Overview of the Research on Key Technologies for AI-powered Integrated Sensing, Communication and Computing
-
摘要: 通感算一体化技术与人工智能算法相结合已成为一个非常重要的领域,因其频谱利用率高、硬件成本低等优点,已经成为第6代(6G)网络中的关键技术之一。人工智能(AI)赋能的通感算一体化系统通过集成感知、通信、计算和人工智能功能,可在日益复杂和动态的环境中实现快速数据处理、实时资源优化和智能决策,已经广泛应用于智能车载网络,包括无人机和自动汽车,以及雷达应用、定位和跟踪、波束成形等领域。该文在引入人工智能算法来提高通感算一体化系统性能的基础上,简要介绍了人工智能和通感算一体化的特征与优势,重点讨论了AI赋能的通感算一体化系统的智能网络框架、应用前景、性能指标和关键技术,并在最后对AI赋能的通感算一体化面临的挑战进行了研究展望,未来的6G无线通信网络将超越纯粹的数据传输管道,成为一个集成传感、通信、计算和智能的综合平台,以提供无处不在的人工智能服务。Abstract:
The Integration of Sensing, Communication and Computing (ISCC) combined with Artificial Intelligence(AI) algorithms has emerged as a critical enabler of Sixth-Generation (6G) networks due to its high spectral efficiency and low hardware cost. AI-powered ISCC systems, which combine sensing, communication, computing, and intelligent algorithms, support fast data processing, real-time resource allocation, and adaptive decision-making in complex and dynamic environments. These systems are increasingly applied in intelligent vehicular networks—including Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and autonomous driving—as well as in radar, positioning, tracking, and beamforming. This overview outlines the development and advantages of AI-enabled ISCC systems, focusing on performance benefits, application potential, evaluation metrics, and enabling technologies. It concludes by discussing future research directions. Future 6G networks are expected to evolve beyond data transmission to form an integrated platform that unifies sensing, communication, computing, and intelligence, enabling pervasive AI services. Significance AI-powered ISCC marks a transformative shift in wireless communication, enabling more efficient spectrum utilization, reduced hardware cost, and improved adaptability in complex environments. This integration is central to the development of 6G networks, which aim to deliver intelligent and efficient services across applications such as autonomous vehicles, UAVs, and smart cities. The significance of this research lies in its potential to reshape the management and optimization of communication, sensing, and computing resources, advancing the realization of a ubiquitously connected and intelligent infrastructure. Progress Recent advances in AI—particularly in machine learning, deep learning, and reinforcement learning—have substantially improved the performance of ISCC systems. These methods enable real-time data processing, intelligent resource management, and adaptive decision-making, which are critical for future 6G requirements. Notable progress includes AI-driven waveform design, beamforming, channel estimation, and dynamic spectrum allocation, all of which enhance ISCC efficiency and reliability. Additionally, the integration of edge computing and federated learning has mitigated challenges related to latency, data privacy, and scalability, facilitating broader deployment of AI-enabled ISCC systems. Conclusions Research on AI-powered ISCC systems highlights the benefits of integrating AI with sensing, communication, and computing. AI algorithms improve resource efficiency, sensing precision, and real-time adaptability, making ISCC systems well suited for dynamic and complex environments. The adoption of lightweight models and distributed learning has broadened applicability to resource-limited platforms such as drones and IoT sensors. Overall, AI-enabled ISCC systems advance the realization of 6G networks, where sensing, communication, and computing are unified to support intelligent and ubiquitous services. Prospects The advancement of AI-powered ISCC systems depends on addressing key challenges, including data quality, model complexity, security, and real-time performance. Future research should focus on developing robust AI models capable of generalizing across diverse wireless environments. Progress in lightweight AI and edge computing will be critical for deployment in resource-constrained devices. The integration of multi-modal data and the design of secure, privacy-preserving algorithms will be essential to ensure system reliability and safety. As 6G networks evolve, AI-powered ISCC systems are expected to underpin intelligent, efficient, and secure communication infrastructures, reshaping human-technology interaction in the digital era. -
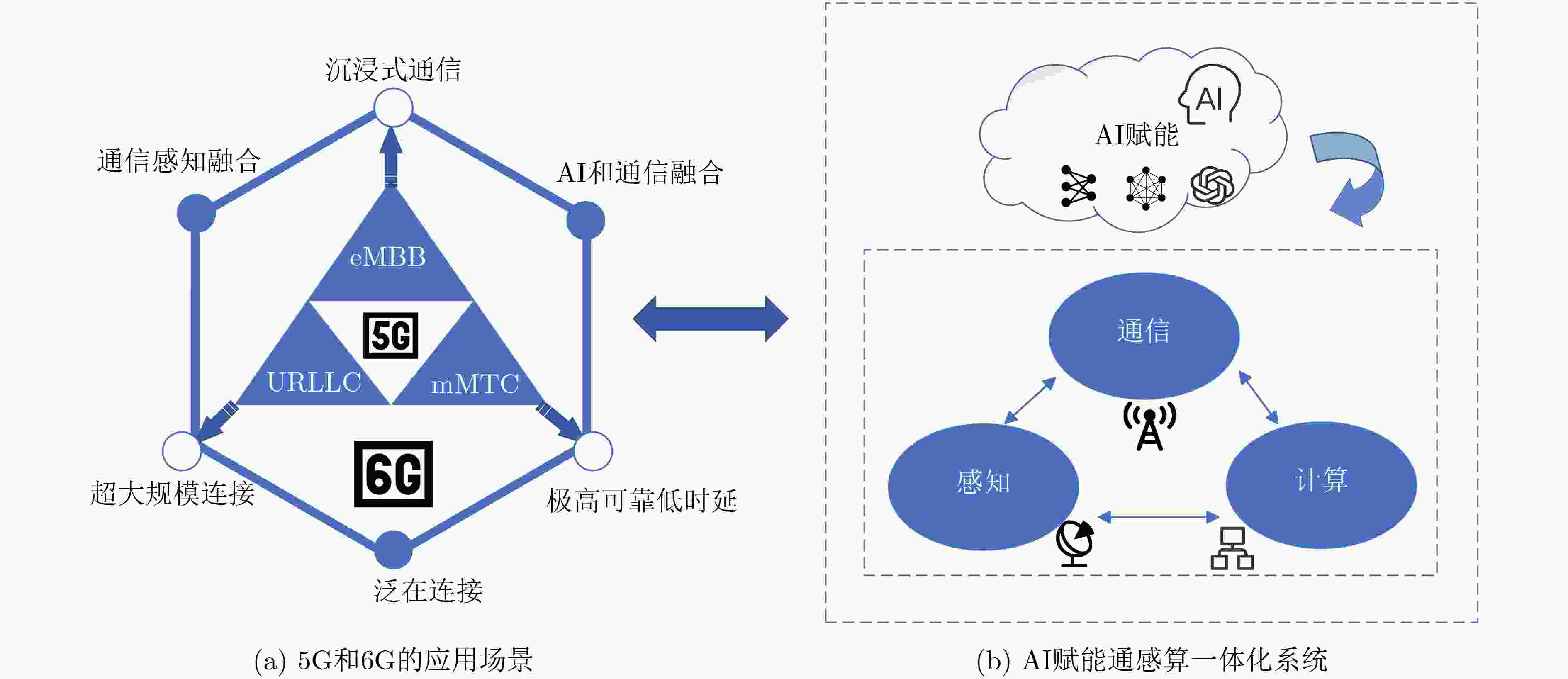
表 1 5G与6G部分性能指标对比
性能指标 5G 6G 提升效果 峰值速率 10~20 Gbit/(s·Hz)(理论值) 100 Gbit/(s·Hz) ~1 Tbit/(s·Hz)(理论值) 10~100倍 用户体验速率 0.1~1 Gbit/(s·Hz) 数十Gbit/(s·Hz) 10~100倍 时延 1 ms 10~100 μs 10~100倍 连接密度 106设备/km2 107~108设备/km2 10~100倍 频谱效率 约100 bit/(s·Hz) 150~300 bit/(s·Hz) 1.5~3倍 覆盖范围 地面基站为主 空天地一体化覆盖 全球无缝覆盖 表 2 AI赋能通感算一体化系统与传统正交频分复用波形系统性能对比
对比维度 AI赋能通感算一体化系统 传统正交频分复用波形系统 关键差异来源 通信性能[18,19] AI优化波束成形,误码率降低10%~30%
频谱效率提升高峰均功率比导致信号失真
固定子载波分配效率受限AI动态优化波形与资源分配 感知精度[19–21] MSE降低20%~50%
支持多目标跟踪与语义提取快速傅里叶变换低信噪比误差大
单目标检测为主AI增强信号去噪能力 计算效率[16,22] 边缘智能降低30%~60%时延
实时信道建模云端集中计算时延高
多径分离需迭代处理云边端协同架构优化 时空频复杂度 LSTM波束预测控制时延
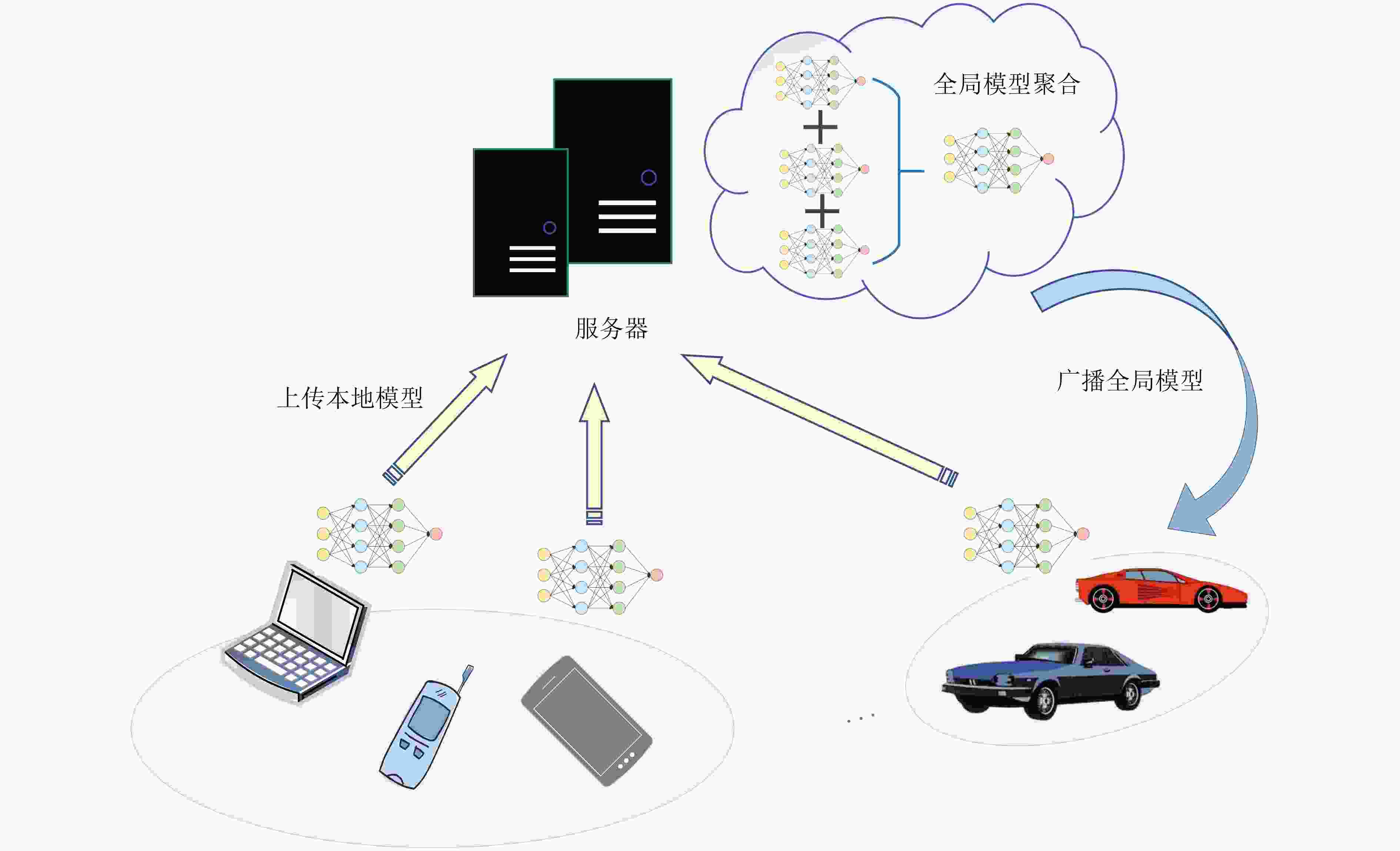
动态频谱共享凸优化算法耗时长
固定子载波分配AI动态资源调度技术 能耗 AI辅助降低功耗 全子载波高功耗 智能功率优化策略 表 3 AI赋能的通感算一体化系统关键技术简要汇总
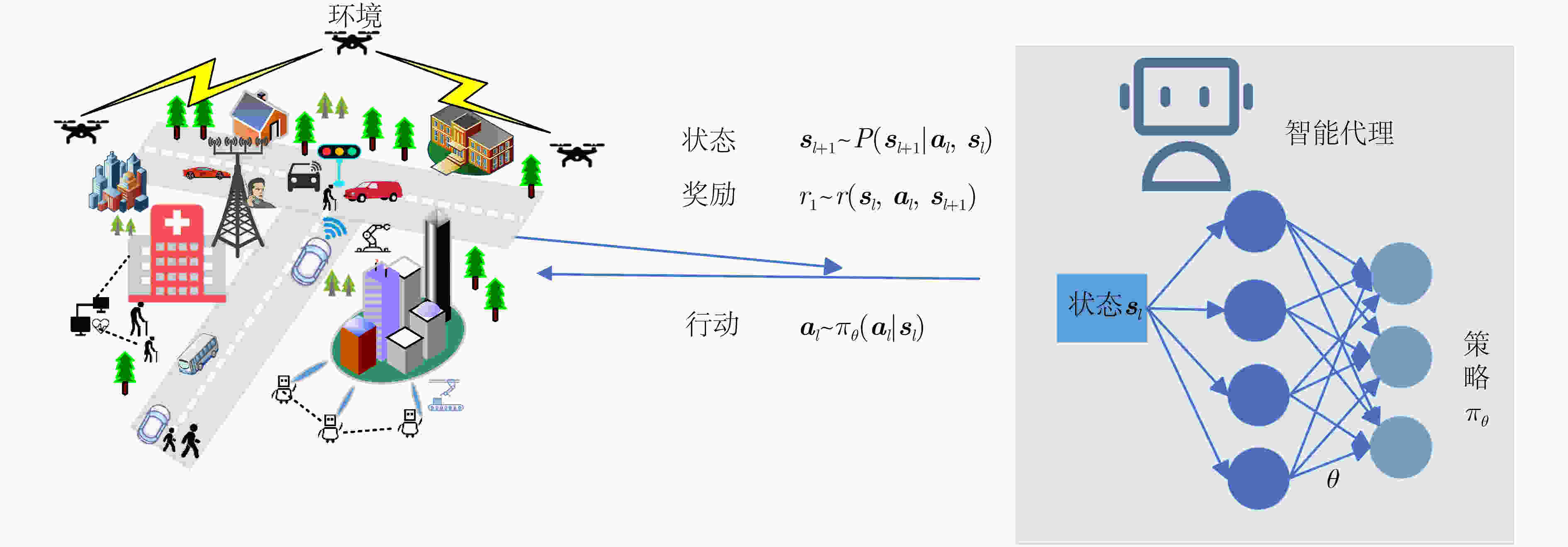
参考文献 关键技术 AI作用 性能指标 训练模型 应用场景 [25] 波形设计 优化波形生成、选择、调整、匹配等,
以适应通信感知双重需求,并降低复杂度保密率 DRL等 自动驾驶 [21,26] 波束赋形 提高了频谱效率,减轻了多径衰落,确保了动态城市
环境中的无缝连接和可靠性和速率 DRL, DL等 自动驾驶 [28–30] 信道估计 提升信道估计的精度、降低计算复杂性,实现动态适配 估计精度 GAN, CNN等 自动驾驶 [32] 干扰管理 在资源有限场景中,实时应对并缓解通信与感知任务中的干扰问题 均方误差 DNN, ML等 无人机监测 [33,34] 动态频谱分配 提供智能化的优化算法和学习模型,
实现高效的动态分配,提升系统性能准确率、频谱效率 DRL, RNN等 工业物联网 -
[1] ZHANG Shunqing, XIANG Chenlu, and XU Shugong. 6G: Connecting everything by 1000 times price reduction[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Vehicular Technology, 2020, 1: 107–115. doi: 10.1109/OJVT.2020.2980003. [2] 余显祥, 姚雪, 杨婧, 等. 面向感知应用的通感一体化信号设计技术与综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 247–261. doi: 10.12000/JR23015.YU Xianxiang, YAO Xue, YANG Jing, et al. Radar-centric DFRC signal design: Overview and future research avenues[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 247–261. doi: 10.12000/JR23015. [3] TAN D K P, HE Jia, LI Yanchun, et al. Integrated sensing and communication in 6G: Motivations, use cases, requirements, challenges and future directions[C]. IEEE International Online Symposium on Joint Communications & Sensing (JC&S), Dresden, Germany, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/JCS52304.2021.9376324. [4] WU Nan, JIANG Rongkun, WANG Xinyi, et al. AI-enhanced integrated sensing and communications: Advancements, challenges, and prospects[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2024, 62(9): 144–150. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2300724. [5] 林奕森, 甘德樵, 葛晓虎. AI赋能6G: 绿色通信的未来[J]. 移动通信, 2024, 48(8): 20–24, 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20240621-0001.LIN Yisen, GAN Deqiao, and GE Xiaohu. AI-powered 6G: The future of green communications[J]. Mobile Communications, 2024, 48(8): 20–24, 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20240621-0001. [6] 闫实, 彭木根, 王文博. 通信-感知-计算融合: 6G愿景与关键技术[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2021, 44(4): 1–11. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2021-081.YAN Shi, PENG Mugen, and WANG Wenbo. Integration of communication, sensing and computing: The vision and key technologies of 6G[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2021, 44(4): 1–11. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2021-081. [7] 王辉, 孟士尧, 贾敏. 空天地一体化场景中的6G通感算融合与数字孪生技术[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2024, 50(6): 1057–1066. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2024.06.001.WANG Hui, MENG Shiyao, and JIA Min. 6G communication-sensing-computing integrated space-air-ground digital twin network[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2024, 50(6): 1057–1066. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2024.06.001. [8] 陈新宇, 王卫斌, 陆光辉. 基于AI agent的6G内生智能技术框架及其应用[J]. 移动通信, 2024, 48(7): 28–32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20240613-0001.CHEN Xinyu, WANG Weibin, and LU Guanghui. 6G native intelligent technology framework and its application based on AI agent[J]. Mobile Communications, 2024, 48(7): 28–32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20240613-0001. [9] ZHAO Junhui, Ren Ruixing, ZOU Dan, et al. IoV-Oriented integrated sensing, computation, and communication: System design and resource allocation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(11): 16283–16294. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3422270. [10] SALEM H, QUAMAR M D M, MANSOOR A, et al. Data-Driven integrated sensing and communication: Recent advances, challenges, and future prospects[J]. arXiv: 2308.09090, 2023. [11] 陈真, 杜晓宇, 唐杰, 等. 基于深度强化学习的RIS辅助通感融合网络: 挑战与机遇[J]. 电子信息学报, 2024, 46(9): 3467–3473. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240086.CHEN Zhen, DU Xiaoyu, TANG Jie, et al. DRL-based RIS-assisted ISAC Network: Challenges and opportunities[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(9): 3467–3473. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240086. [12] HOU Peng, HUANG Yi, ZHU Hongbin, et al. Distributed DRL-based integrated sensing, communication, and computation in cooperative UAV-enabled intelligent transportation systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(5): 5792–5806. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3489655. [13] LIANG Yipeng, XHEN Qimei, and HAO Jiang. Federated learning with integrated sensing, communication, and computation: Frameworks and performance analysis[J]. arXiv: 2409.11240, 2024. [14] LIU Peixi, ZHU Guangxu, WANG Shuai, et al. Toward ambient intelligence: Federated edge learning with task-oriented sensing, computation, and communication integration[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2023, 17(1): 158–172. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3226836. [15] JIAO Licheng, SHAO Yilin, SUN Long, et al. Advanced deep learning models for 6G: Overview, opportunities, and challenges[J] IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 133245–133314. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3418900. [16] 王新奕, 费泽松, 周一青, 等. 面向物联网的通感算智融合: 关键技术与未来展望[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(4): 888-908. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT240806.WANG Xinyi, FEI Zesong, ZHOU Yiqing, et al. Integrated sensing, communication, computation, and intelligence towards IoT: Key technologies and future directions[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(4): 888-908. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT240806. [17] 王友祥, 裴郁杉, 黄蓉, 等. 6G通感算一体化网络架构和关键技术研究[J]. 移动通信, 2023, 47(9): 2–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20230904-0002.WANG Youxiang, PEI Yushan, HUANG Rong, et al. Network architecture and key technologies for 6G integrated communication, sensing and computing[J]. Mobile Communications, 2023, 47(9): 2–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20230904-0002. [18] ZHANG Jifa, GUO Shaoyong, GONG Shiqi, et al. Intelligent waveform design for integrated sensing and communication[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2025, 32(1): 166–173. doi: 10.1109/MWC.003.2400044. [19] KHORAMNEJAD F and HOSSAIN E. Generative AI for the optimization of next-generation wireless networks: Basics, state-of-the-art, and open challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2025. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2025.3535554. [20] LIU Chang, YUAN Weijie, LI Shuangyang, et al. Learning-based predictive beamforming for integrated sensing and communication in vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(8): 2317–2334. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3180803. [21] LIU Yiyang, ZHANG Siyao, LI Xinmin, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based beamforming design in ISAC-assisted vehicular networks[C]. IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC57260.2024.10571018. [22] VALCARCE A, KELA P, MANDELLI S, et al. The role of AI in 6G MAC[C]. 2024 Joint European Conference on Networks and Communications & 6G Summit, Antwerp, Belgium, 2024: 723–728. doi: 10.1109/EuCNC/6GSummit60053.2024.10597082. [23] REN Ruixing. Integrated sensing, communication and computation: Research status and future prospects[J]. 2024. [24] 马丁友, 刘祥, 黄天耀, 等. 雷达通信一体化: 共用波形设计和性能边界[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(2): 198–212. doi: 10.12000/JR21146.MA Dingyou, LIU Xiang, HUANG Tianyao, et al. Joint radar and communications: Shared waveform designs and performance bounds[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(2): 198–212. doi: 10.12000/JR21146. [25] LIU Qian, ZHU Yuqian, LI Ming, et al. DRL-based secrecy rate optimization for RIS-assisted secure ISAC systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(12): 16871–16875. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3297602. [26] ZHONG Kai, HU Jinfeng, PAN Cunhua, et al. Joint waveform and beamforming design for RIS-aided ISAC systems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 165–169. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3242554. [27] 徐明枫, 李阳, 韩凯峰, 等. 基于GAN的导频配置和信道估计联合优化算法[J]. 信息通信技术与政策, 2023, 49(9): 58–66. doi: 10.12267/j.issn.2096-5931.2023.09.009.XU Mingfeng, LI Yang, HAN Kaifeng, et al. GAN-based joint pilot configuration and channel estimation optimization method[J]. Information and Communications Technology and Policy, 2023, 49(9): 58–66. doi: 10.12267/j.issn.2096-5931.2023.09.009. [28] BALEVI E, DOSHI A, and ANDREWS J G. Massive MIMO channel estimation with an untrained deep neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(3): 2079–2090. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2962474. [29] SAFARI M S, POURAHMADI V, and SODAGARI S. Deep UL2DL: Data-driven channel knowledge transfer from uplink to downlink[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Vehicular Technology, 2020, 1: 29–44. doi: 10.1109/OJVT.2019.2962631. [30] DU Ying, LI Yang, XU Mingfeng, et al. A joint channel estimation and compression method based on GAN in 6G communication systems[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(4): 2319. doi: 10.3390/app13042319. [31] NGUYEN C, HOANG T M, and CHEEMA A A. Channel estimation using CNN-LSTM in RIS-NOMA assisted 6G network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Machine Learning in Communications and Networking, 2023, 1: 43–60. doi: 10.1109/TMLCN.2023.3278232. [32] LIU Xiangnan, ZHANG Haijun, LONG Keping, et al. Distributed unsupervised learning for interference management in integrated sensing and communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(12): 9301–9312. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3269815. [33] GAO Kaixuan, WANG Huiqiang, LU Hongwu, et al. Toward 5G NR high-precision indoor positioning via channel frequency response: A new paradigm and dataset generation method[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(7): 2233–2247. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3157397. [34] SAIDUTTA Y M, ABDI A, and FEKRI F. Joint source-channel coding over additive noise analog channels using mixture of variational autoencoders[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(7): 2000–2013. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3078489. [35] LIU Boxun, LIU Yuanyu, GAO Shijian, et al. LLM4CP: Adapting large language models for channel prediction[J]. Communications and Information Networks, 2024, 9(2): 113–125. doi: 10.23919/JCIN.2024.10582829. -





 下载:
下载:
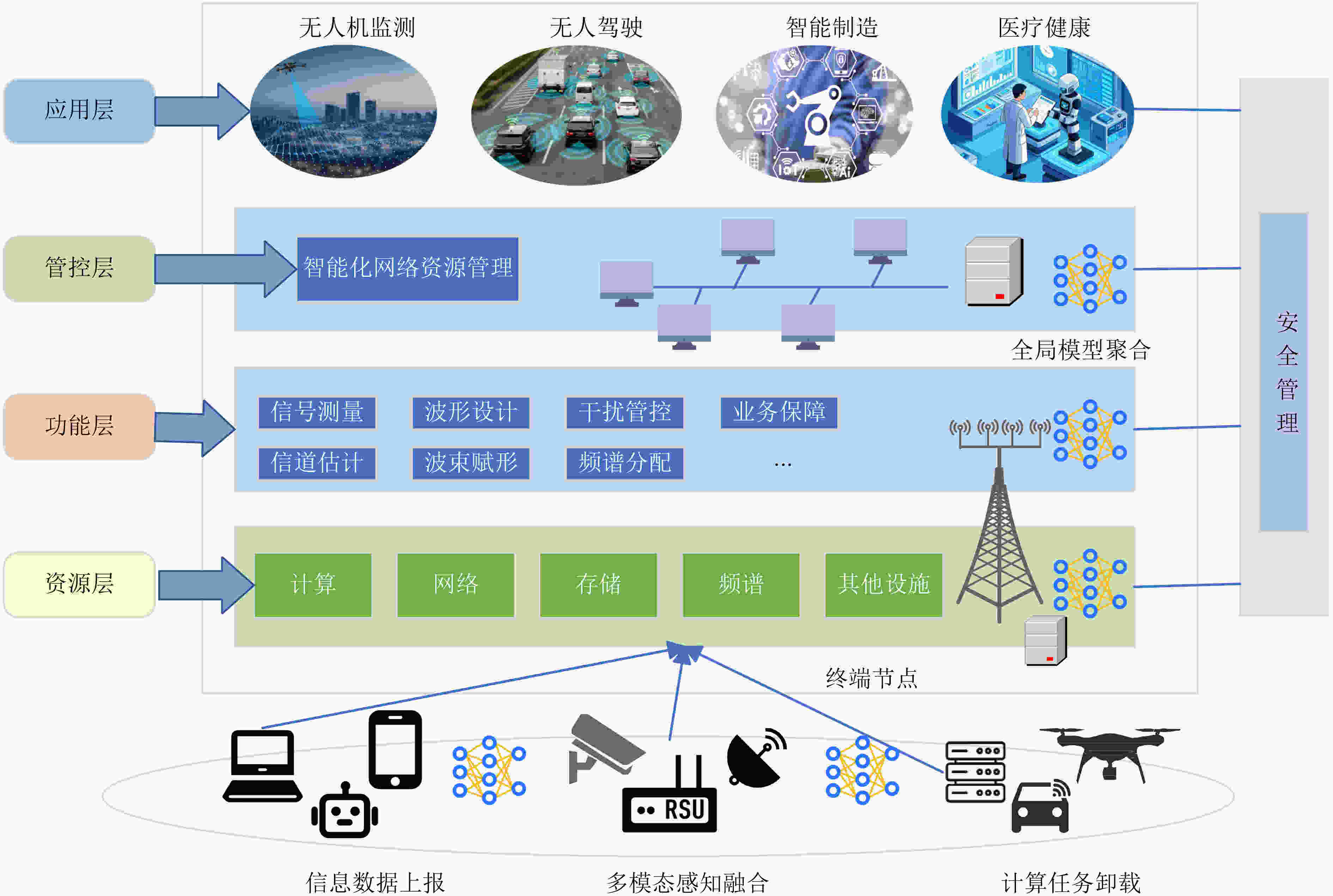


 下载:
下载:
