YOLO-SCDI: A Vehicle Detection Algorithm Based on an Improved YOLOv8
-
摘要: 针对城市复杂道路环境中车辆检测面临的多尺度目标、密集车流遮挡等难题,该文提出了一种轻量化YOLO-SCDI车辆检测算法。首先,采用改进的C2f-SCSA模块替换骨干网络中的C2f模块,通过动态融合多尺度卷积核提取的局部与全局特征,同时结合空间-通道双维度注意力机制,从而实现精准的特征选择。其次,创新性地在颈部网络引入跨尺度特征融合模块(CCFM),通过4个卷积同步完成通道压缩与跨通道信息融合,显著增强了模型对不同尺度目标的适应性,同时降低了模型参数。再次,用Dynamic Head检测头替换传统检测头,通过尺度-空间-任务三维注意力机制动态调节特征响应,并引入动态卷积核生成网络,自适应调整检测头参数配置。最后,提出了Inner-ShapeIoU度量方法以优化边界框回归过程。实验结果表明,在精简后的UA-DETRAC数据集上,YOLO-SCDI在mAP@0.5和精确度(P)上分别达到了95.8%和95.9%,同时模型的参数量为2.37M,相较于基准模型YOLOv8n,精度分别提升了2.5%和4.1%,参数量减少了21.0%,具有更高的检测精度和更精简的模型参数。
-
关键词:
- 车辆检测 /
- SCSA /
- CCFM /
- Dynamic Head
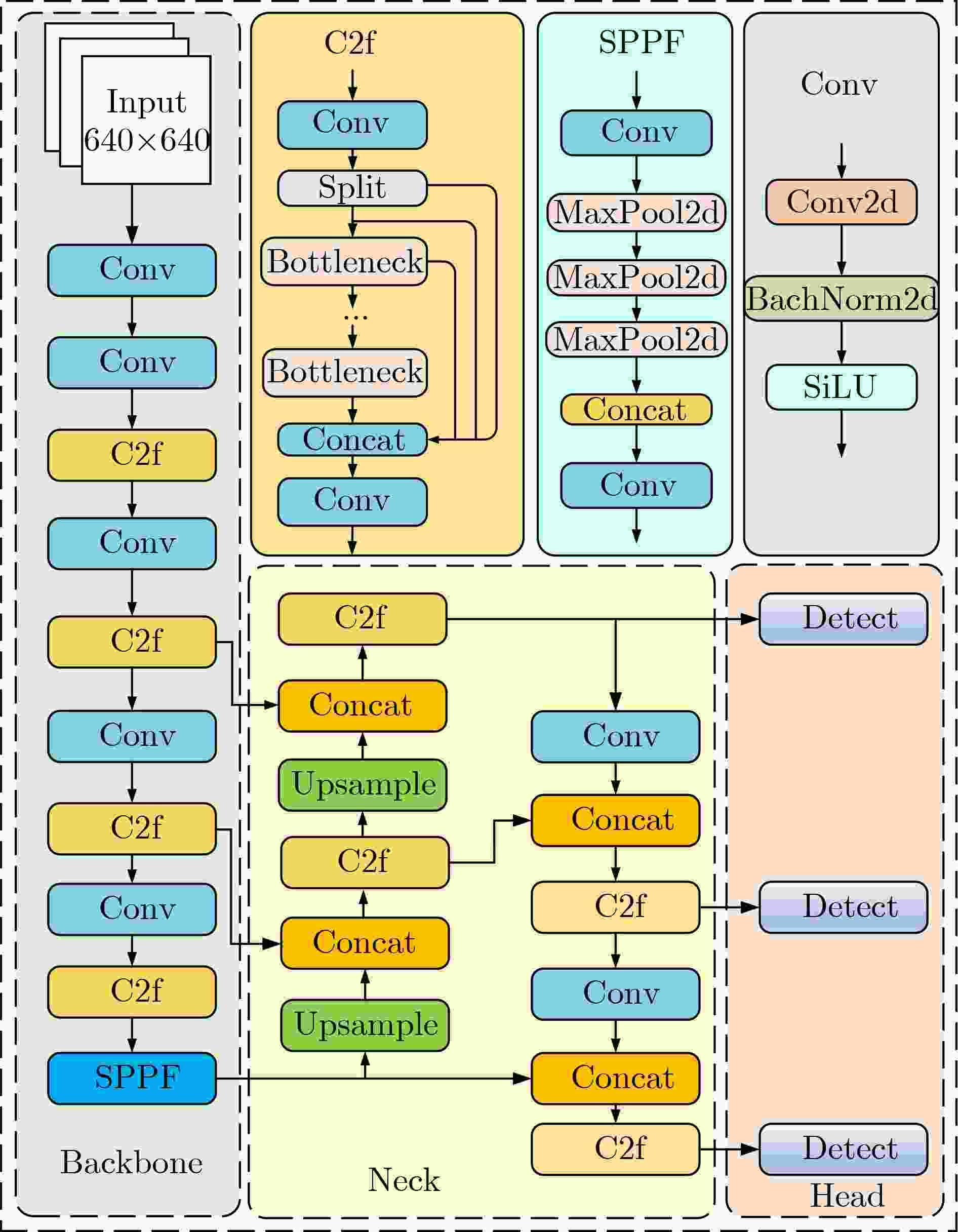
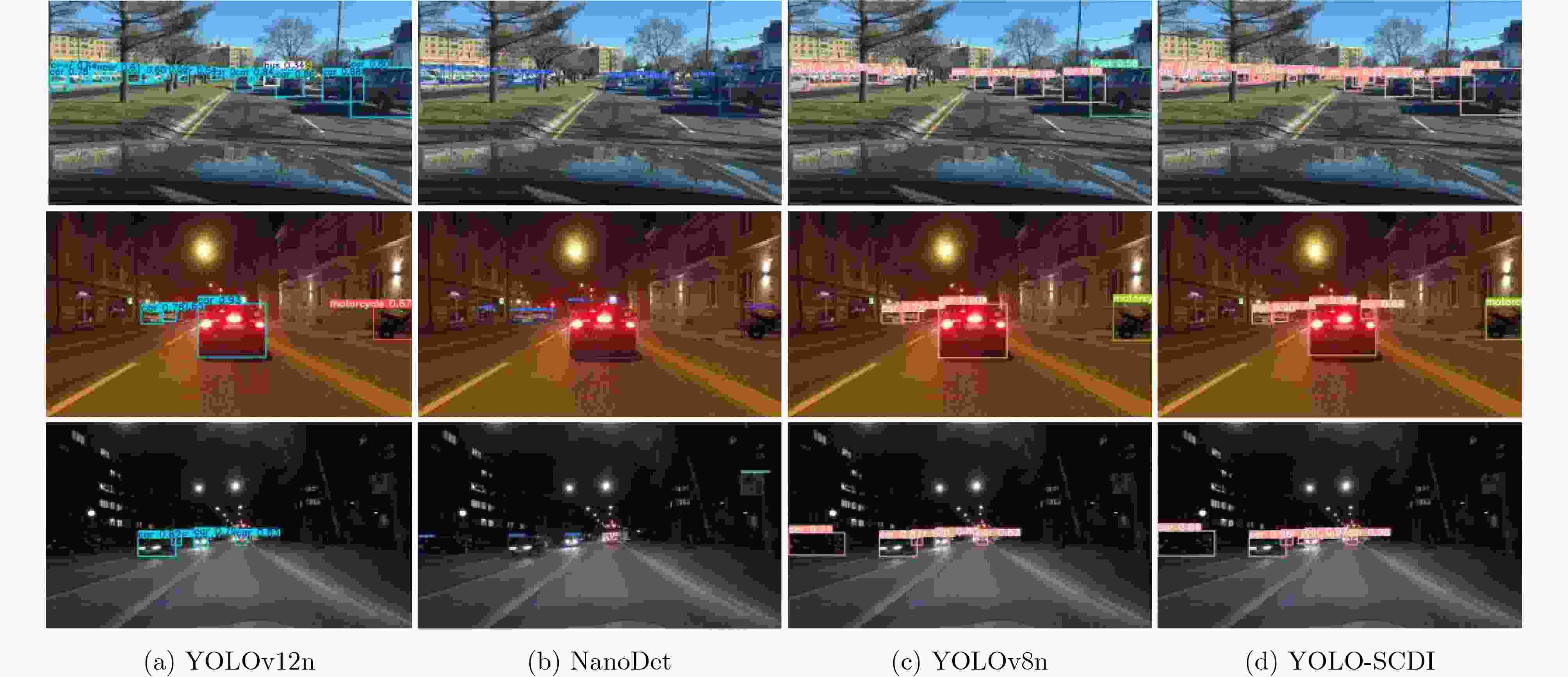
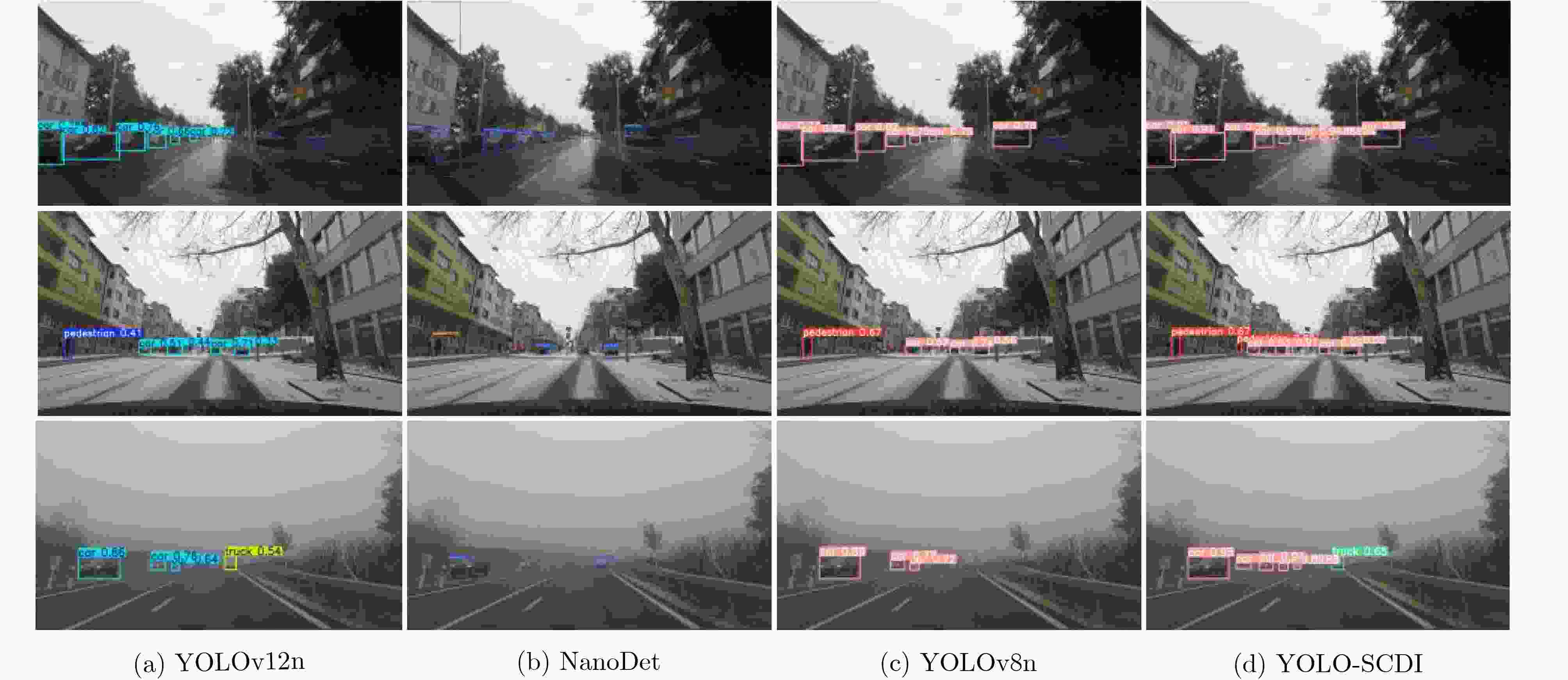
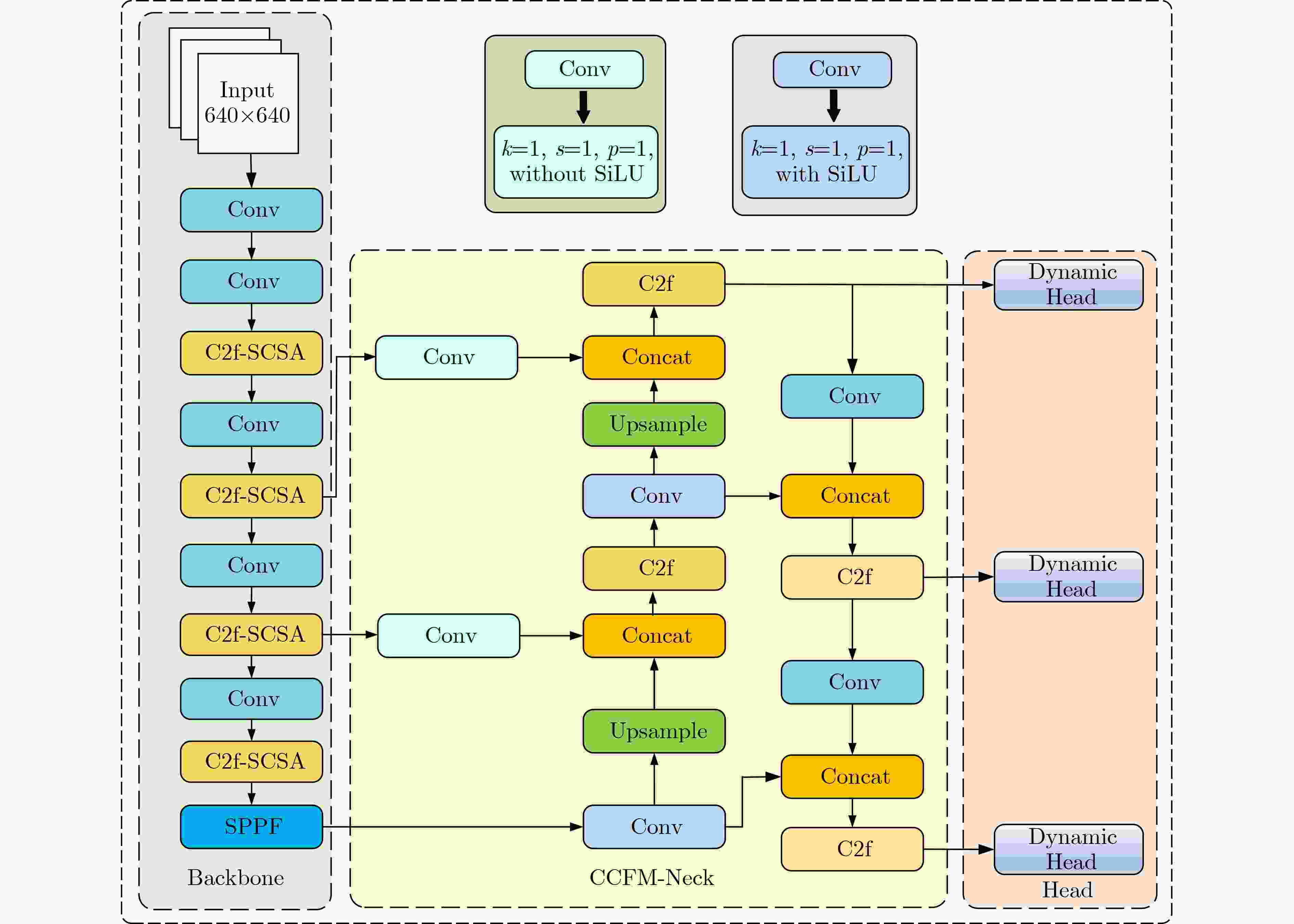
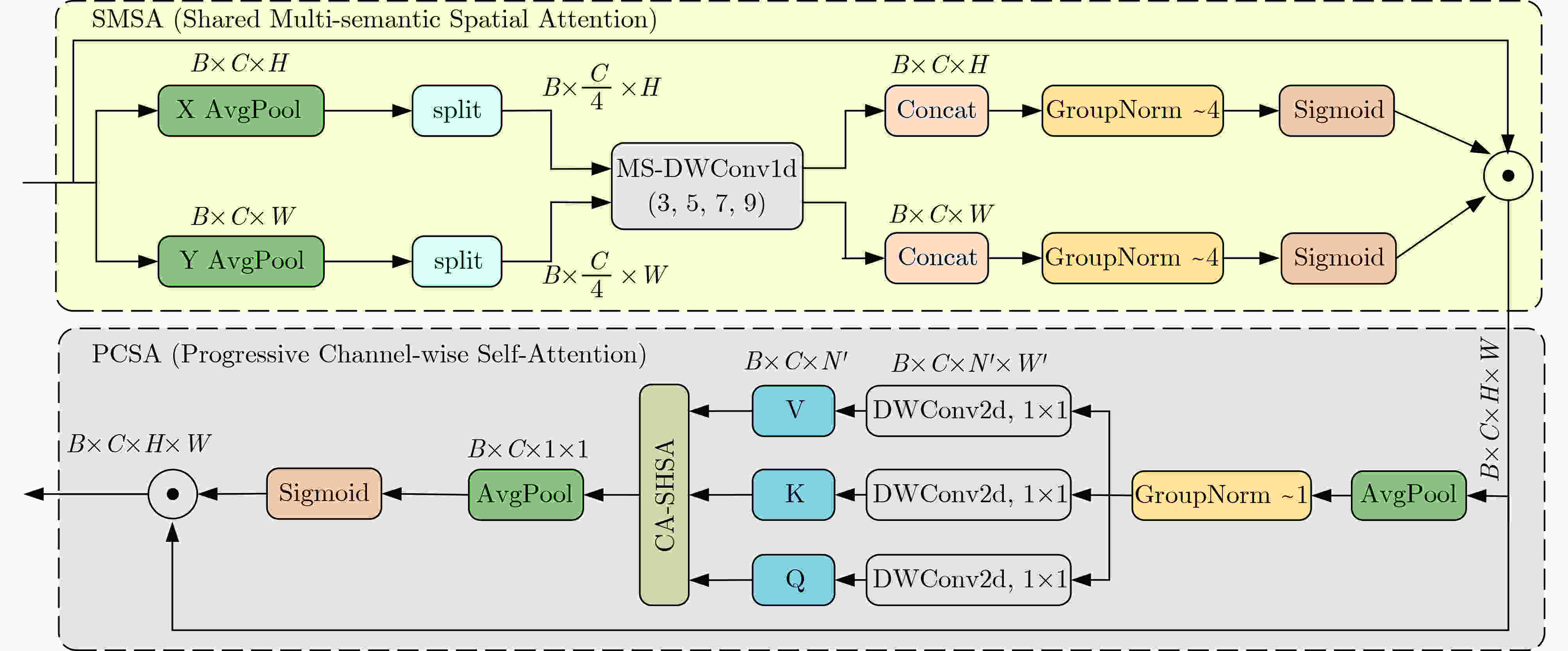
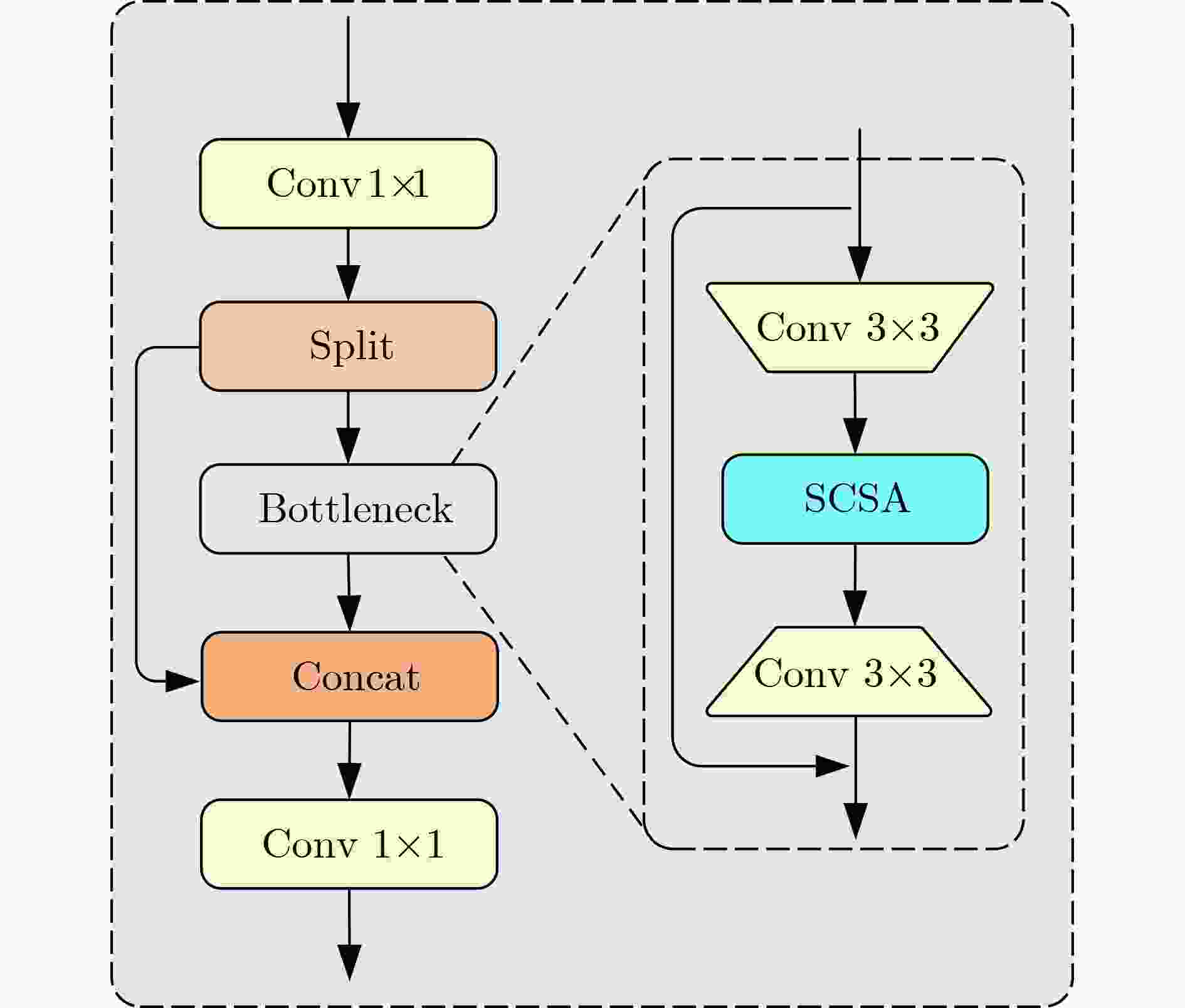
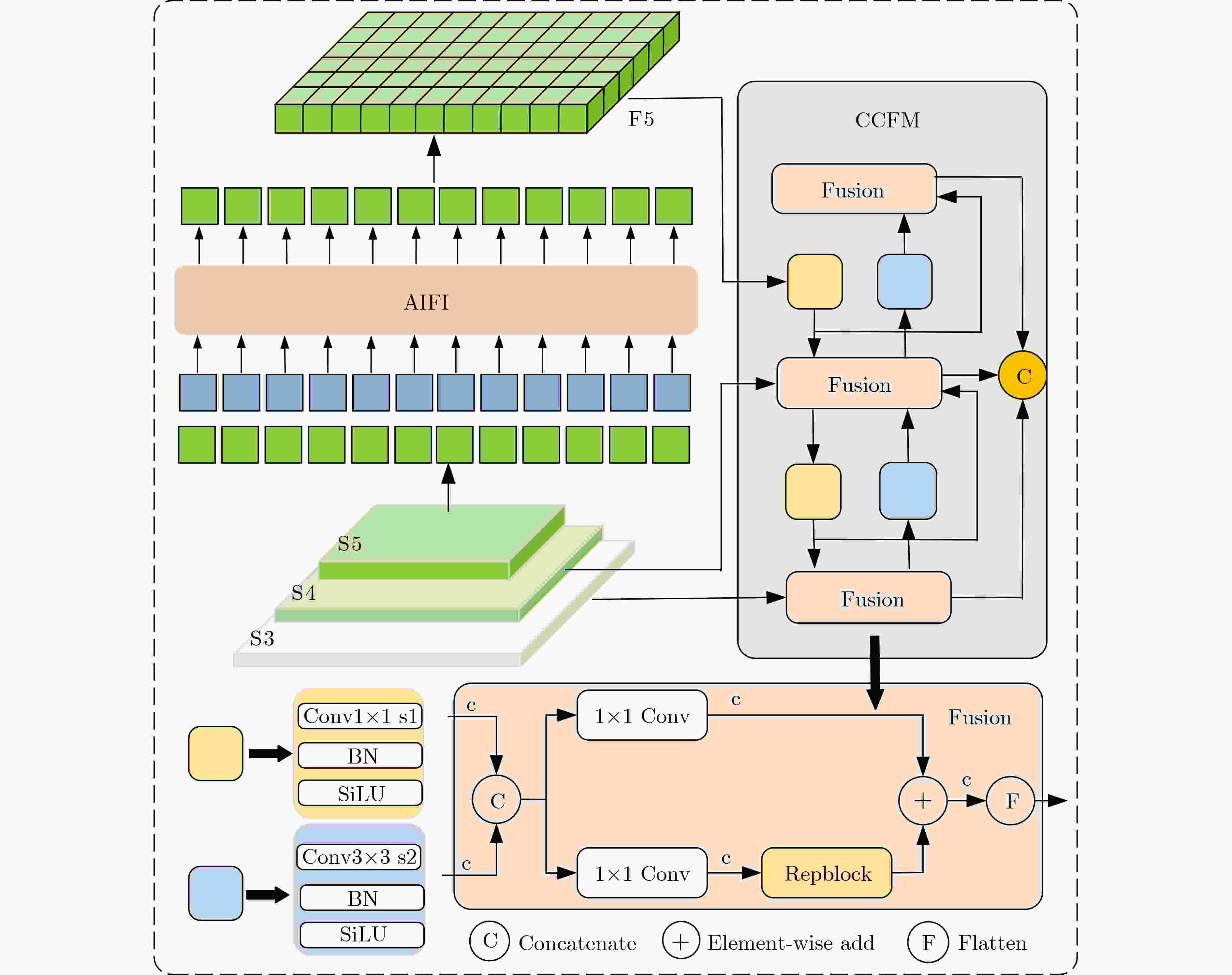
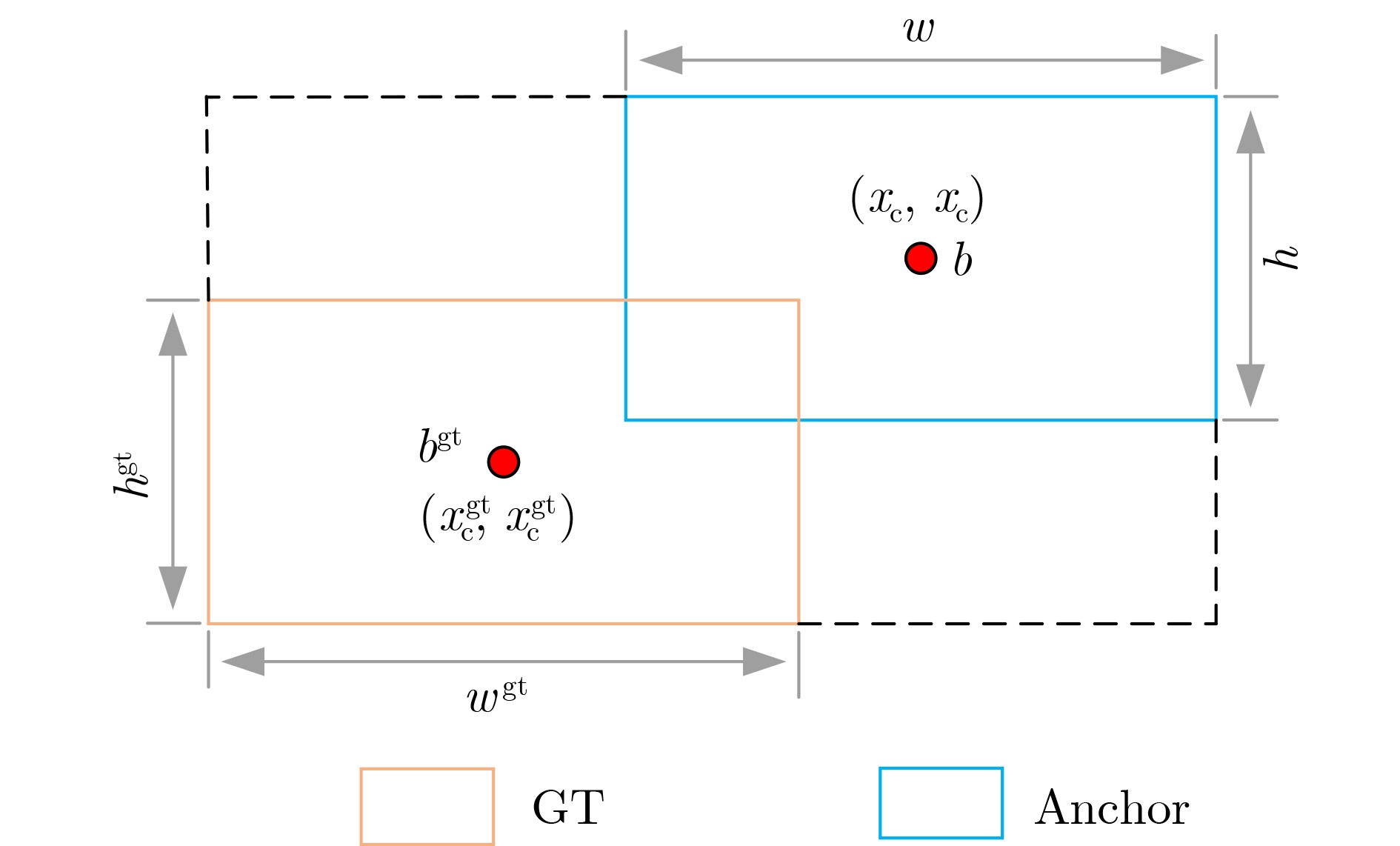
Abstract:Objective As a core task in computer vision, object detection is vital for intelligent transportation, supporting applications such as autonomous driving, Electronic Toll Collection (ETC), and traffic violation monitoring. However, complex urban environments—characterized by extreme weather, dense traffic occlusions, intense illumination, and reflective surfaces—pose substantial challenges, leading traditional methods to high false detection and missed detection rates. Despite recent progress, accuracy issues remain unresolved. To address these limitations, this study proposes YOLO-SCDI, a lightweight and effective vehicle detection model systematically optimized from YOLOv8 across four components: backbone network, neck structure, detection head, and loss function. These improvements significantly enhance detection accuracy and robustness in complex traffic conditions while maintaining model compactness and inference efficiency. Methods Building on the YOLOv8n architecture, four top-down optimization strategies are designed to balance detection accuracy, parameter efficiency, and lightweight deployment. First, to address the limited feature representation capacity, an attention-enhanced C2f-SCSA module ( Fig. 4 ) is proposed. This module dynamically integrates local and global features through multi-scale convolutions and a dual spatial-channel attention mechanism, thereby improving the quality of input features. Second, to achieve effective multi-scale information integration while preserving both detailed and contextual features, a lightweight Cross-scale Feature Fusion Module (CCFM) is introduced into the Neck structure (Fig. 5 ). This results in the CCFM-Neck architecture, which reduces parameter size and enhances sensitivity to small-scale targets. Third, to mitigate the limitations of YOLOv8’s detection head—such as fixed feature fusion patterns and weak dynamic cross-scale interactions—a Dynamic Head module is incorporated. This module jointly models scale, spatial, and task attention, and includes a dynamic convolution-kernel generation network that adjusts convolution weights in real time according to input features. These improvements strengthen classification and regression feature responses, increasing the adaptability and discriminability of the detection head. Finally, because the CIoU loss function shows insufficient localization accuracy for small or irregular targets, ShapeIoU is adopted as the loss function. It is further improved using the Inner-IoU concept, which accelerates model convergence and enhances localization performance.Results and Discussions YOLO-SCDI is evaluated against mainstream detection models on the UA-DETRAC and BDD100K datasets. On the UA-DETRAC dataset ( Table 4 ), YOLO-SCDI achieves an optimal balance between resource efficiency and detection performance. It requires only 2.37 M parameters and 7.6 GFLOPs—substantially fewer than competing models—while attaining 95.8% mAP@0.5, a 2.5% improvement over the baseline YOLOv8n and higher than most mainstream detectors. Under the stricter mAP@0.5:0.95 metric, YOLO-SCDI reaches 80.3%, clearly outperforming other lightweight designs. On the BDD100K dataset (Table 5 ), YOLO-SCDI improves mAP@0.5 and mAP@0.5:0.95 by 1.4% and 1.1%, respectively, compared with the baseline. These results are consistent with those from the UA-DETRAC dataset, confirming strong generalization and robustness. Detection results under varying illumination (Fig. 7 ) and adverse weather (Fig. 8 ) further validate its performance in realistic complex scenarios. Compared with models such as NanoDet, YOLOv12n, and YOLOv8n, YOLO-SCDI effectively reduces missed and false detections while providing higher-confidence predictions and more precise localization. Additionally, ablation studies (Table 3 ) confirm the contributions of the proposed C2f-SCSA, CCFM, Dynamic Head, and Inner-ShapeIoU modules to performance gains. Collectively, these results demonstrate that YOLO-SCDI markedly enhances detection accuracy while maintaining a lightweight structure, thereby meeting practical requirements for vehicle detection in complex traffic environments.Conclusions This study proposes YOLO-SCDI, a vehicle detection algorithm built on an improved YOLOv8 framework. By optimizing the backbone network, neck structure, detection head, and loss function, the method enhances detection accuracy while substantially reducing model parameters. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that YOLO-SCDI exceeds existing approaches in both accuracy and model efficiency, making it well suited for practical vehicle detection tasks in complex traffic environments. -
Key words:
- Vehicle detection /
- SCSA /
- CCFM /
- Dynamic head
-
表 1 不同r值在UA-DETRAC数据集的对比实验
Model mAP@0.5 P(%) YOLOv8n 0.933 91.8 +Inner-ShapeIoU(r=1.5) 0.940 93.0 +Inner-ShapeIoU(r=1.25) 0.936 91.3 +Inner-ShapeIoU(r=1.0) 0.939 92.3 +Inner-ShapeIoU(r=0.75) 0.942 93.3 +Inner-ShapeIoU(r=0.5) 0.941 93.1 表 2 实验参数设置
参数 设置 迭代次数 150 学习率 0.01 动量 0.937 批大小 32 优化器 SGD 图像大小 640×640 表 3 改进模型的消融实验
C2f_SCSA CCFM Dynamic Head Inner-ShapeIoU mAP@0.5 mAP@0.5:0.95 Param(M) GFLOPs 0.933 0.799 3.01 8.2 √ 0.939 0.794 3.05 8.3 √ 0.924 0.779 1.97 6.7 √ 0.961 0.827 4.75 14.8 √ 0.942 0.778 3.01 8.2 √ √ 0.948 0.801 2.37 7.6 √ √ 0.942 0.771 2.37 7.6 √ √ 0.959 0.816 4.76 14.8 √ √ 0.926 0.780 1.97 6.7 √ √ √ 0.951 0.806 2.37 7.6 √ √ √ √ 0.958 0.803 2.37 7.6 表 4 对比实验(UA-DETRAC数据集)
Method mAP@0.5 mAP@0.5:0.95 P(%) R(%) Params(M) GFLOPs YOLOv3tiny 0.935 0.775 92.1 86.6 12.1 19.0 YOLOv5s 0.954 0.823 92.7 90.6 9.1 24.0 YOLOv5m 0.961 0.833 95.9 89.5 25.1 64.4 YOLOv6m 0.942 0.812 92.0 88.6 52.0 161.6 YOLOv8n 0.933 0.800 91.8 88.8 3.0 8.2 YOLOv8s 0.955 0.816 90.6 93.3 11.1 28.7 YOLOv9c 0.959 0.835 92.0 93.3 25.5 103.7 YOLOv11n 0.929 0.786 90.4 86.7 2.6 6.4 YOLOv12n 0.924 0.775 92.4 86.2 2.5 6.0 NanoDet 0.915 0.703 - - 0.94 0.35 RT-DETR 0.937 0.798 93.3 90.9 42.8 134.5 SSD 0.773 - - - 27.2 59.2 Faster-RCNN 0.917 - - - 44.6 70.0 YOLO-SCDI 0.958 0.803 95.9 89.5 2.37 7.6 表 5 对比实验(BDD100K数据集)
Method mAP@0.5(%) mAP@0.5:0.95(%) P(%) R(%) YOLOv5n 0.367 0.205 43.0 39.4 YOLOv8n 0.370 0.190 51.2 38.7 YOLOv11n 0.371 0.207 43.8 37.6 YOLOv12n 0.362 0.203 42.8 37.9 NanoDet 0.175 0.091 - - RT-DETR 0.481 0.270 58.9 48.5 Faster-RCNN 0.215 - - - YOLO-SCDI 0.384 0.201 44.8 38.0 -
[1] 王宇. 基于深度学习的目标检测算法综述[J]. 科技资讯, 2025, 23(2): 64–66. doi: 10.16661/j.cnki.1672-3791.2407-5042-8334.WANG Yu. An overview of object detection algorithm based on deep learning[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2025, 23(2): 64–66. doi: 10.16661/j.cnki.1672-3791.2407-5042-8334. [2] LI Jiewen, ZHAO Zhicheng, WU Yanlan, et al. HOG-VGG: VGG network with HOG feature fusion for high-precision PolSAR terrain classification[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology (New Series), 2024, 31(5): 1–15. doi: 10.11916/j.issn.1005-9113.2023089. [3] 王宁, 智敏. 深度学习下的单阶段通用目标检测算法研究综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2025, 19(5): 1115–1140. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2411032.WANG Ning and ZHI Min. Review of one-stage universal object detection algorithms in deep learning[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2025, 19(5): 1115–1140. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2411032. [4] 陈憶悯, 李万益, 翁汉锐, 等. 基于深度学习的两阶段目标检测算法综述[J]. 信息与电脑(理论版), 2023, 35(14): 112–114.CHEN Yimin, LI Wanyi, WENG Hanrui, et al. Overview of two-stage object detection algorithms based on deep learning[J]. Information & Computer, 2023, 35(14): 112–114. [5] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.81. [6] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031. [7] HE Kaiming, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980–2988. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.322. [8] DING Jian, XUE Nan, LONG Yang, et al. Learning RoI transformer for oriented object detection in aerial images[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2844–2853. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00296. [9] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2. [10] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 29th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91. [11] VARGHESE R and Sambath M. YOLOv8: A novel object detection algorithm with enhanced performance and robustness[C]. 2024 International Conference on Advances in Data Engineering and Intelligent Computing Systems (ADICS), Chennai, India, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ADICS58448.2024.10533619. [12] 张浩晨, 张竹林, 史瑞岩, 等. YOLO-CDC: 优化改进YOLOv8的车辆目标检测算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2025, 61(13): 124–137. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2411-0390.ZHANG Haochen, ZHANG Zhulin, SHI Ruiyan, et al. YOLO-CDC: Improved YOLOv8 vehicle object detection algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2025, 61(13): 124–137. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2411-0390. [13] 许德刚, 王双臣, 尹柯栋, 等. 改进YOLOv8的城市车辆目标检测算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2024, 60(18): 136–146. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2401-0277.XU Degang, WANG Shuangchen, YIN Kedong, et al. Improved YOLOv8 urban vehicle target detection algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(18): 136–146. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2401-0277. [14] 寇发荣, 肖伟, 何海洋, 等. 基于改进YOLOv5的煤矿井下目标检测研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(7): 2642–2649. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220725.KOU Farong, XIAO Wei, HE Haiyang, et al. Research on target detection in underground coal mines based on improved YOLOv5[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(7): 2642–2649. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220725. [15] 项家灏, 徐慧英, 徐广平, 等. MECW-YOLO: 基于改进YOLOv8的无人机视角小目标检测算法[J/OL]. 计算机工程与科学, 1–12[2025-03-20]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/43.1258.TP.20241225.1106.008.XIANG Jiahao, XU Huiying, XU Guangping, et al. MECW-YOLO: An algorithm for detecting small targets in drone perspective using improved YOLOv8[J/OL]. Computer Engineering & Science, 1–12[2025-03-20]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/43.1258.TP.20241225.1106.008. [16] SI Yunzhong, XU Huiying, ZHU Xinzhong, et al. SCSA: Exploring the synergistic effects between spatial and channel attention[J]. Neurocomputing, 2025, 634: 129866. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2025.129866. [17] ZHAO Yian, LV Wenyu, XU Shangliang, et al. DETRs beat YOLOs on real-time object detection[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2024: 16965–16974. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.01605. [18] DAI Xiyang, CHEN Yinpeng, XIAO Bin, et al. Dynamic head: Unifying object detection heads with attentions[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 7369–7378. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00729. [19] TIAN Zhi, SHEN Chunhua, CHEN Hao, et al. FCOS: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C] 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 9626–9635. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00972. [20] WANG Xinjiang, ZHANG Shilong, YU Zhuoran, et al. Scale-equalizing pyramid convolution for object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 13356–13365. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01337. [21] ZHANG Hao and ZHANG Shuaijie. Shape-IoU: More accurate metric considering bounding box shape and scale[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.17663, 2023. [22] ZHANG Hao, XU Cong, and ZHANG Shuaijie. Inner-IoU: More effective intersection over union loss with auxiliary bounding box[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.02877, 2023. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
