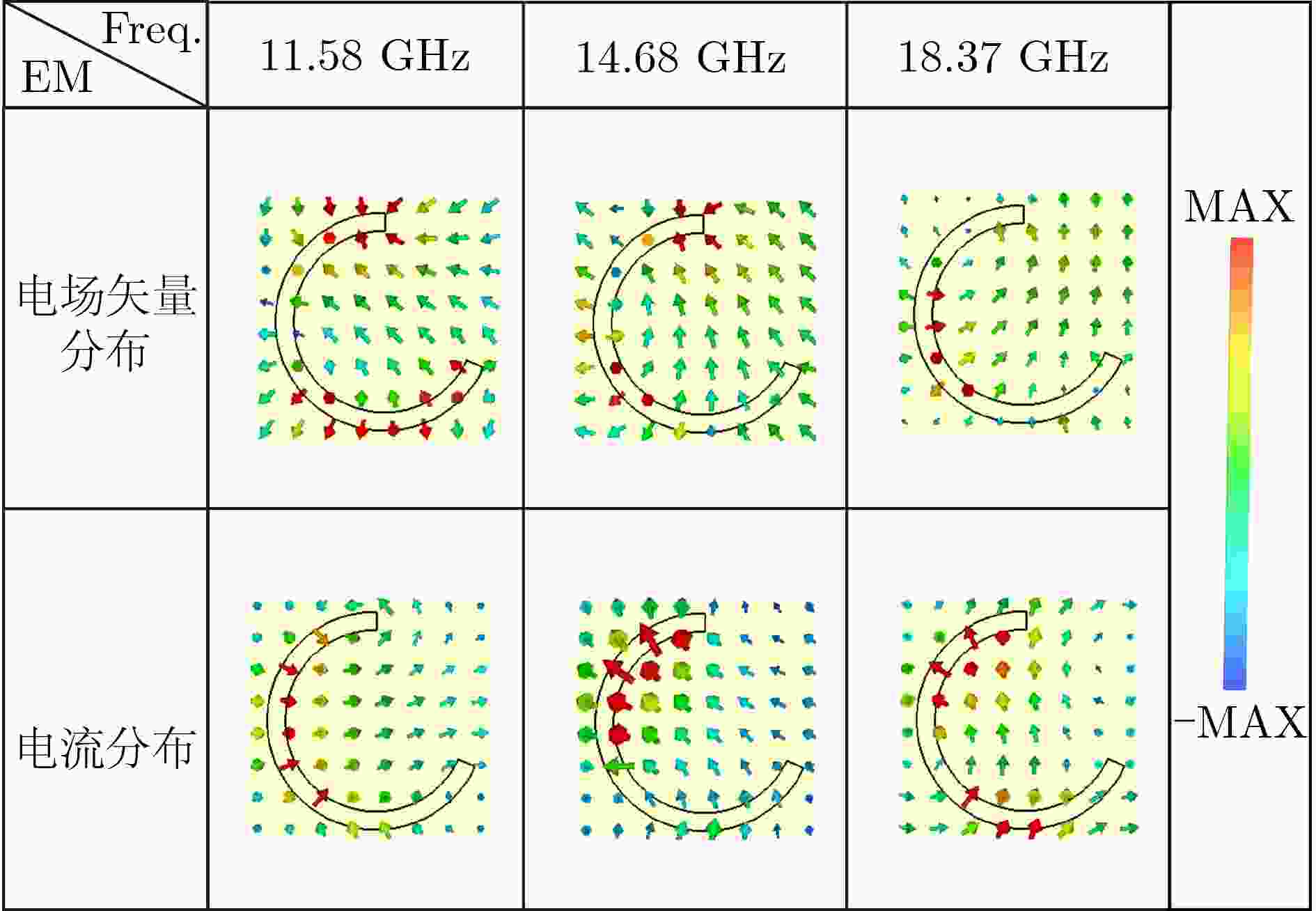
Objective Traditional electromagnetic stealth materials face the practical challenge of simultaneously achieving both microwave absorption and infrared stealth, while conventional solutions (geometric optimization, multi-layer composite coatings) have drawbacks like narrowband operation, complex fabrication, and poor cross-band compatibility. This study aims to propose a genetic algorithm-optimized all-metal random coding metasurface, which enables concurrent broadband radar cross section (RCS) reduction and low infrared emissivity on a monolithic metallic platform, thus addressing the above implementation hurdles. Methods We employ monolithic all-metal C-shaped resonant units (based on the Pancharatnam–Berry (几何) geometric phase, with reflection phase regulated by rotation angle), and design 2/3/4-bit coding (corresponding to 4/8/16 discrete phase states). A MATLAB-CST co-simulation framework is established (CST extracts unit responses via the finite element method (FEM), while MATLAB uses a genetic algorithm to optimize phase distribution for scattering energy diffusion). All-metal metasurface prototypes (150×150 mm2, 10×10 array) are fabricated via computer numerical control (CNC) cutting processing. Results and Discussions Genetic algorithm optimization converges within 6–8 generations, and increased coding bits enhance phase randomness. The 4-bit metasurface achieves an average 10 dB RCS reduction over 11–18.4 GHz, with consistent simulation and anechoic chamber measurement results under 0–60° oblique incidence. Infrared imaging verifies its low emissivity. Compared with traditional composite/multi-layer structures, the all-metal design simplifies fabrication, avoids interfacial mismatches, and ensures structural stability, exhibiting broadband, wide-angle, and cross-band stealth performance. Conclusions This study presents a genetic algorithm-optimized all-metal random coding metasurface that achieves cross-band stealth compatibility for the first time, overcoming the long-standing challenge of concurrently realizing both microwave performance and thermal management in conventional stealth materials. The work advances the field through three key innovations: 1) The monolithic copper structure enables >99.9% infrared reflectivity (8–14 μm band, via FLIR imaging) and an average 10 dB RCS reduction over 11–18.4 GHz; 2) The single-material design eliminates delamination risks, and the CNC-fabricated prototype maintains structural integrity under 60° oblique incidence, reducing fabrication costs by ~78% compared to lithography; 3) The co-simulation framework converges in 8 generations (for 4-bit coding), enabling 7.4 GHz broadband scattering manipulation. This metasurface combines fabrication reliability, cost-effectiveness, and dual-band performance, laying critical groundwork for large-scale deployment in military stealth systems and satellite platforms where multispectral concealment and durability are paramount. -
Key words:
- Coding metasurface /
- Cross-Band Stealth /
- Inverse design /
- Low-cost fabrication
-
表 1 本工作的对比参考文献
文献 相对带宽 RCS缩减带宽(GHz) 最大RCS缩减效果 结构类型 入射角度 是否跨波段 [36] 31.25% 5.4–7.4 20 dB MIM 0–45 否 [37] 9.09% 10.5–11.5 13 dB MIM NO 否 [38] 28.32% 6.94–9.23 35.5 dB MIM 0–40 否 [39] 31.31% 9.26–12.87/ 19.4 dB MIM NO 否 [40] 35.46% 14.84–19.35 / ITO/I/ITO NO 是 [41] 11.58% 5.8–8.3 About 19dB IR-ECD NO 是 本工作 32.18% 11–18.4 15 dB All-Metal 0–60 是 -
[1] RAN Yuzhou, SHI Lihua, WU Shuran, et al. Optically transparent ultrawideband electromagnetic stealth metasurface for microwave absorption and scattering[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2022, 21(12): 2412–2416. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2022.3194724. [2] 王谦喆, 何召阳, 宋博文, 等. 射频隐身技术研究综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(6): 1505–1514. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170945.WANG Qianzhe, HE Zhaoyang, SONG Bowen, et al. Overview on RF stealth technology research[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2018, 40(6): 1505–1514. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170945. [3] YOUSSEF N N. Radar cross section of complex targets[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1989, 77(5): 722–734. doi: 10.1109/5.32062. [4] HOSSAIN M B, FARUQUE M R I, ISLAM M T, et al. Triple band microwave metamaterial absorber based on double E-shaped symmetric split ring resonators for EMI shielding and stealth applications[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022, 18: 1653–1668. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.03.079. [5] WU Yue, TAN Shujuan, ZHAO Yue, et al. Broadband multispectral compatible absorbers for radar, infrared and visible stealth application[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2023, 135: 101088. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2023.101088. [6] GUO Lei, FANG Haiting, SUN Yuxiang, et al. A low-profile and broadband pattern-reconfigurable dielectric resonator antenna with wide spatial coverage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2023, 71(10): 8296–8301. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2023.3293013. [7] GUO Lei, LI Xuwang, SUN Wenjian, et al. Designing and modeling of a dual-band rectenna with compact dielectric resonator antenna[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2022, 21(5): 1046–1050. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2022.3157322. [8] 王文涛, 黄家露. 基于有源对消的装甲目标被动毫米波隐身技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(12): 4178–4184. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210944.WANG Wentao and HUANG Jialu. Research on passive millimeter-wave stealth technology based on active cancellation for armored target[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(12): 4178–4184. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210944. [9] ZHANG Chengyun, ZHANG Bingfeng, GE Shuangkang, et al. Compatible metasurface for ultra-wideband radar and switchable infrared stealth[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(18): 31359–31374. doi: 10.1364/OE.533691. [10] HU Jie, BANDYOPADHYAY S, LIU Yuhui, et al. A review on metasurface: From principle to smart metadevices[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2021, 8: 586087. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2020.586087. [11] WANG Hailin, MA Huifeng, CHEN Mao, et al. A reconfigurable multifunctional metasurface for full-space control of electromagnetic waves[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(25): 2100275. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202100275. [12] 胡杰, 唐紫依, 蓝翔, 等. 基于相变材料 Ge2Sb2Se4Te1 的可切换边缘检测与聚焦成像超表面[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(8): 220284. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220284.HU Jie, TANG Ziyi, LAN Xiang, et al. Switchable edge detection and imaging based on a phase-change metasurface with Ge2Sb2Se4Te1[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2023, 50(8): 220284. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.220284. [13] 马依泽, 李春树, 马鑫, 等. 基于超表面的极化转换和雷达散射截面缩减设计[J]. 光电工程, 2025, 52(10): 250183. doi: 10.12086/oee.2025.250183.MA Yize, LI Chunshu, MA Xin, et al. Design of polarization conversion and radar cross-section reduction based on metasurfaces[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2025, 52(10): 250183. doi: 10.12086/oee.2025.250183. [14] KHAN H A, MAJEED A, ZAHRA H, et al. Transparent conformal metasurface absorber for ultrawideband radar cross section reduction[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2024, 57(13): 135105. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/ad1951. [15] LI Yanling, XU Jianfeng, LIU Fuhai, et al. Broadband achromatic transmission stealth cloak based on all dielectric metasurfaces[J]. Physica Scripta, 2024, 99(7): 075536. doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/ad5803. [16] SHI Haoyang, TIAN Jie, CHEN Nengfu, et al. Wideband high-efficiency scattering reduction in a graphene based optically transparent and flexible metasurface[J]. Carbon, 2024, 225: 119150. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2024.119150. [17] LIU Yahong and ZHAO Xiaopeng. Perfect absorber metamaterial for designing low-RCS patch antenna[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2014, 13: 1473–1476. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2014.2341299. [18] GUO Yuan, DUAN Yuping, LIU Xiaoji, et al. Construction of rGO/MOF-derived CNTs aerogel with multiple losses for multi-functional efficient electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. Carbon, 2024, 230: 119591. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2024.119591. [19] YANG Xuan, XUAN Lixin, MEN Weiwei, et al. Carbonyl iron/glass fiber cloth composites: Achieving multi-spectrum stealth in a wide temperature range[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 491: 151862. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.151862. [20] CHEN Wei, DUAN Yuping, GU Shude, et al. Resonator-free metamaterials based on ferromagnetic dielectrics for mandatory microwave loss and compact stealth cloaks[J]. Advanced Materials, 2025, 37(39): 2507366. doi: 10.1002/adma.202507366. [21] DUAN Yuping, XIA Chenyang, CHEN Wei, et al. A bio-inspired broadband absorption metamaterial: Driven by dual-structure synergistically induced current vortices[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2025, 206: 193–201. doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2024.03.053. [22] GUO Yuan, DUAN Yuping, GU Shude, et al. Carbon nanocoils-assisted formation of tunable pore graphene aerogels for lightweight broadband microwave absorption, thermal insulation, and antifreeze devices[J]. Small, 2025, 21(10): 2412270. doi: 10.1002/smll.202412270. [23] LI Zerui, DUAN Yuping, LIU Xiaoji, et al. Strategy-induced strong exchange interaction for enhancing high-temperature magnetic loss in high-entropy alloy powders[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(44): 2507152. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202507152. [24] LIU Xiaoji, DUAN Yuping, WU Nan, et al. Modulating electromagnetic genes through Bi-phase high-entropy engineering toward temperature-stable ultra-broadband megahertz electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2025, 17(1): 164. doi: 10.1007/s40820-024-01638-4. [25] ZHAO Yi, CAO Xiangyu, GAO Jun, et al. Broadband low-RCS metasurface and its application on antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 64(7): 2954–2962. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2016.2562665. [26] CUI Tiejun, QI Meiqing, WAN Xiang, et al. Coding metamaterials, digital metamaterials and programmable metamaterials[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2014, 3(10): e218. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2014.99. [27] XI Yan, JIANG Wen, WEI Kun, et al. Wideband RCS reduction of microstrip antenna array using coding metasurface with low Q resonators and fast optimization method[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2022, 21(4): 656–660. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2021.3138241. [28] XU Guoqing, KANG Qianlong, ZHANG Xizheng, et al. High-performance long-wavelength infrared Switchable stealth based on In3SbTe2 metasurface[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2025, 207: 109392. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2024.109392. [29] WANG Lei, DONG Jian, ZHANG Wenjie, et al. Deep learning assisted optimization of metasurface for multi-band compatible infrared stealth and radiative thermal management[J]. Nanomaterials, 2023, 13(6): 1030. doi: 10.3390/nano13061030. [30] PANG Huifang, DUAN Yuping, HUANG Lingxi, et al. Research advances in composition, structure and mechanisms of microwave absorbing materials[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 224: 109173. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109173. [31] KNOTT E F, SHAEFFER J F, and TULEY M T. Radar Cross Section[M]. 2nd ed. Raleigh: SciTech Publishing, 2004: 241. [32] SALISBURY J W, WALD A, and D’ARIA D M. Thermal-infrared remote sensing and Kirchhoff's law: 1. Laboratory measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1994, 99(B6): 11897–11911. doi: 10.1029/93JB03600. [33] ZHANG Ming, ZHANG Najiao, DONG Peng, et al. All-metal coding metasurfaces for broadband terahertz RCS reduction and infrared invisibility[J]. Photonics, 2023, 10(9): 962. doi: 10.3390/photonics10090962. [34] LAMBORA A, GUPTA K, and CHOPRA K. Genetic algorithm- A literature review[C]. 2019 International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data, Cloud and Parallel Computing (COMITCon), Faridabad, India, 2019: 380–384. doi: 10.1109/COMITCon.2019.8862255. [35] SONG Rongguo, SI Yunfa, QIAN Wei, et al. Investigation of MXene nanosheets based radio-frequency electronics by skin depth effect[J]. Nano Research, 2024, 17(4): 3061–3067. doi: 10.1007/s12274-023-6127-7. [36] LIU Xiao, GAO Jun, XU Liming, et al. A coding diffuse metasurface for RCS reduction[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2017, 16: 724–727. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2601108. [37] SAIFULLAH Y, WAQAS A B, YANG Guomin, et al. Multi-bit dielectric coding metasurface for EM wave manipulation and anomalous reflection[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(2): 1139–1149. doi: 10.1364/OE.383214. [38] HAN Xinmin, XU Haojun, CHANG Yipeng, et al. Multiple diffuse coding metasurface of independent polarization for RCS reduction[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 162313–162321. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3021650. [39] FU Changfeng, HAN Lianfu, LIU Chao, et al. Combining pancharatnam–berry phase and conformal coding metasurface for dual-band RCS reduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(3): 2352–2357. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2021.3112618. [40] XU Cuilian, WANG Binke, YAN Mingbao, et al. An optically transparent sandwich structure for radar-infrared bi-stealth[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2020, 105: 103108. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2019.103108. [41] ZHANG Zekui, ZHANG Leipeng, REN Zichen, et al. Multifunctional ultrathin metasurface with a low radar cross section and variable infrared emissivity[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(16): 21109–21117. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c01798. -





 下载:
下载:
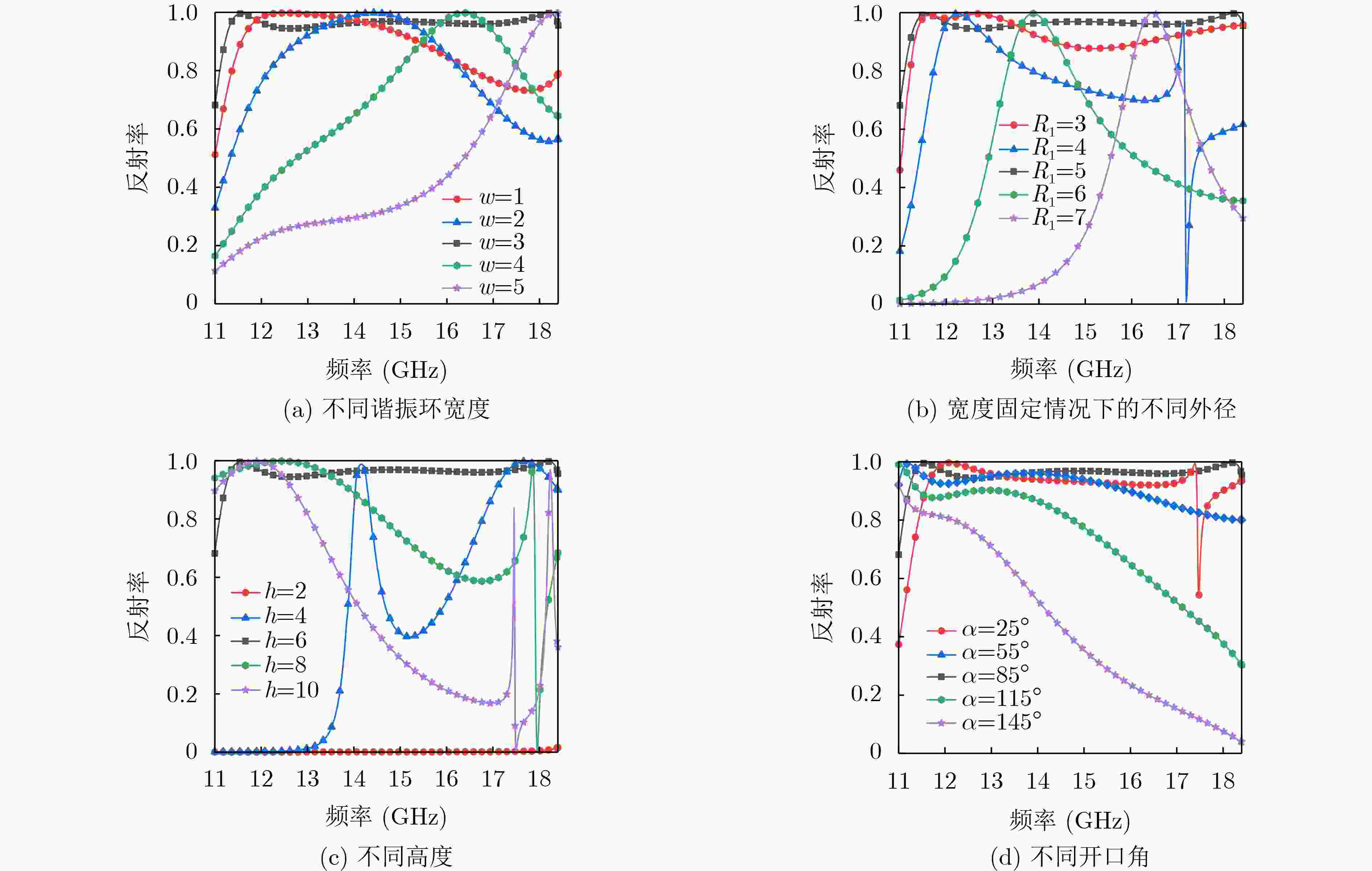
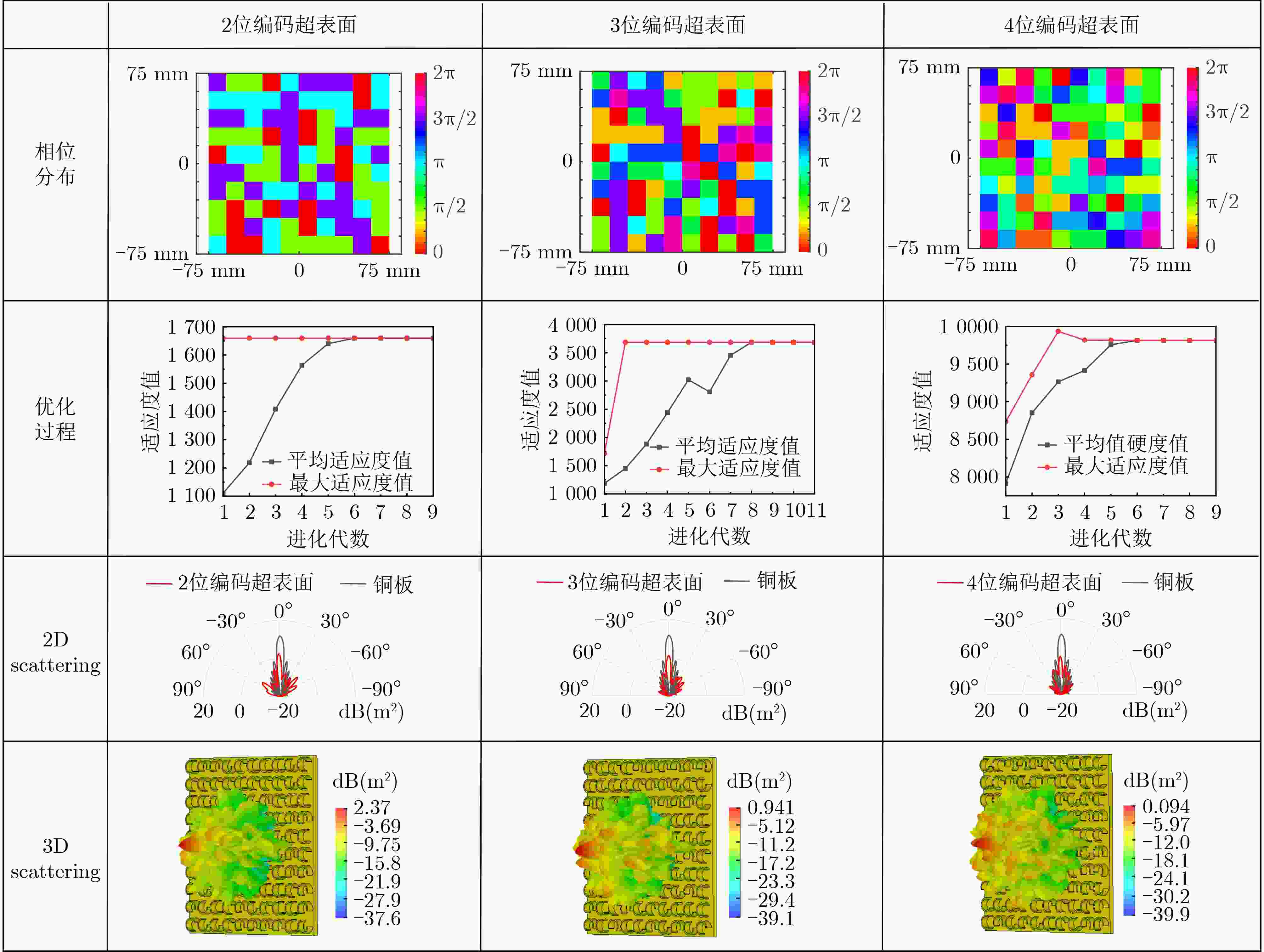
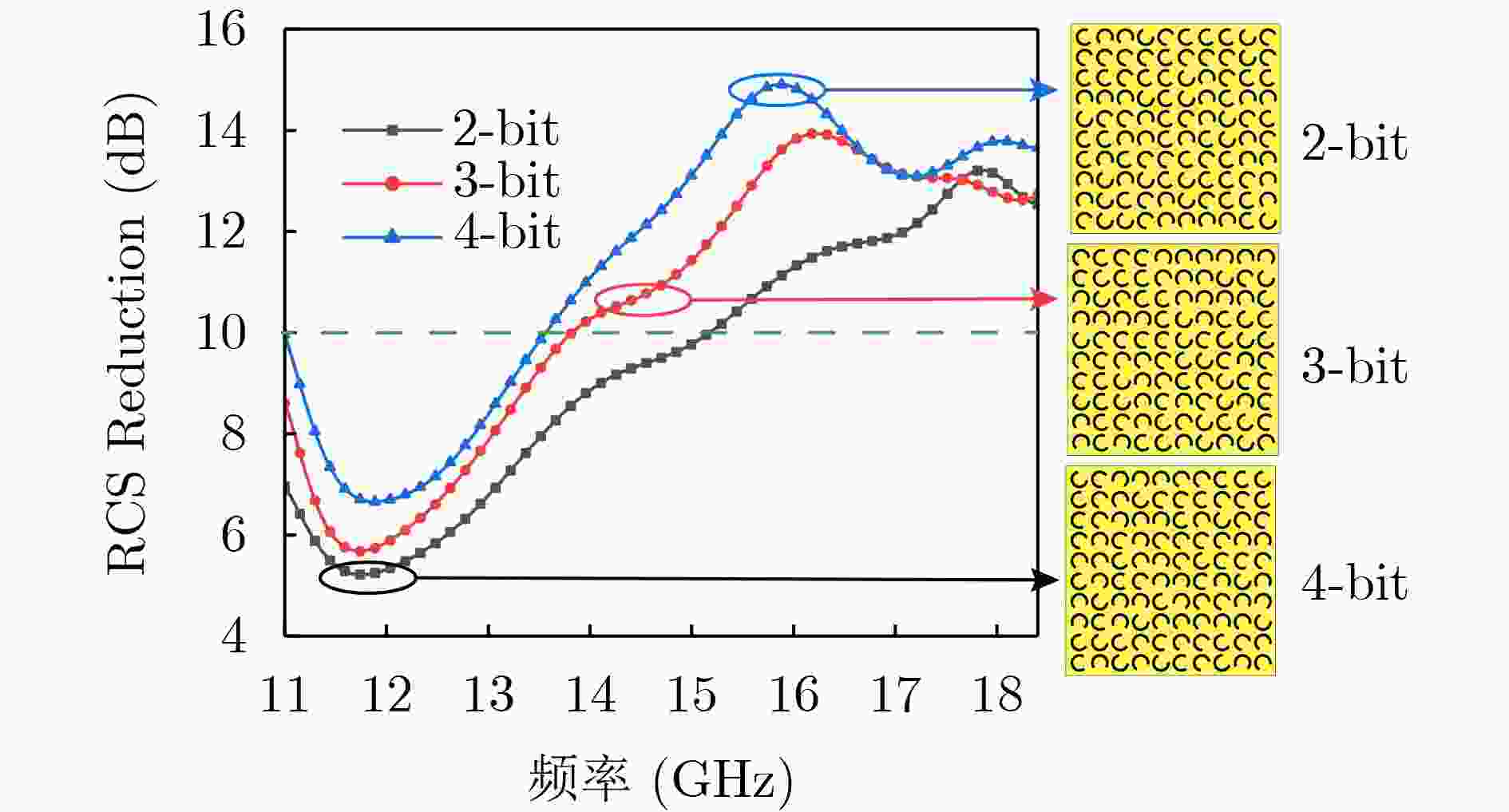
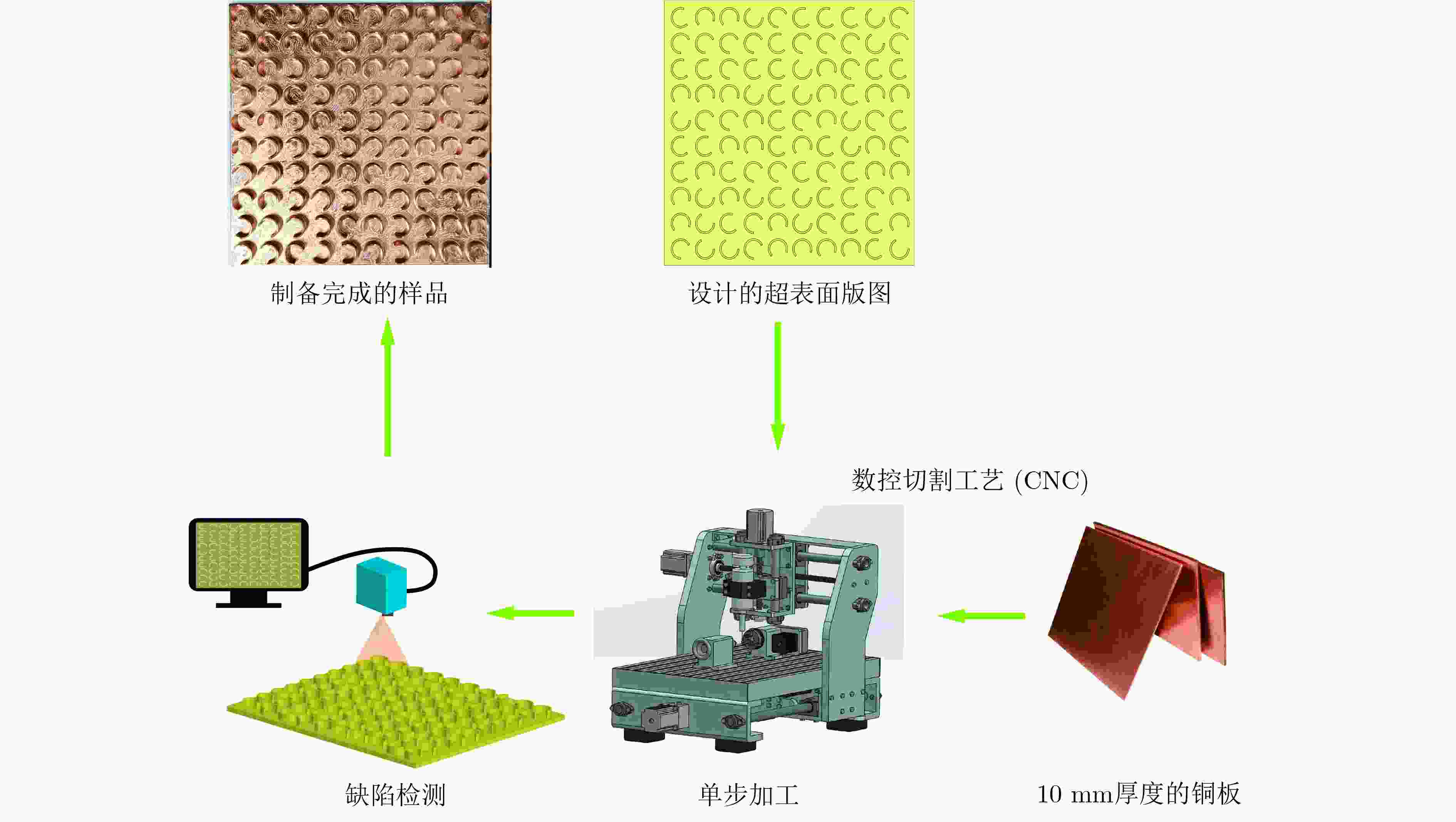


 下载:
下载:
