Entropy Quantum Collaborative Planning Method for Emergency Path of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Driven by Survival Probability
-
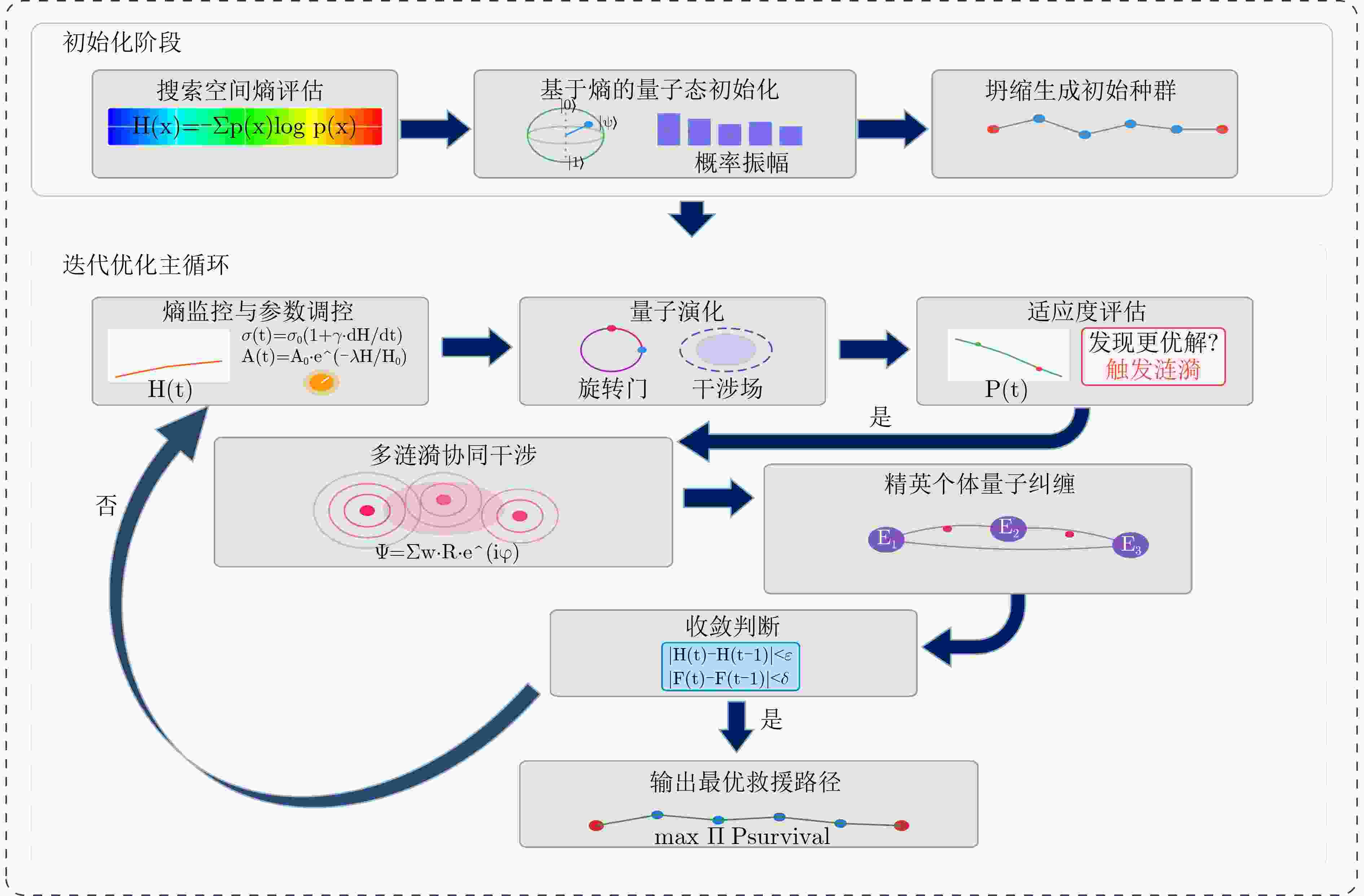
摘要: 针对自然灾害应急救援中无人机路径规划面临的复杂约束和时效性要求,该文提出一种熵增强量子涟漪协同优化算法(E2QRSA)。该文构建了以受困人员生存概率最大化为目标的数学模型,将生存概率随时间指数衰减的特征融入目标函数,并综合考虑禁飞区、警戒区、动态障碍物等多重约束;设计了基于信息熵的量子态初始化策略,通过评估搜索空间的不确定性分布引导初始种群生成;提出多涟漪协同干涉机制,利用干涉场的建设性叠加强化优质解特征传播;建立了熵驱动的参数自适应调控方法,根据搜索熵变化率动态调整涟漪传播参数。结果表明:与PSO, QRO, ATLA, IVCSA, SEWOA等5种算法相比,E2QRSA的平均生存概率较次优算法提升4.3%~5.4%,显著提升了复杂灾害环境下无人机路径规划的时效性、安全性与决策科学性。Abstract:
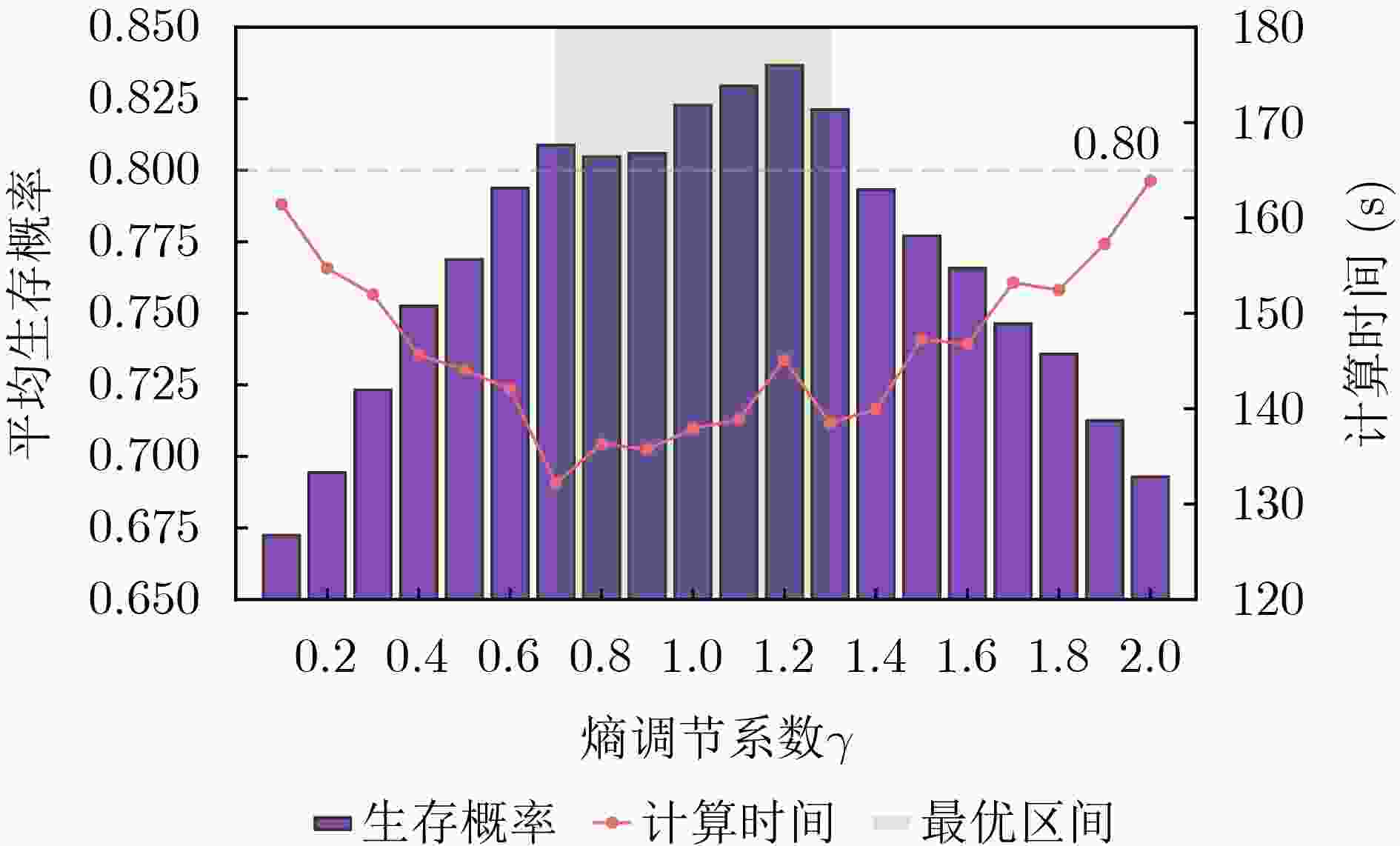
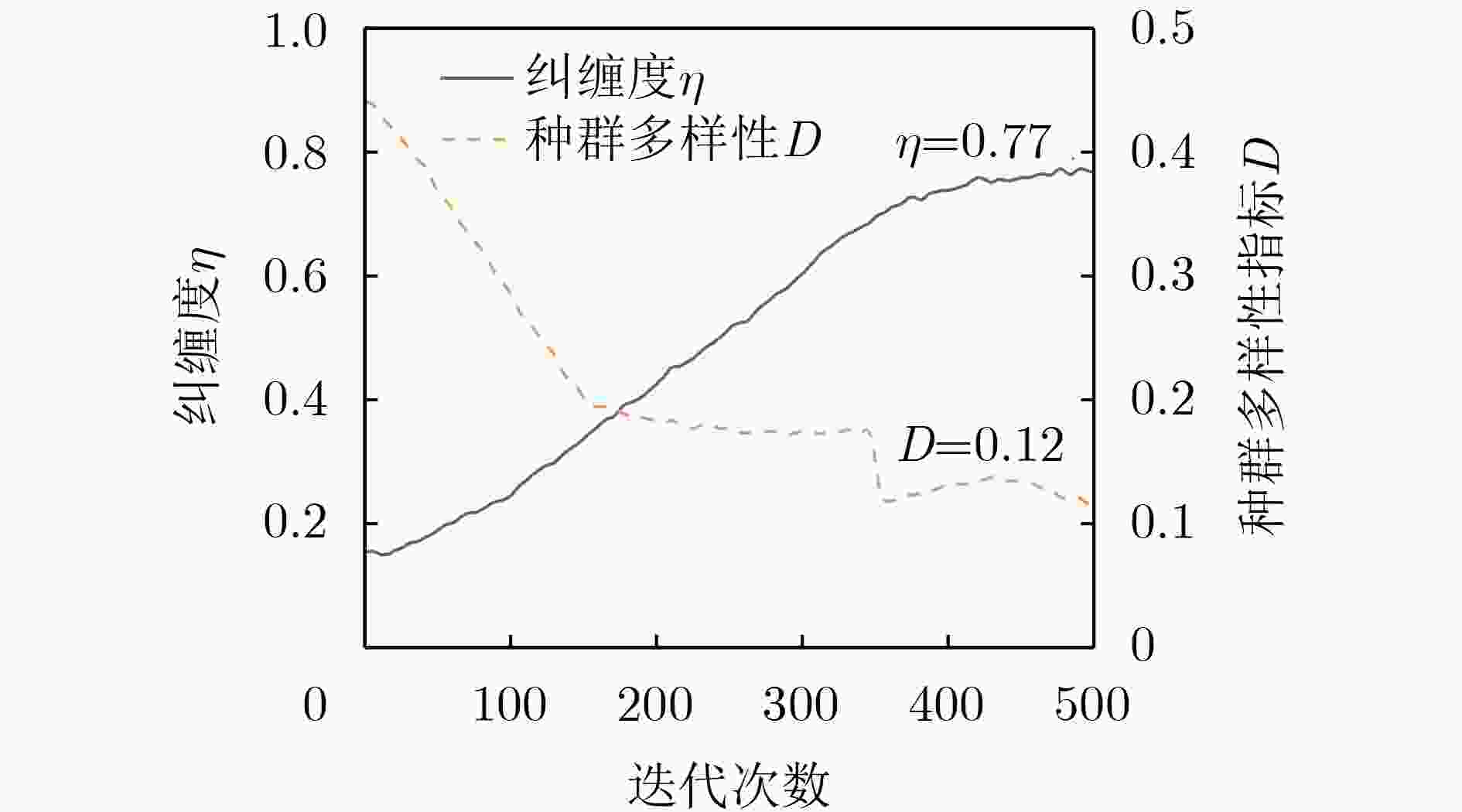
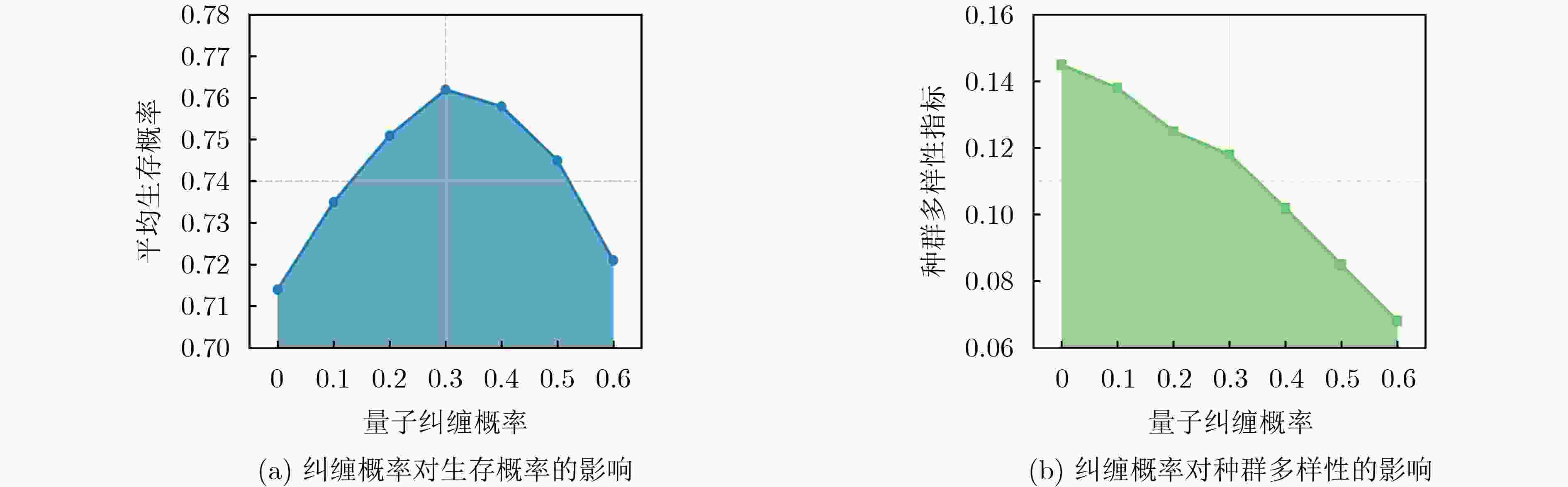
Objective Natural disaster emergency rescue places stringent requirements on the timeliness and safety of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) path planning. Conventional optimization objectives, such as minimizing total distance, often fail to reflect the critical time-sensitive priority of maximizing the survival probability of trapped victims. Moreover, existing algorithms struggle with the complex constraints of disaster environments, including no-fly zones, caution zones, and dynamic obstacles. To address these challenges, this paper proposes an Entropy-Enhanced Quantum Ripple Synergy Algorithm (E2QRSA). The primary goals are to establish a survival probability maximization model that incorporates time decay characteristics and to design a robust optimization algorithm capable of efficiently handling complex spatiotemporal constraints in dynamic disaster scenarios. Methods E2QRSA enhances the Quantum Ripple Optimization framework through four key innovations: (1) information entropy–based quantum state initialization, which guides population generation toward high-entropy regions; (2) multi-ripple collaborative interference, which promotes beneficial feature propagation through constructive superposition; (3) entropy-driven parameter control, which dynamically adjusts ripple propagation according to search entropy rates; and (4) quantum entanglement, which enables information sharing among elite individuals. The model employs a survival probability objective function that accounts for time-sensitive decay, base conditions, and mission success probability, subject to constraints including no-fly zones, warning zones, and dynamic obstacles. Results and Discussions Simulation experiments are conducted in medium- and large-scale typhoon disaster scenarios. The proposed E2QRSA achieves the highest survival probabilities of 0.847 and 0.762, respectively ( Table 1 ), exceeding comparison algorithms such as SEWOA and PSO by 4.2–16.0%. Although the paths generated by E2QRSA are not the shortest, they are the most effective in maximizing survival chances. The ablation study (Table 3 ) confirms the contribution of each component, with the removal of multi-ripple interference causing the largest performance decrease (9.97%). The dynamic coupling between search entropy and ripple parameters (Fig. 2 ) is validated, demonstrating the effectiveness of the adaptive control mechanism. The entanglement effect (Fig. 4 ) is shown to maintain population diversity. In terms of constraint satisfaction, E2QRSA-planned paths consume only 85.2% of the total available energy (Table 5 ), ensuring a safe return, and all static and dynamic obstacles are successfully avoided, as visually verified in the 3D path plots (Figs. 6 and7 ).Conclusions E2QRSA effectively addresses the challenge of UAV path planning for disaster relief by integrating adaptive entropy control with quantum-inspired mechanisms. The survival probability objective captures the essential requirements of disaster scenarios more accurately than conventional distance minimization. Experimental validation demonstrates that E2QRSA achieves superior solution quality and faster convergence, providing a robust technical basis for strengthening emergency response capabilities. -
表 1 不同规模场景下各算法性能对比
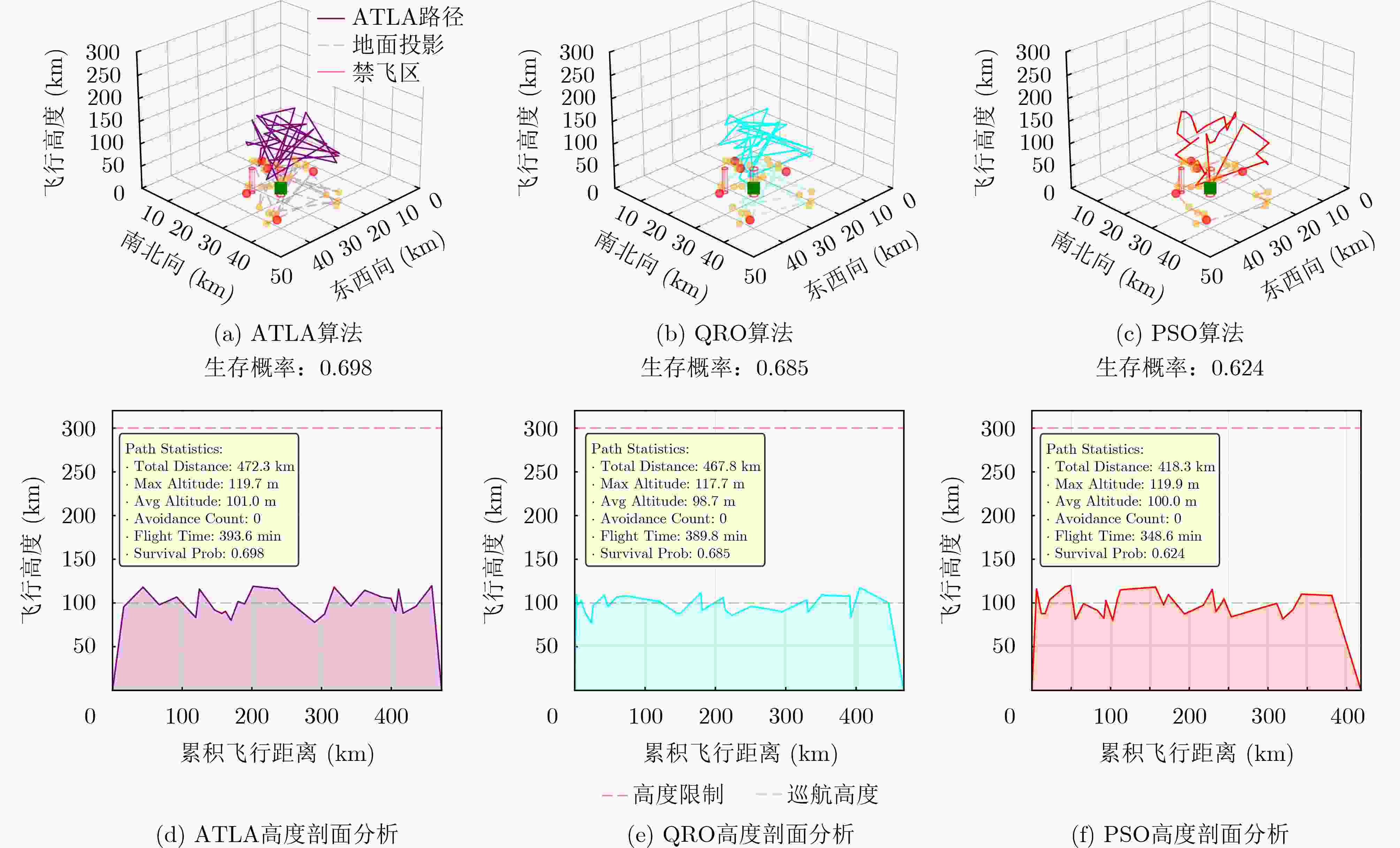
算法 中等规模场景 大规模场景 生存概率 计算时间(s) 路径长度(km) 生存概率 计算时间(s) 路径长度(km) E²QRSA 0.847 42.3 163.8 0.762 138.5 394.4 SEWOA 0.812 58.7 162.5 0.723 187.3 391.2 IVCSA 0.805 54.2 164.1 0.716 176.8 395.7 ATLA 0.793 61.4 167.3 0.698 195.6 472.3 QRO 0.778 52.8 169.7 0.685 171.4 467.8 PSO 0.731 35.6 171.2 0.624 112.3 418.3 表 2 CEC2017测试函数优化结果(均值±标准差)
函数 E²QRSA SEWOA IVCSA ATLA QRO PSO F1 3.67e-06±7.2e-07 2.13e-06±4.8e-07 5.48e-06±9.1e-07 1.27e-05±2.3e-06 8.94e-05±1.5e-05 4.32e-05±8.6e-06 F2 1.24e-04±2.8e-05 3.56e-04±6.1e-05 2.87e-04±9.0e-05 5.13e-04±8.7e-05 7.82e-04±1.3e-04 6.95e-04±1.1e-04 F3 68.4±12.3 57.3±9.8 52.7±8.4 74.6±13.7 89.2±15.8 96.5±17.2 F4 23.86±4.52 31.92±5.84 38.75±6.93 45.28±8.16 52.64±9.43 67.83±11.25 F5 8.74±1.95 7.23±1.62 9.86±2.14 12.47±2.78 15.38±3.21 18.92±3.87 F6 0.318±0.074 0.462±0.091 0.524±0.108 0.687±0.142 0.819±0.165 1.025±0.198 F11 287.4±32.6 342.5±38.9 386.7±44.2 425.3±49.8 478.6±55.4 532.8±61.7 F15 1326.7 ±87.41284.3 ±79.81412.5 ±93.61523.4 ±102.71687.2 ±113.51825.6 ±124.8F21 423.8±18.7 467.2±22.4 492.6±25.8 518.4±28.9 564.7±32.3 612.3±35.6 F28 1823.5 ±67.81756.4 ±58.91698.7 ±52.31942.6 ±74.22087.3 ±81.52234.8 ±89.7表 3 核心组件消融实验结果(大规模场景)
算法变体 生存概率(最优) 相对下降(%) 收敛代数 计算时间(s) E²QRSA完整版 0.762 - 287 138.5 V1(无熵机制) 0.698 8.40 368 156.3 V2(无协同干涉) 0.686 9.97 395 147.8 V3(无量子纠缠) 0.714 6.30 334 142.6 V4(距离目标) 0.635 16.67 236 125.7 表 4 涟漪初始振幅$ \mathrm{\mathit{A}}_0 $对算法性能的影响(大规模场景下)
$ \mathrm{\mathit{A}}_0 $ 生存概率 收敛代数 能量消耗(%) 0.5 0.698 412 78.3 0.8 0.736 334 81.7 1.0 0.762 287 85.2 1.2 0.745 318 88.6 1.5 0.721 365 92.4 2.0 0.682 423 96.8 表 5 算法能量消耗与约束满足对比分析
算法 总能耗
(%)剩余电量
(%)安全余量 最大段
耗能(%)能耗
标准差E²QRSA 85.2 14.8 是 3.8 2.1 SEWOA 88.6 11.4 是 4.4 2.6 IVCSA 89.3 10.7 是 3.6 3.1 ATLA 96.8 3.2 否 5.2 4.3 QRO 97.4 2.6 否 5.8 4.8 PSO 87.4 12.6 是 4.2 4.6 -
[1] YUCESOY E, BALCIK B, and COBAN E. The role of drones in disaster response: A literature review of operations research applications[J]. International Transactions in Operational Research, 2025, 32(2): 545–589. doi: 10.1111/itor.13484. [2] KHAN A, GUPTA S, and GUPTA S K. Emerging UAV technology for disaster detection, mitigation, response, and preparedness[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2022, 39(6): 905–955. doi: 10.1002/rob.22075. [3] 刘勇, 陈卓, 马良. 地震应急救援中卡车-无人机多目标协同调度问题及优化算法[J/OL]. 计算机应用研究. https://doi.org/10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2025.03.0111, 2025.LIU Yong, CHEN Zhuo, and MA Liang. Multi-objective cooperative scheduling optimization for truck-drone systems in earthquake emergency rescue operations[J/OL]. Application Research of Computers. https://doi.org/10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2025.03.0111, 2025. [4] DIAO Qifeng, ZHANG Jinfeng, LIU Min, et al. A disaster relief UAV path planning based on APF-IRRT* fusion algorithm[J]. Drones, 2023, 7(5): 323. doi: 10.3390/drones7050323. [5] HAYAT S, YANMAZ E, BETTSTETTER C, et al. Multi-objective drone path planning for search and rescue with quality-of-service requirements[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2020, 44(7): 1183–1198. doi: 10.1007/s10514-020-09926-9. [6] LI Jing, XIONG Yonghua, SHE Jinhua, et al. Optimal path planning for unmanned aerial vehicles with multiple round-trip flights in coverage tasks[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2025, 189: 104970. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2025.104970. [7] 田宇, 唐阳山, 李冬月, 等. 基于改进灰狼优化算法的多无人机应急救援任务分配[J]. 现代电子技术, 2025, 48(11): 163–168. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2025.11.025.TIAN Yu, TANG Yangshan, LI Dongyue, et al. Multi-UAV emergency rescue task planning based on improved grey wolf optimization algorithm[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2025, 48(11): 163–168. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2025.11.025. [8] ABDOLLAHZADEH B, KHODADADI N, BARSHANDEH S, et al. Puma Optimizer (PO): A novel metaheuristic optimization algorithm and its application in machine learning[J]. Cluster Computing, 2024, 27(4): 5235–5283. doi: 10.1007/s10586-023-04221-5. [9] GHAREHCHOPOGH F S. Quantum-inspired metaheuristic algorithms: Comprehensive survey and classification[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2023, 56(6): 5479–5543. doi: 10.1007/S10462-022-10280-8. [10] AGRAWAL R K, KAUR B, and AGARWAL P. Quantum inspired Particle Swarm Optimization with guided exploration for function optimization[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 102: 107122. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107122. [11] 甄然, 王攀, 武晓晶, 等. 基于量子遗传算法的无人机冲突解脱方法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(17): 6963–6969. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.17.038.ZHEN Ran, WANG Pan, WU Xiaojing, et al. A method of unmanned aerial vehicles conflict resolution based on quantum genetic algorithm[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(17): 6963–6969. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.17.038. [12] LIANG Peng, CHEN Yangtao, SUN Yafeng, et al. An information entropy-driven evolutionary algorithm based on reinforcement learning for many-objective optimization[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 238: 122164. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122164. [13] FERNÁNDEZ-SÁNCHEZ D, GARRIDO-MERCHÁN E C, and HERNÁNDEZ-LOBATO D. Alpha entropy search for new information-based Bayesian optimization[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2025, 322: 113612. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2025.113612. [14] 张运凯, 高金, 李青, 等. 基于信息熵的自适应多分类器交通数据插值模型[J]. 河北科技大学学报, 2025, 46(3): 248–256. doi: 10.7535/hbkd.2025yx03002.ZHANG Yunkai, GAO Jin, LI Qing, et al. Adaptive multi classifier traffic data interpolation model based on information entropy[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2025, 46(3): 248–256. doi: 10.7535/hbkd.2025yx03002. [15] XU Longyan, XI Mao, GAO Ren, et al. Dynamic path planning of UAV with least inflection point based on adaptive neighborhood A* algorithm and multi-strategy fusion[J]. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1): 8563. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92406-w. [16] ALI H, XIONG Gang, HAIDER M H, et al. Feature selection-based decision model for UAV path planning on rough terrains[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 232: 120713. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120713. [17] AMRALLAH A, MOHAMED E M, TRAN G K, et al. UAV trajectory optimization in a post-disaster area using dual energy-aware bandits[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(3): 1402. doi: 10.3390/s23031402. [18] 俞佳晨, 胡剑虹, 郑恩辉. 基于CMA-ES算法的无人机群协同救援任务分配优化[J]. 现代电子技术, 2025, 48(10): 92–96. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2025.10.015.YU Jiachen, HU Jianhong, and ZHENG Enhui. UAV swam cooperative rescue task assignment optimization based on CMA-ES algorithm[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2025, 48(10): 92–96. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2025.10.015. [19] ABBAS A, AMBAINIS A, AUGUSTINO B, et al. Challenges and opportunities in quantum optimization[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2024, 6(12): 718–735. doi: 10.1038/s42254-024-00770-9. [20] HAN Xiaokuang, DU Xianjun, and YU Ping. ATLA: A novel metaheuristic optimization algorithm inspired by the mating search behavior of longicorn beetles in the nature[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 782(5): 052028. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/782/5/052028. [21] SHETA A, BRAIK M, AL-HIARY H, et al. Improved versions of crow search algorithm for solving global numerical optimization problems[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2023, 53(22): 26840–26884. doi: 10.1007/s10489-023-04732-z. [22] QU Shizheng, LIU Huan, XU Yinghang, et al. Application of spiral enhanced whale optimization algorithm in solving optimization problems[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 24534. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74881-9. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
