Adaptive Multi-Mode Blind Equalization Scheme for OFDM-NOMA Systems
-
摘要: 面向基于正交频分复用的非正交多址接入(NOMA)系统,针对下行链路中非规则星座点均衡困难的问题,该文提出了一种无监督的多模盲均衡方案。该方案联合软决策导向算法,通过结合NOMA功率分配因子,构建指数型代价函数,有效补偿了信道引起的幅度和相位失真。为了最小化代价函数,提出了一种改进的牛顿算法,以快速搜索最优权值。仿真结果表明,相比传统多模均衡算法,所提出的算法稳态最大失真降低了约10倍。此外,在GNURadio平台上搭建软件无线电系统,验证了算法的有效性和可实现性。Abstract:
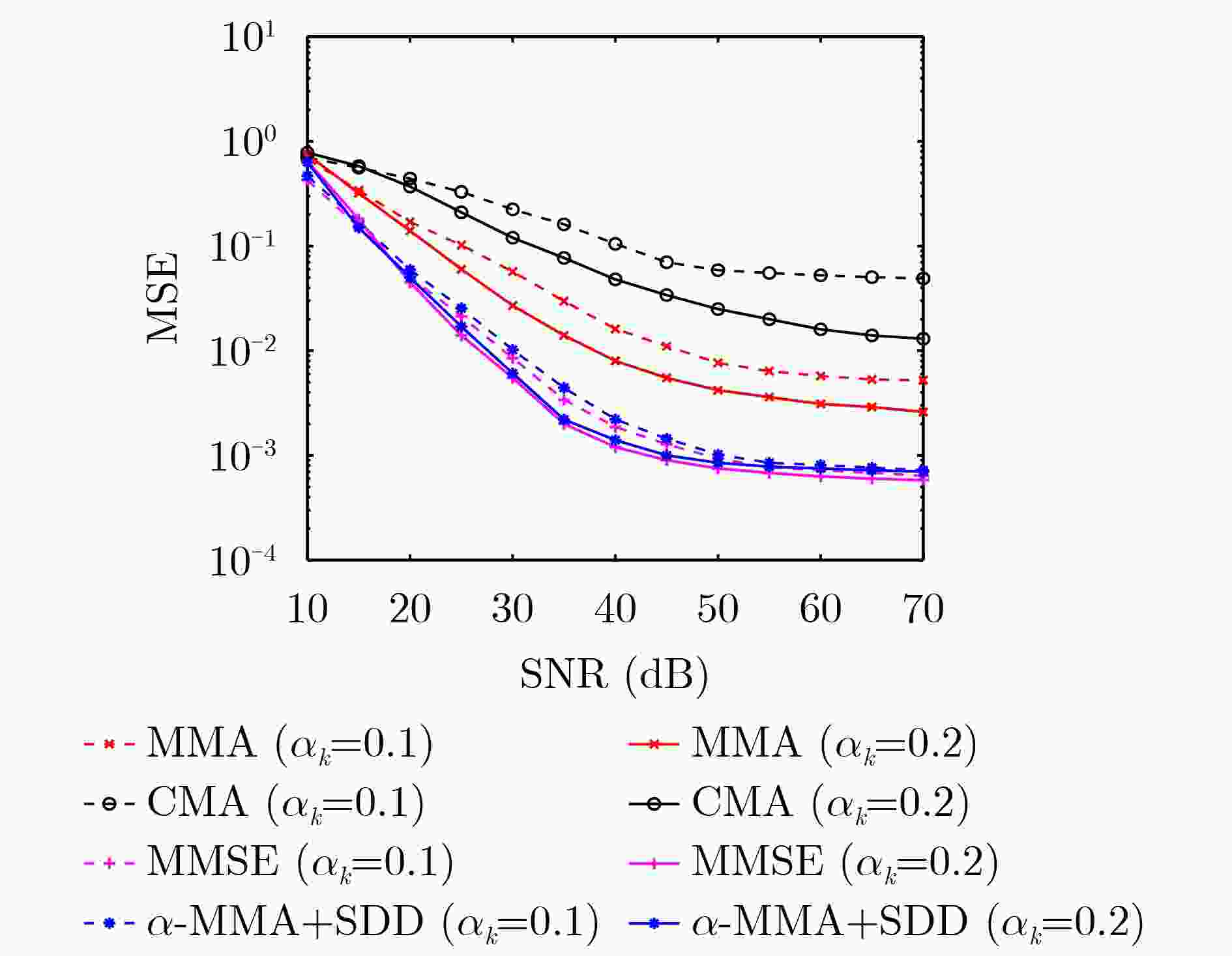
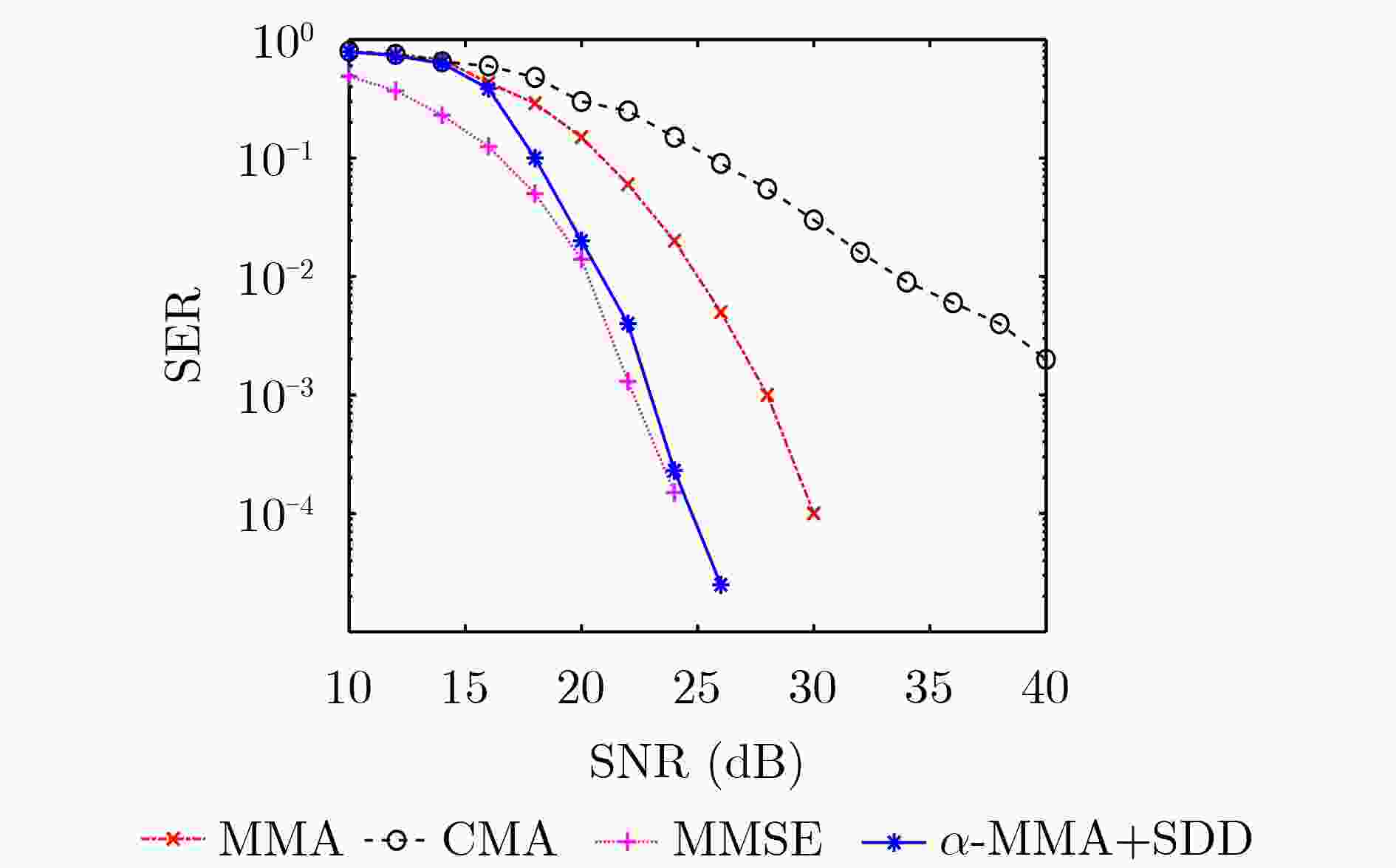
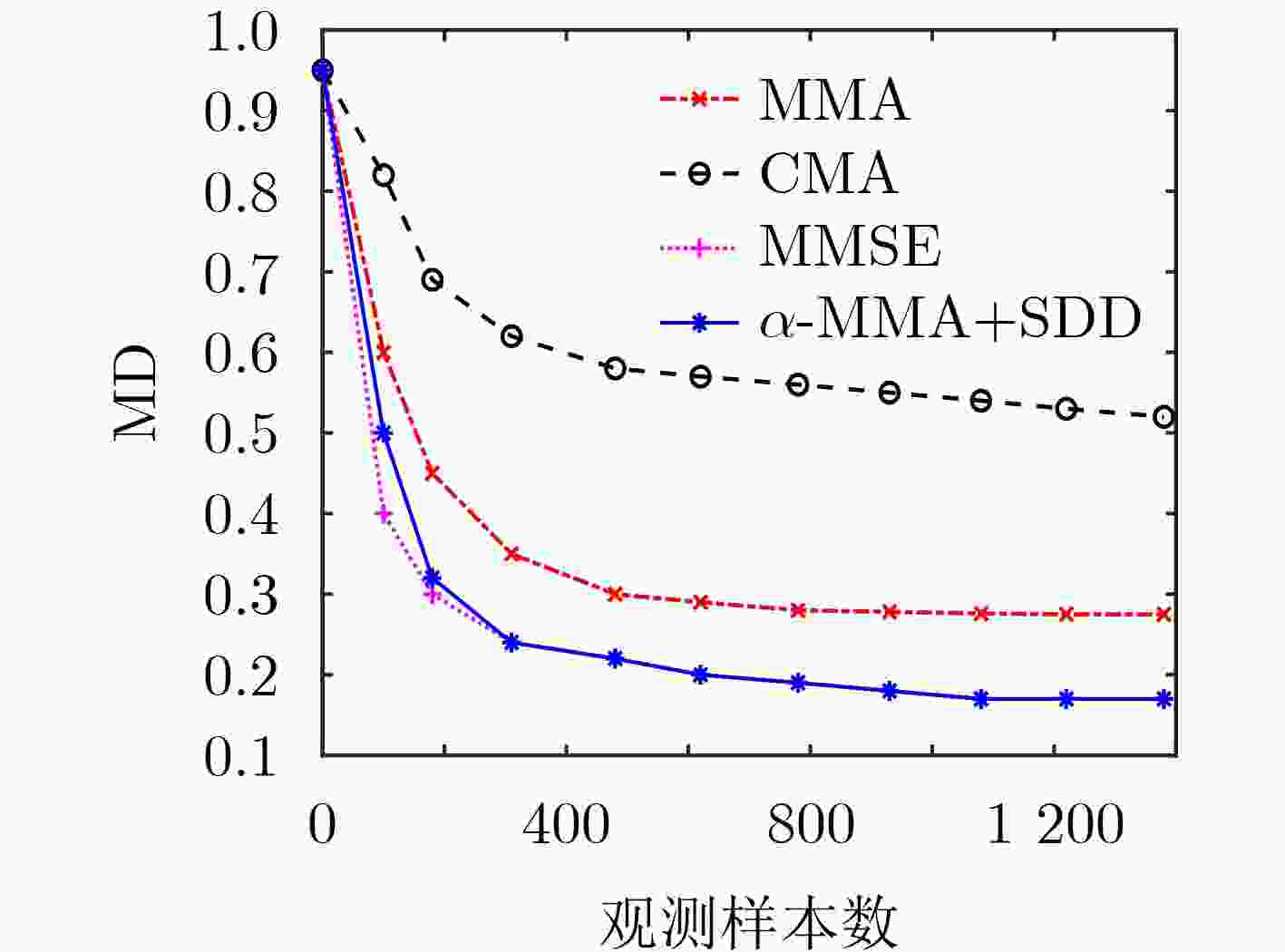
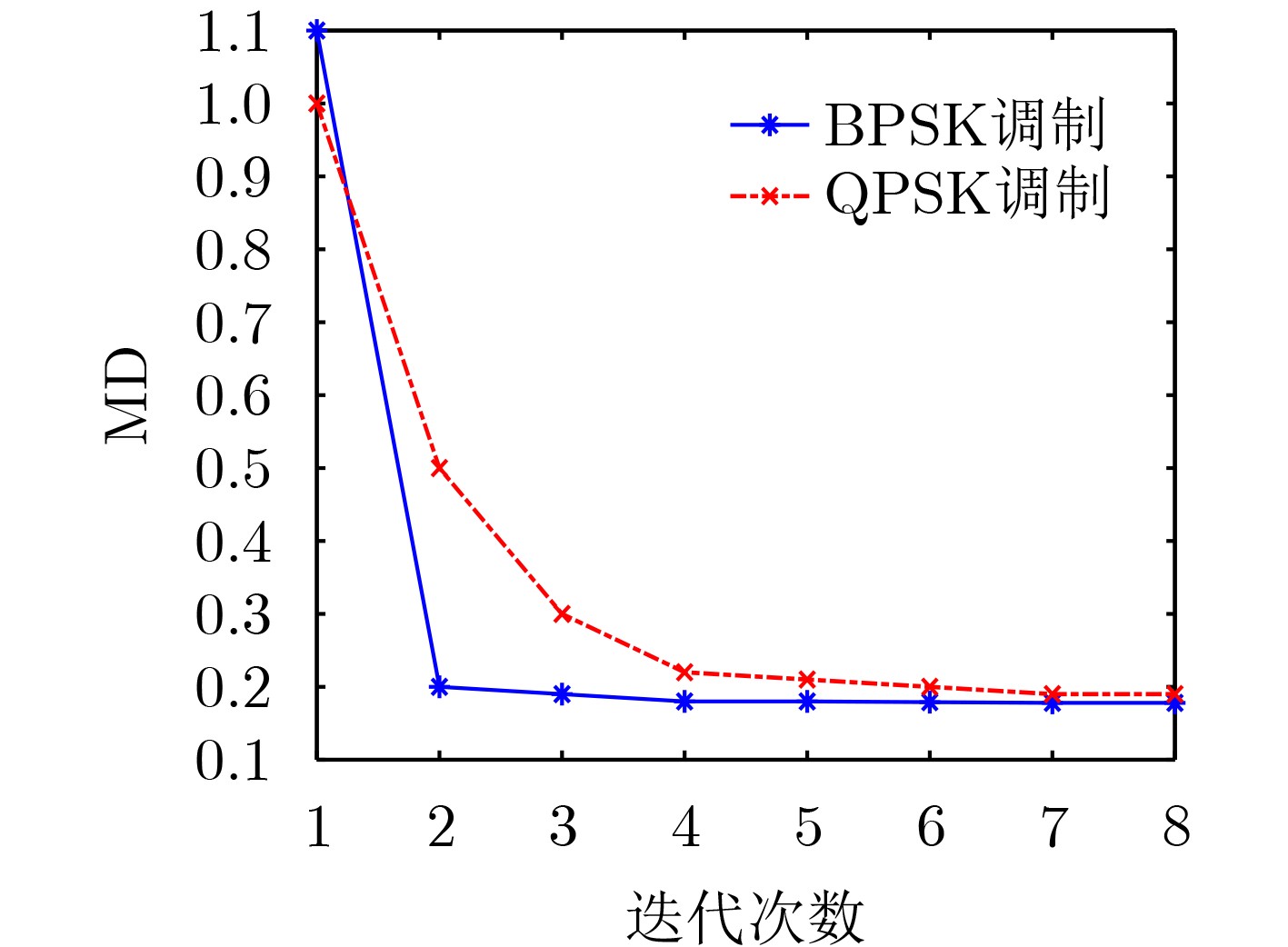
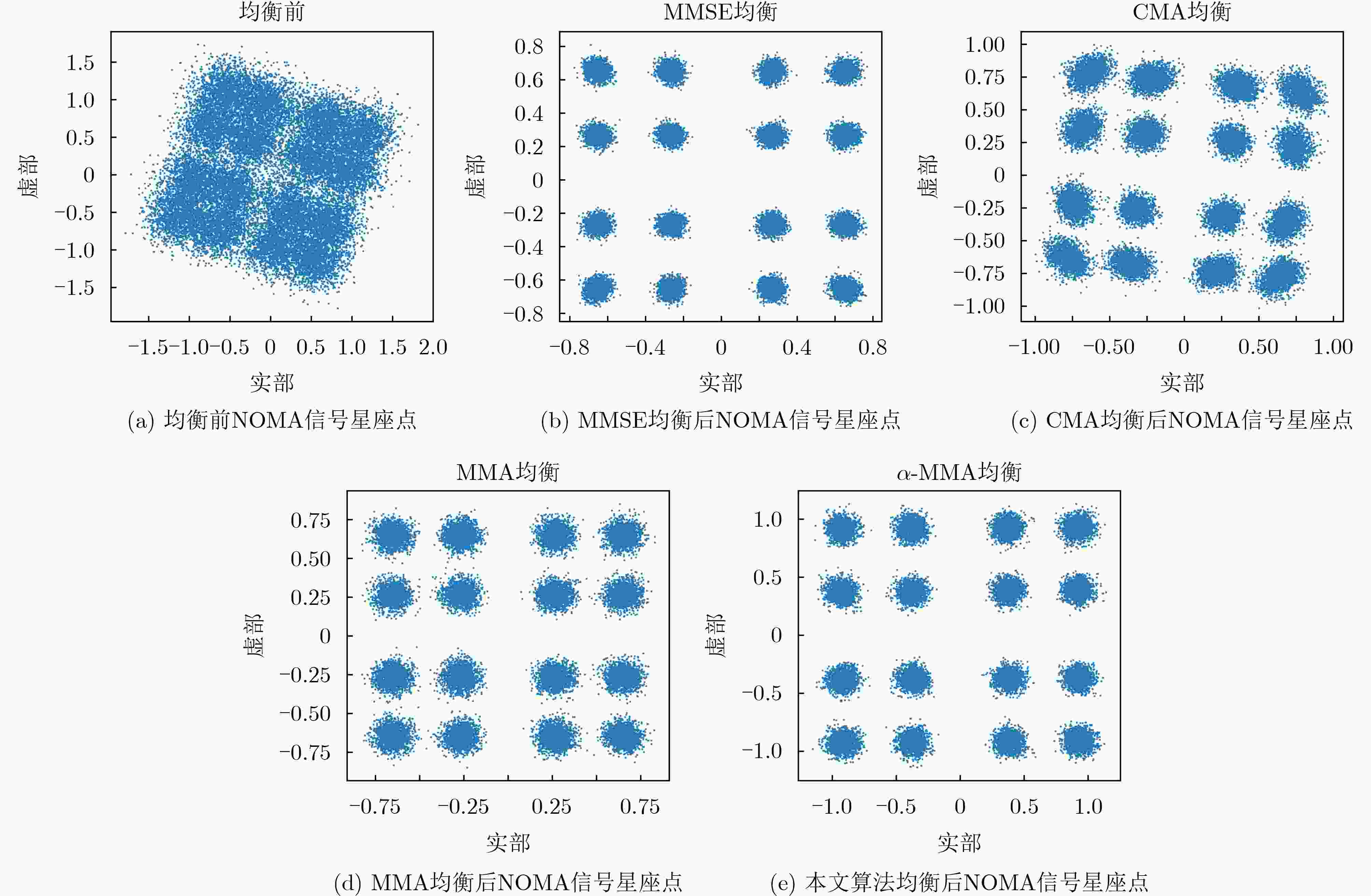
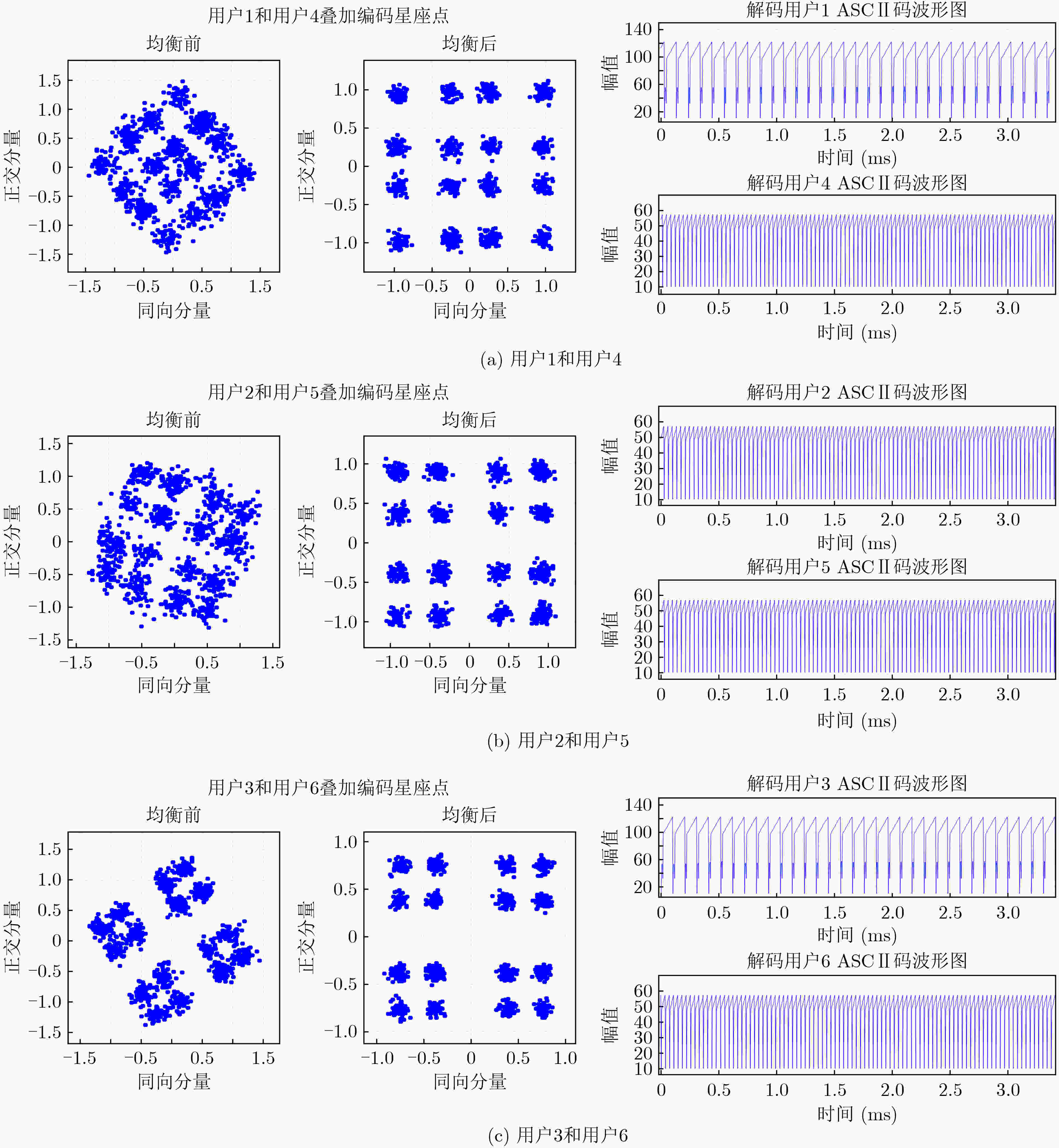
Objective Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) combined with Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) is widely applied in next-generation wireless communication systems for its high spectral efficiency and support for concurrent multi-user transmission. However, in downlink transmission, the superposition of signals from multiple users on the same subcarrier yields non-standard Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) constellations, rendering conventional equalization techniques ineffective. In addition, channel variability and impulsive noise introduce severe distortion, further degrading system performance. To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes an unsupervised adaptive multi-mode blind equalization scheme designed for OFDM-NOMA systems. Methods The proposed equalization scheme combines the Multi-Mode Algorithm (MMA) with a Soft-Decision Directed (SDD) strategy to construct an adaptive cost function. This function incorporates the power allocation factors of NOMA users to compensate for amplitude and phase distortions introduced by the wireless channel. To minimize the cost function efficiently, an optimized Newton method is employed, which avoids direct matrix inversion to reduce computational complexity. An iterative update rule is derived to enable fast convergence with low processing overhead. The algorithm is implemented on a real-time Software-Defined Radio (SDR) system using the GNURadio platform for practical validation. Results and Discussions Simulation results show that the proposed equalization algorithm substantially outperforms conventional methods in both convergence speed and accuracy. Compared with the traditional Minimum Mean Square Error (MMSE) algorithm, it reduces convergence time by 90% while achieving comparable performance without the use of pilot signals ( Fig. 8 ). Constellation diagrams before and after equalization confirm that the algorithm effectively restores non-standard QAM constellations distorted by NOMA signal superposition (Fig. 9 ). The method also demonstrates strong robustness to impulsive noise and dynamic channel variations. Complexity analysis indicates that the proposed algorithm incurs lower computational overhead than conventional Newton-based equalization approaches (Table 1 ). Experimental validation on the GNURadio platform confirms its ability to separate user signals and support accurate decoding in real-world OFDM-NOMA downlink conditions (Fig. 12 ).Conclusions This study presents a blind equalization scheme for OFDM-NOMA systems based on an MMA-SDD adaptive cost function and an optimized Newton method. The proposed algorithm compensates for amplitude and phase distortions, enabling reliable signal recovery without pilot information. Theoretical analysis, simulation results, and experimental validation confirm its fast convergence, robustness to noise, and low computational complexity. These characteristics support its potential for practical deployment in future NOMA-based wireless communication networks. -
表 1 算法复杂度对比
算法 $\alpha $-MMA+SDD算法 传统牛顿法 复杂度 $ O(K{L^3} + K{L^2}\lambda ) $ $O(K{L^3}\tilde T + K{L^2}\tilde T\lambda )$ 1 基于功率分配改进的$\alpha $-MMA+SDD均衡迭代算法
(1)初始化:设置所有子载波的初始均衡器权值,其中子载波$ {\text{S}}{{\text{C}}_k} $的权值为$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}_{k,0}} = {[0, \cdots ,1, \cdots ,0]^{\text{H}}} $,元素1位于向量的中心,精度误差$\varepsilon $,
最大迭代步数$T$。(2)对子载波循环for($ k = 1,2, \cdots ,K $): (3) 初始化:初始化迭代步数索引$ t = 0 $,将初始误差$\eta $设置为大于$\varepsilon $,计算输入信号${{\boldsymbol{X}}_k}$的协方差逆矩阵$ {{\stackrel \frown{{\boldsymbol{R}}} }} $。 (4) 迭代均衡权值while$\eta > \varepsilon $和$t < T$do (5) 计算均衡器输出:$ {Y_{k,t}}(n) = {\boldsymbol{w}}_{k,t}^{\text{H}}{{\boldsymbol{x}}_k}(n),\quad \forall n = 1,2, \cdots ,\lambda $; (6) 计算代价函数:根据式(4)计算$ J({{\boldsymbol{w}}_k}) $; (7) 计算误差修正向量:根据式(5)、式(13)和式(14)计算$ {\tilde g_{k,t}}(n) $,根据式(11)和式(15)计算$ {{\boldsymbol{X}}_k}{{\boldsymbol{g}}_{k,t}} $; (8) 更新均衡器权值:$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}_{k,t + 1}} = {{\stackrel \frown{\boldsymbol{R}} }}{{\boldsymbol{X}}_k}{{\boldsymbol{g}}_{k,}}_t $; (9) 更新误差:$\eta = {\left\| {{{\boldsymbol{w}}_{k,t + 1}} - {{\boldsymbol{w}}_{k,t}}} \right\|_2}$; (10) 更新迭代步数:$ t = t + 1 $; (11) 输出子载波$ {{\mathrm{SC}}_k} $上的最终优化权值$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}_k} = {{\boldsymbol{w}}_{k,t}} $; (12)结束 表 2 系统仿真参数设置
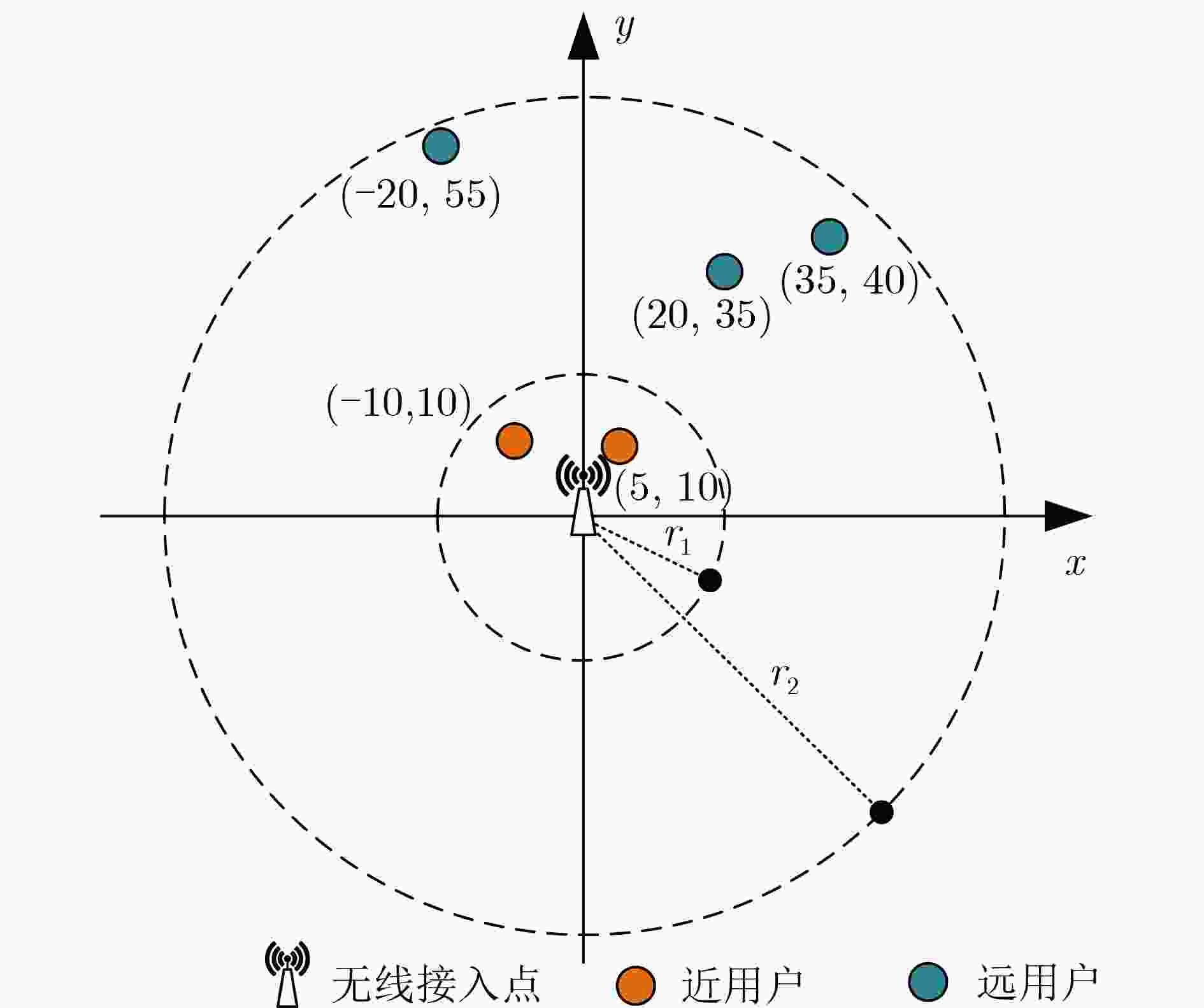
参数 值 AP坐标 (0, 0) $ {N_1} $, $ {N_2} $坐标 (5, 10), (–10, 10) $ {F_1} $, $ {F_2} $, $ {F_3} $坐标 (20, 35), (35, 40), (–20, 55) 近用户覆盖半径$ {r_1} $ 20 m 远用户覆盖半径$ {r_2} $ 60 m 子载波数$ K $ 48 路径损耗常数$ C $ –30 dB 路径损耗指数$ \gamma $ 3 样本个数$ \tilde K $ 20 滤波器阶数$ L $ 7 方差$ {\sigma ^2} $ 0.25 -
[1] HAYKIN S S. Adaptive Filter Theory[M]. 4th ed. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education, 2002. [2] BIGUESH M and GERSHMAN A B. Training-based MIMO channel estimation: A study of estimator tradeoffs and optimal training signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(3): 884–893. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.863008. [3] CHEN Dongyan, HONG Yiguang, and TRIVEDI K S. Optimal estimation of training interval for channel equalization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2004, 3(5): 1844–1853. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2004.828021. [4] AN Zeliang, XU Yuqing, TAHIR A, et al. Collaborative learning-based modulation recognition for 6G multibeam satellite communication systems via blind and semi-blind channel equalization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 5226–5246. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3387447. [5] LIU Na, WANG Zuoxun, and WEI Haiwen. Trigonometric coordinate transformation blind equalization algorithm based on bi-direction long and short-term memory neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 30653–30660. doi: 10.1109/access.2024.3368857. [6] ZHOU Junjie and CHEN Ke. An energy efficient CMA equalizer based on approximate computing[C]. 2024 IEEE 7th International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT), Xi’an, China, 2024: 402–406. doi: 10.1109/ICEICT61637.2024.10671152. [7] CIMINI L. Analysis and simulation of a digital mobile channel using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1985, 33(7): 665–675. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1985.1096357. [8] ALAYYAN F O, ZOUBIR A M, and LEUNG Y H. Adaptive blind equalization algorithm for QAM signals in OFDM systems by GI-restoration[C]. 2007 9th International Symposium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2007: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ISSPA.2007.4555590. [9] ATAPATTU L, ARACHCHIGE G M, ZIRI-CASTRO K, et al. Linear adaptive channel equalization for multiuser MIMO-OFDM systems[C]. Australasian Telecommunication Networks and Applications Conference (ATNAC) 2012, Brisbane, Australia, 2012: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ATNAC.2012.6398080. [10] DING Zhiguo, LIU Yuanwei, CHOI J, et al. Application of non-orthogonal multiple access in LTE and 5G networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(2): 185–191. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1500657CM. [11] DING Zhiguo, LEI Xianfu, KARAGIANNIDIS G K, et al. A survey on non-orthogonal multiple access for 5G networks: Research challenges and future trends[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(10): 2181–2195. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2725519. [12] LI Xingwang, GAO Xuesong, LIU Yingting, et al. Overlay CR-NOMA assisted intelligent transportation system networks with imperfect SIC and CEEs[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2023, 32(6): 1258–1270. doi: 10.23919/cje.2022.00.071. [13] 李兴旺, 田志发, 张建华, 等. IRS辅助NOMA网络下隐蔽通信性能研究[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2024, 54(6): 1502–1515. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0174.LI Xingwang, TIAN Zhifa, ZHANG Jianhua, et al. Performance analysis of covert communication in IRS-assisted NOMA networks[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2024, 54(6): 1502–1515. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0174. [14] LI Jin, FENG Dazheng, and ZHENG Weixing. Space-time semi-blind equalizer for dispersive QAM MIMO system based on modified newton method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2014, 13(6): 3244–3256. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.041714.121735. [15] WANG Liang and WEN Hewen. Soft decision adjusted modulus algorithm for blind equalization[C]. 2022 IEEE 10th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 2022: 1881–1884. doi: 10.1109/ITAIC54216.2022.9836582. [16] ZHOU Shanyu, CHU Ran, LIU Guangzu, et al. Design and implementation of high-speed and low-complexity blind equalization algorithm[C]. 2023 8th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Wuxi, China, 2023: 597–602. doi: 10.1109/ICSIP57908.2023.10271005. -





 下载:
下载:

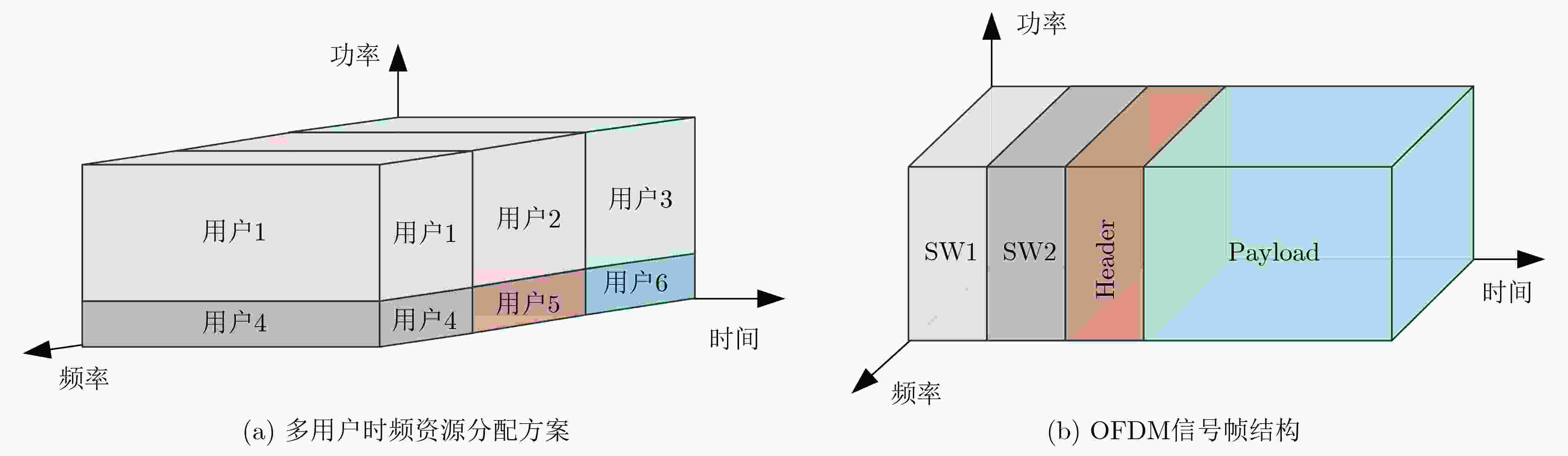



 下载:
下载:
