An Overview of Resource Management Technology of 6G Integrated Communication, Sensing, and Computation Enabled Satellite-Terrestrial Intelligent Network
-
摘要: 针对6G天地一体通感算智能协同网络(6G Integrated Communication, Sensing, and Computation Enabled Satellite-Terrestrial Intelligent Network, 6G-ICSC-STIN),该文在总结其研究现状的基础上,阐述了未来天地一体通感算智能协同网络的关键技术,分析了频谱共享技术、高精度感知算法、动态计算资源调度以及人工智能(Artificial Intelligence, AI)技术等四大关键领域的研究进展,并讨论了通感算融合衡量指标,提出了6G-ICSC-STIN架构。为满足未来通信网络对高带宽、低时延、广覆盖的多元化需求,设计了高效分布式智能资源管理策略,并在此策略的基础上进一步提出了基于博弈论-多智能体强化学习的资源管理架构。最后,基于跨域技术融合创新以及资源融合表征等未来重点研究方向进行了讨论与展望。
-
关键词:
- 6G /
- 网络架构 /
- 天地一体通感算智能协同网络 /
- 资源管理
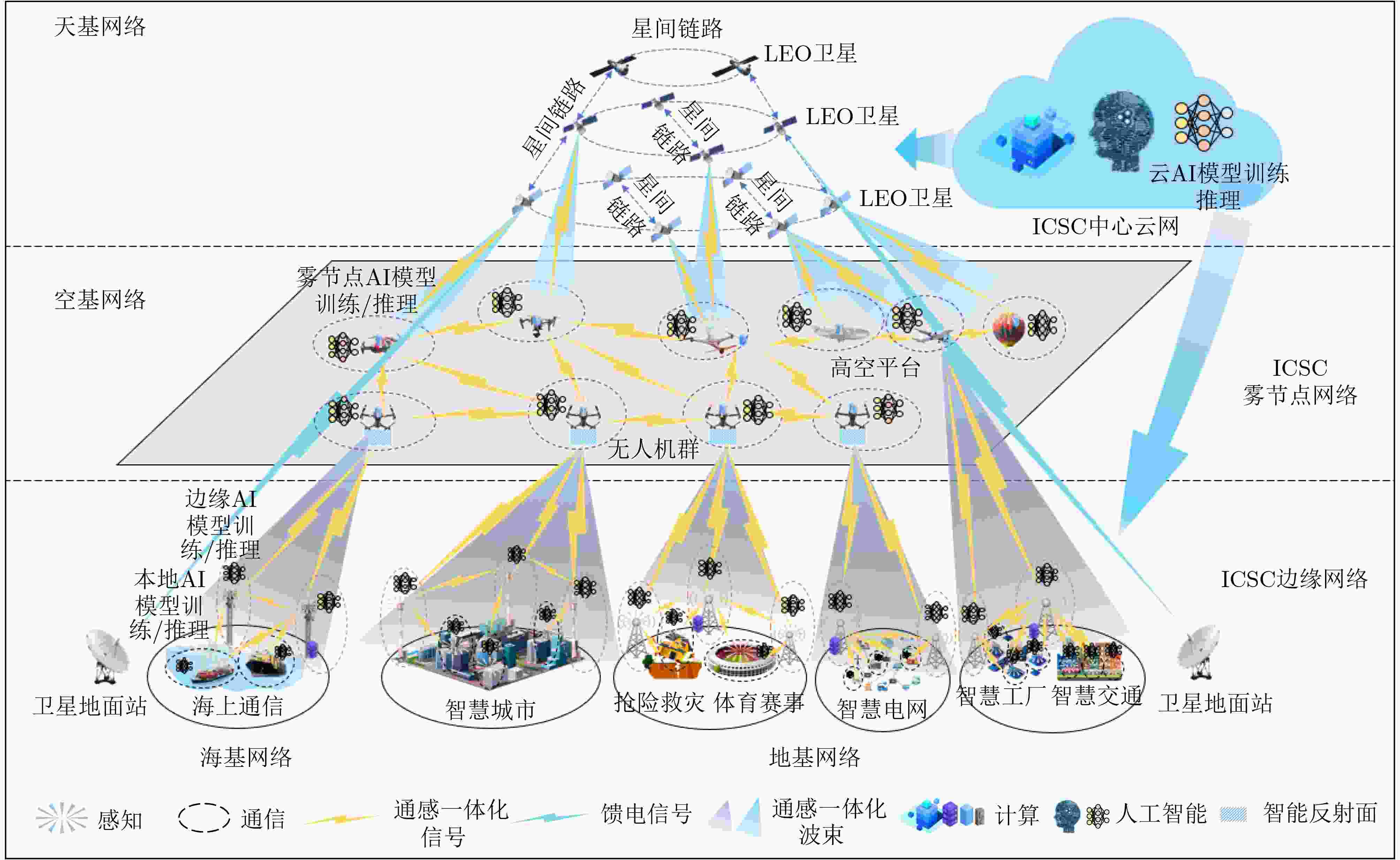
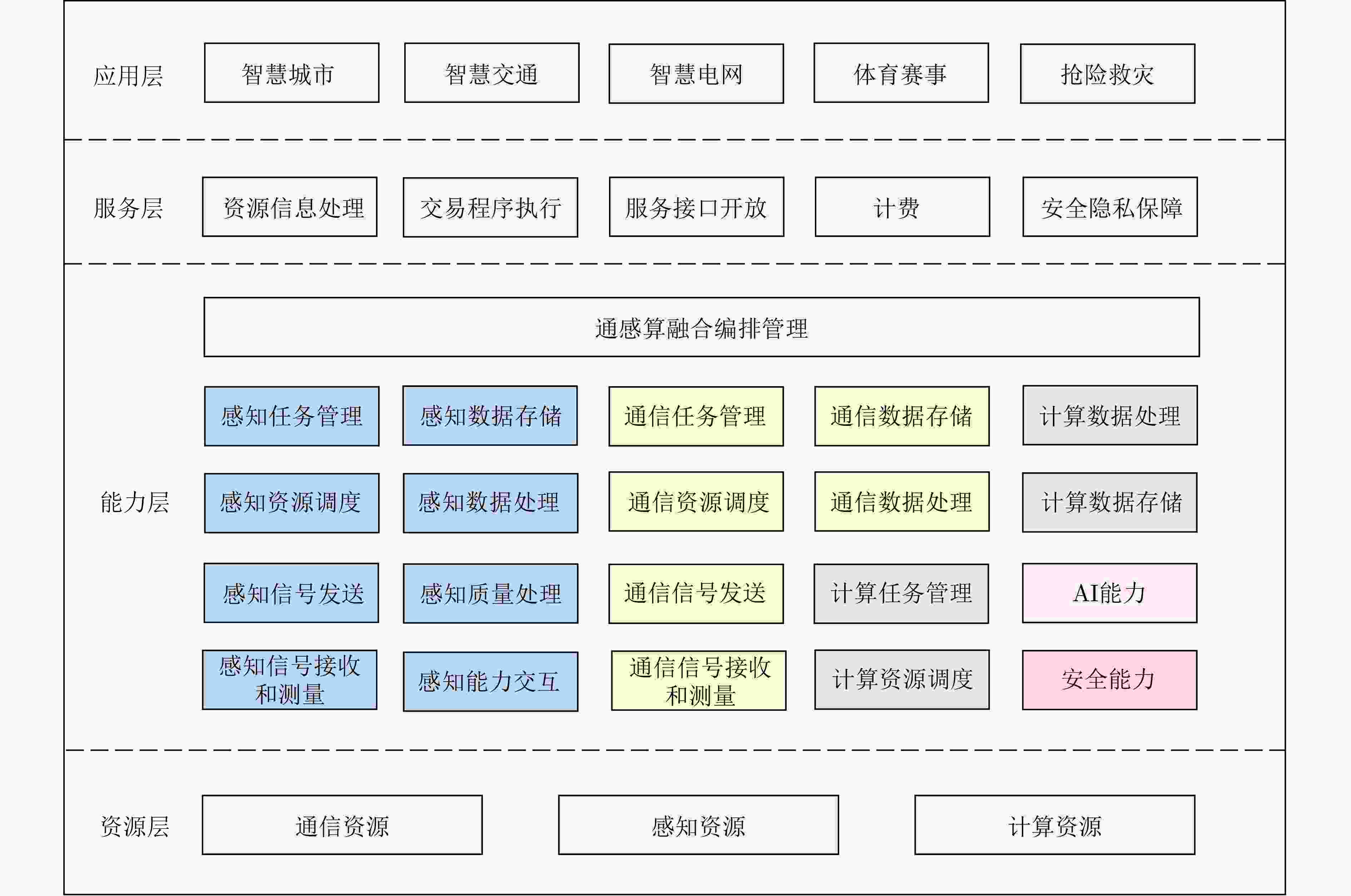
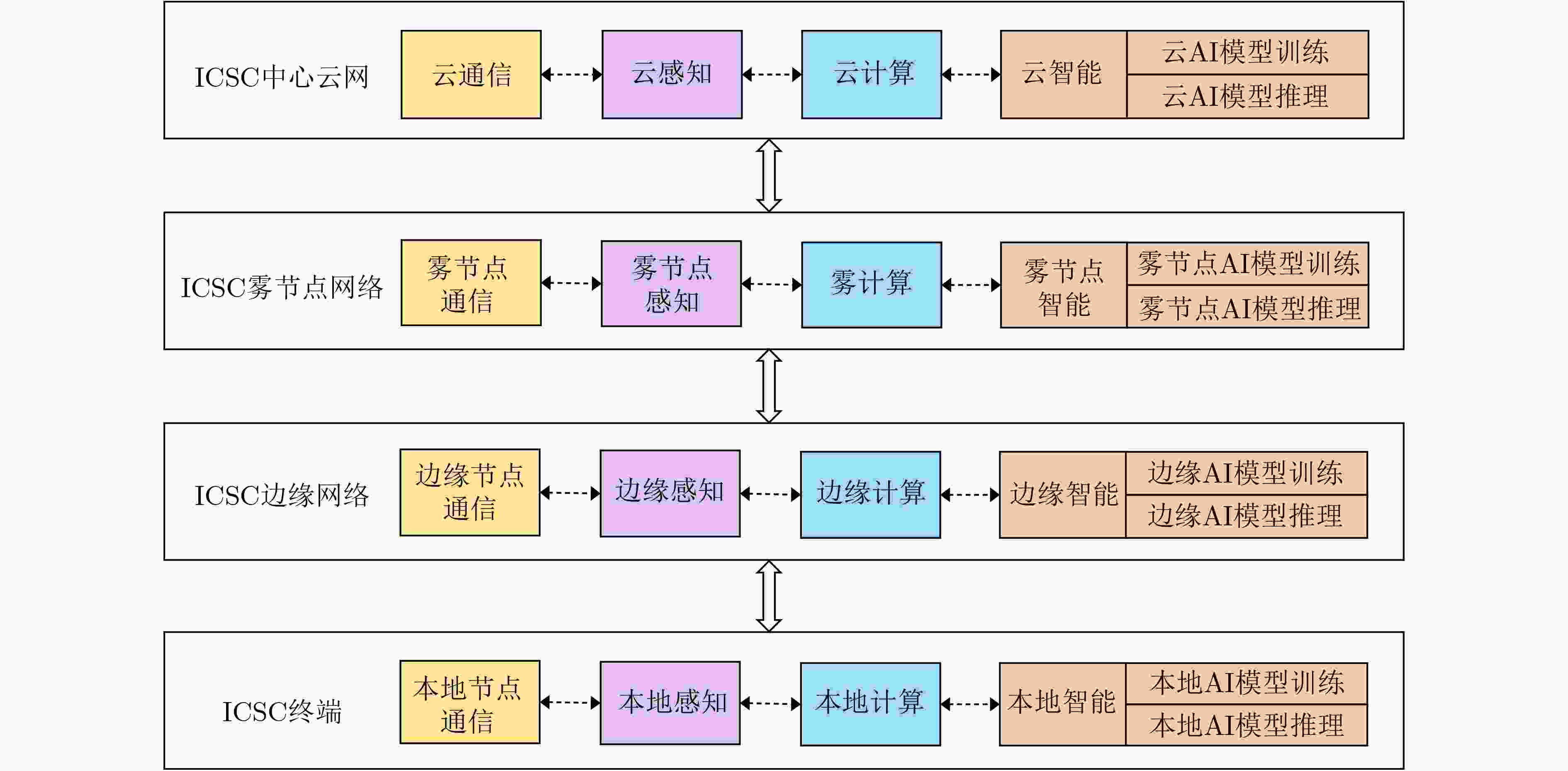
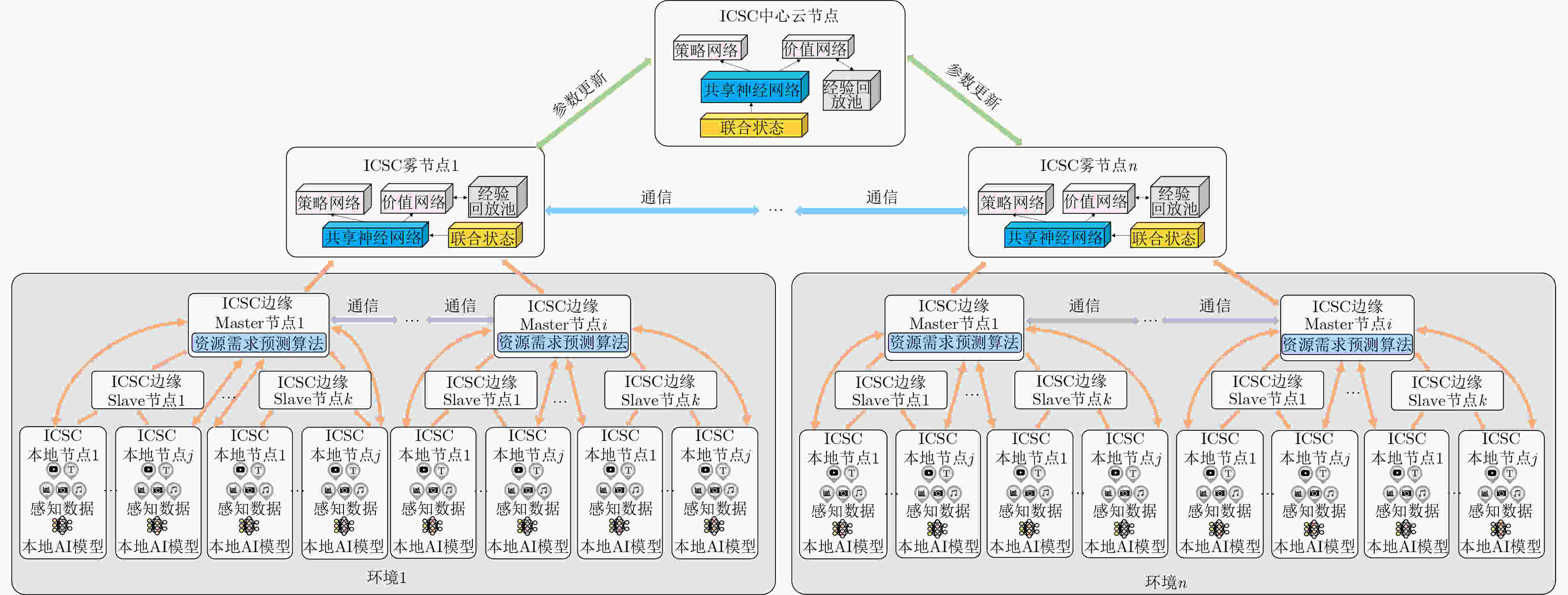
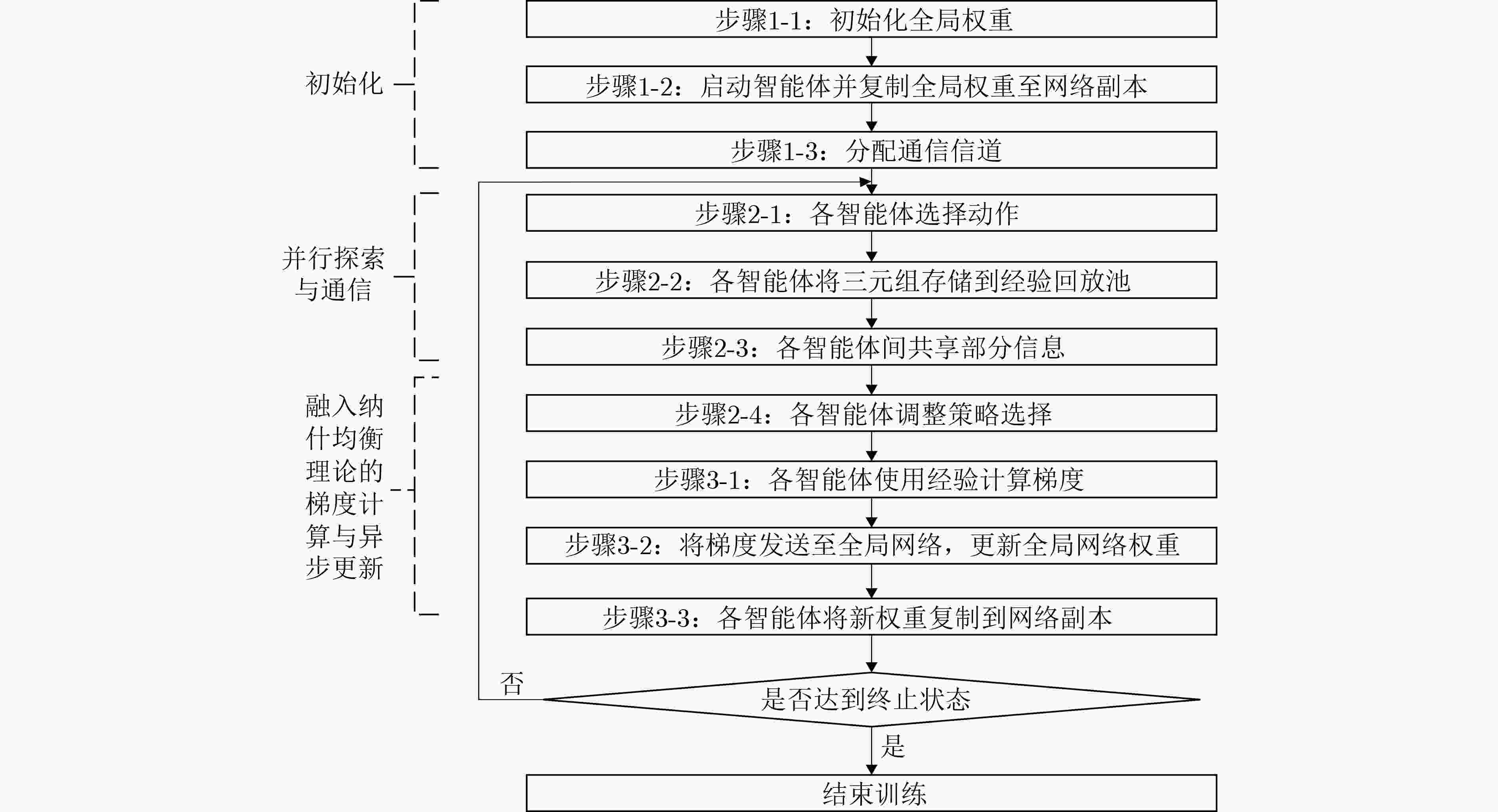
Abstract:Significance As 6G mobile communication systems continue to evolve, Integrated Communication, Sensing, and Computation (ICSC) technology has emerged as a key area of research. ICSC not only improves network performance but also meets increasingly diverse and personalized user requirements. Recent progress in spectrum sharing, high-precision sensing algorithms, dynamic computing resource scheduling, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) has supported the development of 6G networks. However, several challenges remain. These include inefficient spectrum utilization, limited accuracy and real-time performance of sensing algorithms, and insufficient adaptability and intelligence in computing resource scheduling strategies. Moreover, integrating these technologies into the 6G ICSC Enabled Satellite-Terrestrial Intelligent Network (6G-ICSC-STIN) for effective resource management and optimal allocation is an unresolved issue. To address demands for high bandwidth, low latency, and wide coverage in future networks, a distributed intelligent resource management strategy is designed. Based on this approach, a resource management framework combining game theory and multi-agent reinforcement learning is proposed, offering guidance for advancing resource management in 6G-ICSC-STIN systems. Progress This paper provides a comprehensive discussion of resource management technologies for 6G ICSC Enabled Satellite–Terrestrial Intelligent Networks (6G-ICSC-STIN). It summarizes key technological advances driving the field and presents recent progress in four core areas: spectrum sharing, high-precision sensing algorithms, dynamic computing resource scheduling, and the application of AI in ICSC systems. Measurement indicators for ICSC performance are also examined. Based on this review, a 6G-ICSC-STIN architecture is proposed ( Fig. 2 ), integrating 6G communication, sensing, computation, and intelligent coordination technologies. This architecture fully leverages the capabilities of satellites, unmanned aerial vehicles, High-Altitude Platforms (HAPs), and ground terminals to enable seamless and full-domain coverage across space, air, ground, and sea. It supports deep integration of communication, sensing, computation, intelligence, and security, resulting in a unified network system characterized by more precise perception and transmission, improved resource coordination, lower system overhead, and enhanced user experience. To address complex resource management challenges, a functional block diagram comprising the application, service, capability, and resource layers is introduced (Fig. 3 ), aiming to identify new approaches for efficient resource allocation. A distributed intelligent resource management strategy is further proposed for the ICSC central, fog node, edge networks and terminal (Fig. 4 ). Within the integrated edge network, a novel “Master–Slave two-level edge node” architecture is designed, in which the Master node deploys a resource demand prediction model to estimate regional demand in real time (Fig. 6 ). Building on this strategy, a resource management framework based on game theory and multi-agent reinforcement learning is proposed (Fig. 5 ). This framework employs the Nash-Equilibrium Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic (Nash-E-A3C) algorithm, adopts a parallelized multi-agent and distributed computing approach, and integrates Nash equilibrium theory (Fig. 7 ), with the aim of achieving intelligent, collaborative, and efficient network resource management.Conclusions The distributed intelligent resource management strategy is essential for achieving efficient resource coordination and optimal utilization in the 6G-ICSC-STIN architecture. By decentralizing computing, storage, and communication resources across network nodes, it enables resource sharing and collaborative operation. The proposed architecture, grounded in game theory and multi-agent reinforcement learning, supports dynamic resource allocation and optimization. Agents are deployed at each node, where they make decisions based on local demands and environmental conditions using game-theoretic reasoning and Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms. This approach enables globally efficient resource management across the network. Prospects Cross-domain technological integration is fundamental to the realization of 6G-ICSC-STIN. Deep integration of sensing, communication, and computing capabilities can substantially enhance overall network performance and efficiency. However, this integration faces several challenges, including heterogeneous network compatibility, complex resource scheduling, fragmented security mechanisms, and slow progress in standardization. Efficient resource representation is critical for effective resource management and performance optimization. Existing studies show that resources in satellite-terrestrial integrated networks are heterogeneous, multidimensional, and unevenly distributed across large spatiotemporal scales, posing new challenges to resource coordination. This paper outlines future development trends in intelligent resource management for 6G-ICSC-STIN, synthesizing current research progress, key challenges, and future directions in cross-domain technology fusion and resource representation. These emerging technologies together form a foundation for intelligent and efficient resource management in 6G-ICSC-STIN and offer new pathways for the advancement of next-generation wireless communication systems. -
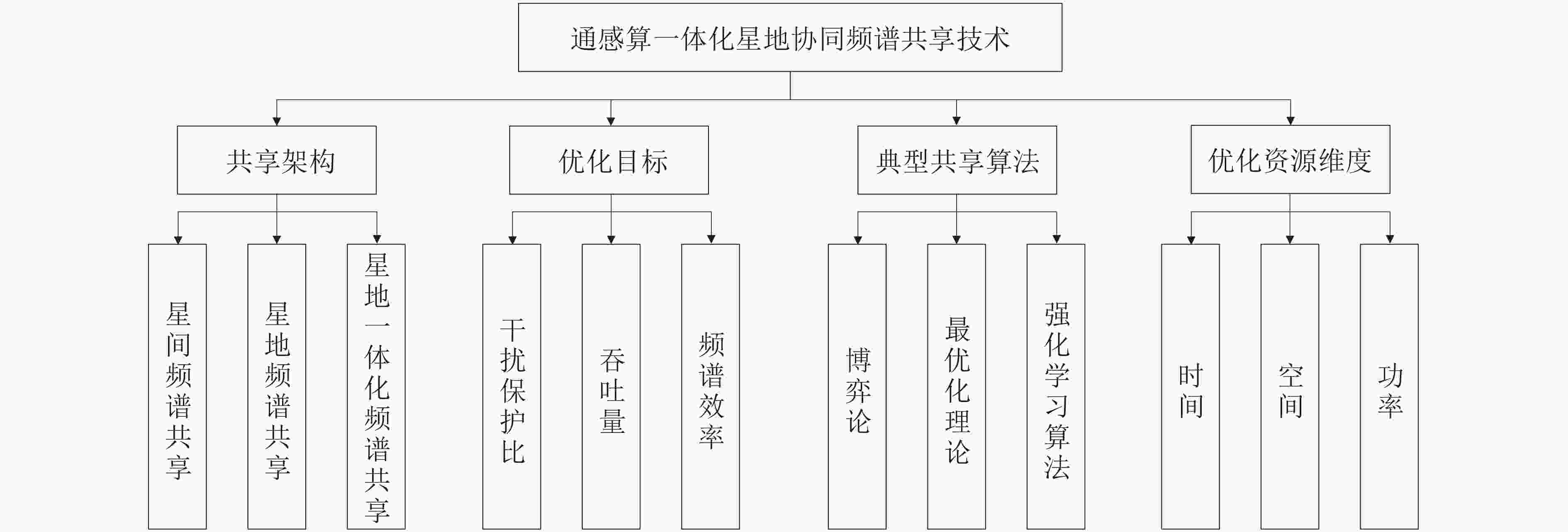
表 1 频谱共享技术研究现状
频谱共享架构 优化目标 频谱共享算法 优化资源维度 代表文献 星间频谱共享架构 提升频谱利用率与
系统吞吐量最优化理论 多维度联合优化(时间、功率、空间) [5] 星地频谱共享(高轨卫星(High Elliptical Orbit, HEO)、低轨卫星(Low Earth Orbit, LEO)、地面基站、
卫星及基站各自用户)频谱资源高效利用以及系统SINR更高 DRL算法 联合优化多域(卫星域、波束域、功率域、
频谱域)[4] 星地一体化频谱共享 最大化加权和速率(Weighted Sum Rate, WSR) 最优化理论 功率 [25] 星地一体化频谱共享 最大化最小速率(Max-Min Rate, MMR) 最优化理论(基于WMMSE(Weighted Minimum Mean Square Error)的改进交替优化(AO)算法) 功率 [27] 星地频谱共享架构 用户收益最大化、公平分配、系统效用提升 Stackelberg博弈及 双目标WOA 以频率为主,空间为辅 [21] 星地频谱共享(LEO、地面基站、
卫星及基站各自用户)提升LEO网络的服务满意度和频谱效率 最优化理论(李雅普诺夫框架(Lyapunov框架)) 时间、空间 [28] 星地频谱共享(一对非静止轨道(NGSO)
星座和多个地面基站)增强频谱利用效率 利用AI和LLMs来检测干扰和优化频谱共享 时间、空间、频率 [26] 表 2 通信、感知、计算的核心性能指标
核心性能指标1 核心性能指标2 核心性能指标3 代表文献 通信 效率指标:包括峰值速率、频谱效率(单位带宽传输能力)、能量效率(单位能耗传输比特数),反映资源利用效率 可靠性指标:如BER、中断概率(通信链路稳定性)、传输成功率,直接影响数据完整性 网络化指标:包括覆盖范围、多用户接入能力、网络协作效率(如基站间协同调度) [56] 感知 可靠性指标:
(1)检测可靠性:检测概率(发现目标的概率)、虚警概率(误报率)
(2)估计可靠性:距离/角度/速度的MSE、克拉美罗界(理论精度下限)
(3)识别可靠性:目标分类准确率、环境重构分辨率效率指标:单位资源下的感知范围、目标数量上限、感知更新频率 网络化指标:多节点协作感知能力、移动目标跟踪连续性、感知资源共享效率 [56,57] 计算 处理能力:算力密度(单位时间计算量)、任务处理延迟(端到端响应时间) 资源利用率:计算负载均衡度、分布式任务调度效率 智能水平:算法复杂度、模型推理精度(如AI模型的准确率) [58] 表 3 典型应用场景的指标需求、技术挑战及解决方案
场景 核心指标 技术挑战 解决方案示例 智慧交通 定位精度(≤10 cm)、时延(≤5 ms)、多目标跟踪密度(> 1000 个/km2)[63]高速移动场景下的信号多普勒效应、计算资源动态分配 动态波束成形及AI信道预测[7] 智能制造 设备状态识别准确率(≥99%)、云化控制延迟(≤20 ms)、抗干扰能力[62] 工业环境电磁干扰、异构设备协议兼容性 轻量级协议转换中间件[64] 智慧城市 环境监测覆盖率(≥95%)、数据融合效率(TB级/小时)、能耗效率(W/bit) 海量异构数据实时处理、长期运行的系统稳定性 利用DL算法,结合注意力机制、多任务学习和正则化技术,设计模型以适应
数据的多样性和实时性需求[65]无人机应用 低空感知分辨率(≤0.1 m2)、通信-计算协同时延(≤50 ms)、续航优化 弱反射信号处理、机载算力受限 调整资源分配以实现任务卸载和本地计算的均衡,同时考虑公平性[66] DT 模型更新频率(≥3 0Hz)、多源数据一致性(误差<1%)、虚实同步精度 高维数据实时渲染、跨平台数据标准化 借助云端渲染引擎,利用分布式GPU集群进行高性能计算,降低对终端设备
的依赖[67]表 4 网络资源表征主要方法特点及研究现状
通信
资源存储
资源具有单
一计算
功能的
计算
资源具有多
个计算
功能的
计算
资源优点 缺点 代表
文献SSG $ \surd $ – $ \surd $ – 通过离散的快照序列刻画网络拓扑的动态变化,适用于基于静态图设计的路由算法。
简单直观,易于理解和实现。信息丢失:每个快照仅保留特定时间点的状态,忽略快照内部的时序交互细节。
存储开销大:随着时间片数量增加,快照的存储成本显著上升。
资源表征不完整:忽略了存储资源,且无法表征节点的多计算功能。[84] TEG $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ – 时空联合建模:通过存储链路连接快照,同时表征通信和存储资源,提高资源利用率和网络性能。
高表征精度:能够精确描述网络拓扑的时序演进过程,适用于需要精细化建模的场景。计算与存储复杂度高:节点和链路的复制导致模型规模膨胀,尤其在大规模网络和长周期场景下,路由计算复杂度极高。
无法表征计算资源:仅关注通信和存储资源,未包含节点的多计算功能。[85] 存储时间
聚合图$ \surd $ $ \surd $ – – 精简模型:通过聚合TEG减少冗余信息,降低空间复杂度。
路由算法高效:一次计算可得出TEG中的多条路径,适合需要快速决策的场景。信息简化:聚合过程可能丢失部分时序细节,表征精度低于TEG。
仍缺乏计算资源表征:与TEG类似,未涵盖节点的计算能力。[86] 多功能
时间
扩展图$ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ 全面资源表征:同时建模通信、存储和计算资源,适用于软件定义的复杂网络
(如星地融合网络)。
灵活性与适应性:支持动态资源分配和功能调整,适合多任务协同场景。极高的时间复杂度:在网络规模大或时间周期长时,优化问题的求解复杂度呈指数级增长,实际应用受限。
实现复杂:需设计低复杂度算法以平衡性能与效率,目前仍是研究难点。[84] -
[1] 刁兆坤, 杨丽, 王振章. 6G通感算一体化网络关键技术和设计关键点[J]. 通信世界, 2024(14): 36–39. doi: 10.13571/j.cnki.cww.2024.14.002.DIAO Zhaokun, YANG Li, and WANG Zhenzhang. The key technology and design point of 6G integrated communication, sensing, and computing network[J]. Communications World, 2024(14): 36–39. doi: 10.13571/j.cnki.cww.2024.14.002. [2] 瞿重希, 毛浩斌, 许憧, 等. 面向6G的星地融合网络频谱共享技术[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2024, 30(4): 50–56. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202404008.QU Chongxi, MAO Haobin, XU Chong, et al. Spectrum sharing technology for satellite-terrestrial integrated networks towards 6G[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2024, 30(4): 50–56. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202404008. [3] 葛君刚. 面向未来无线网络的智能频谱共享技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2024. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2024.000259.GE Jungang. Research on intelligent spectrum sharing technology for future wireless networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2024. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2024.000259. [4] 任壮壮. 基于多域资源联合调度的星地频谱共享网络干扰减缓技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京邮电大学, 2023. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2023.001307.REN Zhuangzhuang. Research on interference mitigation technology for spectrum-sharing satellite-ground integrated networks via jointly scheduling multi-domain resource[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2023.001307. [5] 王运峰. 面向低轨卫星的协同频谱感知与共享技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 南京邮电大学, 2022. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2022.001798.WANG Yunfeng. Research on cooperative spectrum sensing and sharing technology for LEO satellites[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2022. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2022.001798. [6] 雷钥, 陈希, 王妮炜, 等. 天空地网络频谱共享技术综述[C]. 第十九届卫星通信学术年会论文集, 北京, 2023: 8.LEI Yao, CHEN Xi, WANG Niwei, et al. A survey of space-air-ground integrated network spectrum sharing[C]. Proceedings of the 1994–2024 China Academic Journal Electronic Publishing House, Beijing, China, 2023: 8. [7] 王晓云, 张小舟, 马良, 等. 6G通信感知一体化网络的感知算法研究与优化[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(2): 219–230. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023054.WANG Xiaoyun, ZHANG Xiaozhou, MA Liang, et al. Research and optimization on the sensing algorithm for 6G integrated sensing and communication network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(2): 219–230. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023054. [8] 姜旺俊. 基于通信感知一体化的网络化感知关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2024. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2024.000157.JIANG Wangjun. Research on network sensing techniques based on integrated sensing and communication[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2024. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2024.000157. [9] 胡伟. 基于通感一体节点互感知的无人机分布式集群网络拓扑构建方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2024. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2024.001819.HU Wei. Research on the UAV distributed cluster network topology construction method under the node mutual sensing of integrated sensing and communication[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2024. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2024.001819. [10] 柏义阳. 基于深度学习的OFDM通信感知一体化研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2024. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2024.000614.BAI Yiyang. Research on deep learning based integrated sensing and communication for OFDM system[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2024. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2024.000614. [11] 曲瀚洋. 基于导频-数据位联合感知的感知通信一体化信号设计和信号处理方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2023. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2023.002933.QU Hanyang. Research on signal design and signal processing method of ISAC based on pilot and data[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2023.002933. [12] 于雅娴. 大数据驱动的云计算资源动态调度算法研究[J]. 信息与电脑, 2024, 36(18): 160–163.YU Yaxian. Research on dynamic scheduling algorithm of cloud computing resources driven by big data[J]. Information & Computer, 2024, 36(18): 160–163. [13] 王琦. 基于动态随机需求的分布式云计算资源调度研究[D]. [硕士论文], 河南工业大学, 2023. doi: 10.27791/d.cnki.ghegy.2023.000806.WANG Qi. Research on resource scheduling of distributed cloud computing based on dynamic stochastic demand[D]. [Master dissertation], Henan University of Technology, 2023. doi: 10.27791/d.cnki.ghegy.2023.000806. [14] 王少星. 边缘计算环境下的资源调度与优化策略研究[J]. 信息与电脑, 2024, 36(4): 178–180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9767.2024.04.057.WANG Shaoxing. Research on resource scheduling and optimization strategy in edge computing environment[J]. Information & Computer, 2024, 36(4): 178–180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9767.2024.04.057. [15] 田昊. 面向边缘智能的资源管理关键技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京信息工程大学, 2023. doi: 10.27248/d.cnki.gnjqc.2023.000252.TIAN Hao. Research on key technologies of resource management for edge intelligence[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2023. doi: 10.27248/d.cnki.gnjqc.2023.000252. [16] 郑雅俪. 数能一体化网络中的动态资源分配算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2024. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2024.000272.ZHENG Yali. Resource scheduling design in data and energy integrated networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2024. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2024.000272. [17] 王随园. 云环境下计算资源调度算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 天津科技大学, 2022. doi: 10.27359/d.cnki.gtqgu.2022.000749.WANG Suiyuan. Research on computing resource scheduling algorithm in cloud environment[D]. [Master dissertation], Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2022. doi: 10.27359/d.cnki.gtqgu.2022.000749. [18] 周雪, 张子扬, 刘向南, 等. 通信-感知-计算-存储深度融合下的无线资源管控[J]. 移动通信, 2024, 48(3): 26–39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20240125-0004.ZHOU Xue, ZHANG Ziyang, LIU Xiangnan, et al. Wireless resource management under the deep integration of communication, sensing, computing, and caching[J]. Mobile Communications, 2024, 48(3): 26–39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20240125-0004. [19] 王金龙, 徐煜华, 陈瑾. 无线通信网络智能频谱协同与对抗[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2020, 50(11): 1767–1778. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0101.WANG Jinlong, XU Yuhua, and CHEN Jin. Intelligent spectrum collaboration and confrontation in wireless communication networks[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2020, 50(11): 1767–1778. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0101. [20] 王运峰, 丁晓进, 张更新. 基于联盟博弈的分布式多星协同频谱感知策略[C]. 第四届“空间信息网络”学术论坛会议论文集, 2019: 354–362.WANG Yunfeng, DING Xiaojin, and ZHANG Gengxin. Coalition formation games for multi-satellite cooperative sensing[C]. Proceedings of the 4th “Space Information Networks” Academic Forum, 2019: 354–362. [21] 张力, 廖天, 何业军. 基于Stackelberg博弈的双目标WOA频谱共享算法[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(9): 170–178. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020156.ZHANG Li, LIAO Tian, and HE Yejun. Dual-target WOA spectrum sharing algorithm based on Stackelberg game[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(9): 170–178. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020156. [22] 陈山枝, 孙韶辉, 康绍莉, 等. 6G星地融合移动通信关键技术[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2024, 54(5): 1177–1214. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0348.CHEN Shanzhi, SUN Shaohui, KANG Shaoli, et al. Key technologies for 6G integrated satellite-terrestrial mobile communication[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2024, 54(5): 1177–1214. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0348. [23] 亚森江•阿布都热合曼, 段卓君, 刘向南, 等. 6G星地融合网络资源管理关键技术[J]. 移动通信, 2024, 48(1): 47–55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20231209-0001.YASENJIANG A, DUAN Zhuojun, LIU Xiangnan, et al. Key technologies for resource management of 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks[J]. Mobile Communications, 2024, 48(1): 47–55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20231209-0001. [24] 李高, 王威, 吴启晖. 面向低轨卫星的频谱认知智能管控[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2021, 27(5): 7–11. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202105003.LI Gao, WANG Wei, and WU Qihui. Cognitive intelligent spectrum management and control for low earth orbit satellite system[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2021, 27(5): 7–11. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202105003. [25] LI Zhiqiang, HAN Shuai, PENG Mugen, et al. Dynamic multiple access based on RSMA and spectrum sharing for integrated satellite-terrestrial networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(6): 5393–5408. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3326245. [26] HEYDARISHAHREZA N, HAN Tao, and ANSARI N. Spectrum sharing and interference management for 6G LEO satellite-terrestrial network integration[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2024.3507019. [27] HAN Shuai, LI Zhiqiang, XUE Qiang, et al. Joint broadcast and unicast transmission based on RSMA and spectrum sharing for integrated satellite–terrestrial network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2024, 10(3): 1090–1103. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2024.3350596. [28] ZHU Jianfeng, SUN Yaohua, and PENG Mugen. Beam management in low earth orbit satellite communication with handover frequency control and satellite-terrestrial spectrum sharing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2025, 73(7): 5247–5263. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2024.3516479. [29] 海振坤. 通感算控一体化方案, 开辟5G应用新蓝海[EB/OL]. https://www.zte.com.cn/china/about/magazine/zte-technologies/2023/_5g-advanced/3/8.html, 2024.HAI Zhenkun. The integrated solution of comprehensive sensing, computing and control opens up a new blue ocean of 5G applications[EB/OL]. https://www.zte.com.cn/china/about/magazine/zte-technologies/2023/_5g-advanced/3/8.html, 2024. [30] 付降寅, 郭庆. 面向星地一体化网络的频谱共享方法研究[J]. 移动通信, 2024, 48(9): 64–70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20240725-0003.FU Jiangyin and GUO Qing. Spectrum sharing methods for satellite-terrestrial integrated networks[J]. Mobile Communications, 2024, 48(9): 64–70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20240725-0003. [31] 哈尔滨工业大学, 中国空间技术研究院. 一种基于联合功率和频率分配的星地一体化网络频谱共享方法[P]. 中国, 117956479A, 2024.Harbin Institute of Technology, China Academy of Space Technology. Satellite-ground integrated network spectrum sharing method based on joint power and frequency allocation[P]. CN, 117956479A, 2024. [32] 张曦木, 贾敏, 顾学迈, 等. 基于无线环境地图的星地智能频谱共享方法[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2024, 10(1): 32–37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2024.01.0032.ZHANG Ximu, JIA Min, GU Xuemai, et al. Satellite and terrestrial intelligent spectrum sharing method based on wireless environment map[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2024, 10(1): 32–37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2024.01.0032. [33] 王海涛, 茆习文, 张晨, 等. 基于天基干扰绘图的星地一体化系统频谱共享研究[J]. 通信学报, 2024, 45(3): 155–165. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2024056.WANG Haitao, MAO Xiwen, ZHANG Chen, et al. Study of spectrum sharing in integrated satellite-terrestrial system based on space-based interference cartography[J]. Journal on Communications, 2024, 45(3): 155–165. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2024056. [34] ZHOU Zizhen, ZHANG Qianqian, GE Jungang, et al. Hierarchical cognitive spectrum sharing in space-air-ground integrated networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2025, 24(2): 1430–1447. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2024.3509443. [35] 景毅, 姜春晓, 詹亚锋. 面向卫星通信的6G通感算融合架构、技术与挑战[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2023, 49(1): 10–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2023.01.002.JING Yi, JIANG Chunxiao, and ZHAN Yafeng. 6G communication, sensing and computing integration for satellite communication: Architectures, technologies and challenges[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2023, 49(1): 10–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2023.01.002. [36] 高曌, 高杨, 高梓贺, 等. 应用动态感知的卫星分布式集群管理平台设计与实现[J]. 航天器工程, 2024, 33(2): 125–132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2024.02.018.GAN Zhao, GAO Yang, GAO Zihe, et al. Design and implementation of satellite distributed cluster management platform using dynamic perception[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2024, 33(2): 125–132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2024.02.018. [37] 齐俏. 面向边缘智能网络的通信、感知和计算一体化研究[D]. [博士论文], 浙江大学, 2023. doi: 10.27461/d.cnki.gzjdx.2023.000533.QI Qiao. Research on integrated communication, sensing and computing for edge-intelligent networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2023. doi: 10.27461/d.cnki.gzjdx.2023.000533. [38] 陈一. 移动边缘计算系统中状态更新的通感算联合优化[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2024. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2024.002007.CHEN Yi. Joint optimization of sensing, communication and computation for status updates in mobile edge computing system[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2024. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2024.002007. [39] 宿洪智, 郑少明, 董鹏, 等. 融合深度学习与云计算的智能调度系统优化策略[J/OL]. 自动化技术与应用, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1474.TP.20241218.1142.048.html, 2024.SU Hongzhi, ZHENG Shaoming, DONG Peng, et al. Intelligent scheduling system optimization strategy integrating deep learning and cloud computing[J/OL]. Techniques of Automation and Applications, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1474.TP.20241218.1142.048.html, 2024. [40] 郑青碧, 邓娟, 刘奕彤, 等. 基于强化学习的基站多维度资源协同分配方案[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2022, 48(4): 638–645. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2022.04.009.ZEHNG Qingbi, DENG Juan, LIU Yitong, et al. A multi-dimensional resource collaborative allocation solution of base stations based on reinforcement learning[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2022, 48(4): 638–645. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2022.04.009. [41] 艾天羿. 面向分布式多云的动态资源调度系统设计与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 贵州大学, 2024. doi: 10.27047/d.cnki.ggudu.2024.002454.AI Tianyi. Design and implementation of dynamic resource scheduling system for distributed multi-cloud[D]. [Master dissertation], Guizhou University, 2024. doi: 10.27047/d.cnki.ggudu.2024.002454. [42] 吴金戈. 基于深度强化学习的云资源调度方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 贵州大学, 2023. doi: 10.27047/d.cnki.ggudu.2023.001727.WU Jinge. Research on cloud resource scheduling method based on deep reinforcement learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Guizhou University, 2023. doi: 10.27047/d.cnki.ggudu.2023.001727. [43] 王友祥, 裴郁杉, 黄蓉, 等. 6G通感算一体化网络架构和关键技术研究[J]. 移动通信, 2023, 47(9): 2–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20230904-0002.WANG Youxiang, PEI Yushan, HUANG Rong, et al. Network architecture and key technologies for 6G integrated communication, sensing and computing[J]. Mobile Communications, 2023, 47(9): 2–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20230904-0002. [44] 杨恒. 面向通感算一体化车联网的资源分配与优化研究[D]. [博士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2023. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2023.000294.YANG Heng. Research on resource allocation and optimization for joint communication, sensing, and computation enabled vehicular networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2023.000294. [45] ZUO Yong, YUE Mingyang, YANG Huiyuan, et al. Integrating communication, sensing and computing in satellite internet of things: Challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2024, 31(3): 332–338. doi: 10.1109/MWC.019.2200574. [46] AN Qier and SHEN Yuan. Air-ground integrated mobile edge computing in vehicular visual sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(24): 24395–24405. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3216963. [47] WANG Diao, WEN Dingzhu, HE Yinghui, et al. Joint device scheduling and resource allocation for ISCC-based multiview–multitask inference[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(24): 40814–40830. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3456569. [48] 崔新雨, 伍杰, 周一青, 等. 空天地一体化融合组网的挑战与关键技术[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2023, 50(1): 1–11. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2023.01.001.CUI Xinyu, WU Jie, ZHOU Yiqing, et al. Challenges of and key technologies for the air-space-ground integrated network[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2023, 50(1): 1–11. doi: 10.19665/j.issn1001-2400.2023.01.001. [49] 王雪, 孟姝宇, 钱志鸿. 面向6G全域融合的智能接入关键技术综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(5): 1613–1631. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231224.WANG Xue, MENG Shuyu, and QIAN Zhihong. An overview of key technologies for intelligent access toward 6G full-domain convergence[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(5): 1613–1631. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231224. [50] 刘雪芳, 毛伟灏, 杨清海. 基于深度强化学习的空天地一体化网络资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(7): 2831–2841. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231016.LIU Xuefang, MAO Weihao, and YANG Qinghai. A resource allocation algorithm for space-air-ground integrated network based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(7): 2831–2841. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231016. [51] 宫永康. 空天地一体化网络资源智能管理机制[D]. [博士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2023. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2023.000283.GONG Yongkang. Intelligent resource orchestration mechanism in space-air-ground integrated networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2023.000283. [52] 赵明. 空天地一体化网络分层协同学习与激励机制研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2023. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2023.000776.ZHAO Ming. Research on hierarchical collaborative learning and incentive mechanism in space-air-ground integrated network[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2023. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2023.000776. [53] 张平, 许文俊, 王凤玉, 等. 智简空天地一体化网络[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2022, 48(3): 381–384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2022.03.001.ZHANG Ping, XU Wenjun, WANG Fengyu, et al. Intellicise air-space-ground integrated networks[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2022, 48(3): 381–384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2022.03.001. [54] 段向阳, 杨立, 夏树强, 等. 通感算智一体化技术发展模式[J]. 电信科学, 2022, 38(3): 37–48. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2022039.DUAN Xiangyang, YANG Li, XIA Shuqiang, et al. Technology development mode of communication/sensing/ computing/intelligence integration[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2022, 38(3): 37–48. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2022039. [55] 李露, 李福昌, 马艳君, 等. 6G通感智算一体化无线网络技术研究[J]. 信息通信技术与政策, 2023, 49(9): 7–12. doi: 10.12267/j.issn.2096-5931.2023.09.002.LI Lu, LI Fuchang, MA Yanjun, et al. Research on 6G wireless network technology integrating communication, sensing, intelligence and computing[J]. Information and Communications Technology and Policy, 2023, 49(9): 7–12. doi: 10.12267/j.issn.2096-5931.2023.09.002. [56] 江甲沫, 韩凯峰, 徐晓燕. 6G通信感知一体化系统的性能指标[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2022, 28(5): 29–45. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202205008.JIANG Jiamo, HAN Kaifeng, and XU Xiaoyan. Performance metric for 6G integrated sensing and communication system[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2022, 28(5): 29–45. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202205008. [57] 李萍, 郭晓江. 通感一体化关键技术与应用[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2023, 29(2): 72–78. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202302014.LI Ping and GUO Xiaojiang. Key technologies and application of ISAC[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2023, 29(2): 72–78. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202302014. [58] 尉志青, 马昊, 张奇勋, 等. 感知-通信-计算融合的智能车联网挑战与趋势[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2020, 26(1): 45–49. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202001010.WEI Zhiqing, MA Hao, ZHANG Qixun, et al. Challenge and trend of sensing, communication and computing integrated intelligent internet of vehicles[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2020, 26(1): 45–49. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202001010. [59] 彭木根, 刘喜庆, 刘子乐, 等. 6G通信感知一体化理论与技术[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(1): 22–38. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.1332.PENG Mugen, LIU Xiqing, LIU Zile, et al. Principles and techniques in communication and sensing integrated 6G systems[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(1): 22–38. doi 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.1332. [60] 李晓阳, 周梓钦, 贡毅. 通信感知计算一体化波束赋形设计[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2022, 28(5): 23–28. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202205006.LI Xiaoyang, ZHOU Ziqin, and GONG Yi. Beamforming design for integrated sensing, communication and computation[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2022, 28(5): 23–28. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202205006. [61] 王文博, 侯跃峰, 田峰, 等. 面向扩展现实的通信感知计算一体化视频传输及QoE评价[J]. 移动通信, 2022, 46(5): 84–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.05.013.WANG Wenbo, HOU Yuefeng, TIAN Feng, et al. Video transmission and QoE evaluation of integrated communication, sensing and computation for extended reality[J]. Mobile Communications, 2022, 46(5): 84–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2022.05.013. [62] 裴郁杉, 唐雄燕, 黄蓉, 等. 通信感知计算融合在工业互联网中的愿景与关键技术[J]. 邮电设计技术, 2022(3): 14–18. doi: 10.12045/j.issn.1007-3043.2022.03.003.PEI Yushan, TANG Xiongyan, HUANG Rong, et al. Vision and key technologies of communication sensing and computing integration in industrial internet[J]. Designing Techniques of Posts and Telecommunications, 2022(3): 14–18. doi: 10.12045/j.issn.1007-3043.2022.03.003. [63] LIU Fan, CUI Yuanhao, MASOUROS C, et al. Integrated sensing and communications: Toward dual-functional wireless networks for 6G and beyond[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1728–1767. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3156632. [64] 刁兆坤, 汤清华, 蔡杰. 6G新型异构融合组网技术探析[J]. 通信世界, 2024(11): 41–44. doi: 10.13571/j.cnki.cww.2024.11.019.DIAO Zhaokun, TANG Qinghua, and CAI Jie. Analysis of 6G new heterogeneous converged networking technology[J]. Communications World, 2024(11): 41–44. doi: 10.13571/j.cnki.cww.2024.11.019. [65] 张瀚文. 基于深度学习的异构大数据实时处理与分析算法研究[J]. 国际科学, 2024(4): 97–99. doi: 10.62639/sspis31.20240104.ZHANG Hanwen. Research on real-time processing and analysis algorithm of heterogeneous big data based on deep learning[J]. International Scientific Studies Press Limited, 2024(4): 97–99. doi: 10.62639/sspis31.20240104. [66] XU Fangcheng, YU Xiangbin, CAI Jiali, et al. Computation efficiency optimization in UAV-enabled mobile edge computing system with multi-carrier non-orthogonal multiple access[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2020, 2020(1): 178. doi: 10.1186/s13638-020-01778-2. [67] 数字孪生世界企业联盟, 杭州易知微科技有限公司. 数字孪生世界白皮书(2022)[R]. 2022.Digital-Twin-World Enterprise Aliance, Hangzhou Yizhi Micro Technology Co. , Ltd. Digital twin world white paper[R]. 2022. [68] 刘梦, 马睿, 刘晨熙. 基于雾计算的智能无人机通信系统: 架构与关键技术[J]. 移动通信, 2023, 47(3): 19–24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20230217-0001.LIU Meng, MA Rui, and LIU Chenxi. Intelligent UAV communication system based on fog computing: Architecture and key technologies[J]. Mobile Communications, 2023, 47(3): 19–24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20230217-0001. [69] 谭少林, 谷海波, 刘克新. 多智能体博弈中的分布式学习: 原理与算法[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2024, 10(2): 127–136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2024.02.0127.TAN Shaolin, GU Haibo, and LIU Kexin. Distributed learning for multi-agent games: Theory and algorithms[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2024, 10(2): 127–136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2024.02.0127. [70] 王臆淞, 张鹏翼, 顾启佳, 等. ASM2: 面向海空联合场景的多对手多智能体博弈算法[J/OL]. 控制理论与应用, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1240.TP.20240830.1341.055.html, 2024.WANG Yisong, ZHANG Pengyi, GU Qijia, et al. ASM2: Multi-agent multi-opponent game algorithm for joint sea-air scenarios[J/OL]. Control Theory & Applications, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1240.TP.20240830.1341.055.html, 2024. [71] 潘昭天. 基于博弈论和多智能体强化学习的城市道路网络交通控制方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 吉林大学, 2021. doi: 10.27162/d.cnki.gjlin.2021.002784.PAN Zhaotian. Urban road network traffic control method based on game theory and multi-agent reinforcement learning[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Jilin University, 2021. doi: 10.27162/d.cnki.gjlin.2021.002784. [72] 徐东红, 李彬, 齐勇. 面向云数据中心基于改进A2C算法的任务调度策略[J]. 计算机科学, 2025, 52(2): 310–322. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.240500111.XU Donghong, LI Bin, and QI Yong. Task scheduling strategy based on improved A2C algorithm for cloud data center[J]. Computer Science, 2025, 52(2): 310–322. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.240500111. [73] MNIH V, BADIA A P, MIRZA M, et al. Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning[J]. arXiv: 1602.01783, 2016. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1602.01783. [74] C114通信网. 中国科学院院士尹浩: 6G通感融合网络架构需加强跨域技术融合创新[EB/OL]. https://www.g6gconference.com/index/Details/index.html?id=785, 2024.C114 Communication. Chinese Academy of Sciences Academician Yin Hao: 6G communication fusion network architecture demand increase cross-region technology fusion innovation[EB/OL]. https://www.g6gconference.com/index/Details/index.html?id=785, 2024. [75] 尹浩, 黄宇红, 韩林丛, 等. 6G通信–感知–计算融合网络的思考[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2023, 53(9): 1838–1842. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0135.YIN Hao, HUANG Yuhong, HAN Lincong, et al. Thoughts on 6G integrated communication, sensing and computing networks[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2023, 53(9): 1838–1842. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0135. [76] 中信科移动通信技术股份有限公司, 无线移动通信全国重点实验室(中国信科). 星地融合通信白皮书[R]. 2023.CICT Mobile Communication Technology Co. , Ltd, State Key Laboratory of Wireless Mobile Communications, China Academy of Telecommunications Technology (CICT). White paper on integrated terrestrial-satellite communication (ITSC)[R]. 2023. [77] 戴翠琴, 卞梦玥, 杜涛, 等. 星地融合边云协同网络下的资源调度研究[J]. 移动通信, 2024, 48(1): 25–32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20231210-0004.DAI Cuiqin, BIAN Mengyue, DU Tao, et al. Resource scheduling in satellite-terrestrial integrated networks with edge-cloud collaboration[J]. Mobile Communications, 2024, 48(1): 25–32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20231210-0004. [78] 罗延, 权伟, 张宏科. 6G关键技术标准化的思考与建议[J]. 中国工程科学, 2023, 25(6): 18–26. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.06.003.LUO Yan, QUAN Wei, and ZHANG Hongke. Standardization of 6G key technologies: Thoughts and suggestions[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2023, 25(6): 18–26. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2023.06.003. [79] 2024全球6G技术大会重磅发布20本6G白皮书[J]. 电信快报, 2024(5): 18.2024 global 6G technology tournament heavy paper 20 books 6G white paper[J]. Telecommunications Information, 2024(5): 18. [80] 中移智库, 中国移动通信研究院. 面向6G的天地一体融合网络技术白皮书[R]. 2024.China Mobile Intelligence, China Mobile Research Institute. White paper on 6G-oriented space-ground converged network technology[R]. 2024. [81] 中移智库, 中国移动通信研究院. 6G天地一体分布式自治网络白皮书[R]. 2024.China Mobile Intelligence, China Mobile Research Institute. 6G earth-sky integrated distributed autonomous network white paper[R]. 2024. [82] 徐晖, 陈山枝, 艾明. 面向6G的星地融合网络架构[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2023, 29(5): 9–15. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202305003.XU Hui, CHEN Shanzhi, and AI Ming. Integrated satellite and terrestrial network architecture for 6G[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2023, 29(5): 9–15. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202305003. [83] 买天乐, 姚海鹏, 忻向军, 等. 基于时空关联表征的空天地一体化网络资源精准管控方法[J]. 天地一体化信息网络, 2024, 5(2): 34–42. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-8930.2024014.MAI Tianle, YAO Haipeng, XIN Xiangjun, et al. Spatiotemporal correlation representation based precise resource management in space-air-ground integrated network[J]. Space-Integrated-Ground Information Networks, 2024, 5(2): 34–42. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-8930.2024014. [84] 杨惠婷, 刘伟. 空间信息网络时变图建模方法[J]. 移动通信, 2024, 48(1): 13–18,39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20231130-0002.YANG Huiting and LIU Wei. Time-varying graph modeling method for space information networks[J]. Mobile Communications, 2024, 48(1): 13–18,39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20231130-0002. [85] 王鹏. 应用驱动的卫星互联网多维资源调度方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2023. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2023.000213.WANG Peng. Application-driven multi-dimensional resources scheduling for satellite networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2023. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2023.000213. [86] 张嘉然, 杨雅婷, 嵩天. 卫星CDN中基于DQN的资源编排算法[J]. 天地一体化信息网络, 2022, 3(4): 45–54. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-8930.2022042.ZHANG Jiaran, YANG Yating, and SONG Tian. Resource scheduling algorithm based on DQN in satellite CDN[J]. Space-Integrated-Ground Information Networks, 2022, 3(4): 45–54. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-8930.2022042. [87] ZHANG Ziang, WANG Zehan, LIU Luping, et al. Extending multi-modal contrastive representations[C]. Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 2915. [88] 杨丹. 星地融合网络多域编排方案研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2023. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2023.002912.YANG Dan. Multi-domain orchestration scheme for satellite-terrestrial integrated networks[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2023.002912. [89] 曹欢, 苏泳涛, 周一青, 等. 基于星地协同处理的资源管理技术研究[J]. 高技术通讯, 2020, 30(12): 1205–1214. doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1002-0470.2020.12.001.CAO Huan, SU Yongtao, ZHOU Yiqing, et al. Research on resource management technology based on satellite-ground collaborative processing[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2020, 30(12): 1205–1214. doi: 10.3772/j.issn.1002-0470.2020.12.001. [90] 袁硕. 星地融合无线网络的资源调配理论与方法[D]. [博士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2024. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2024.000013.YUAN Shuo. Theories and methods of resource allocation in integrated satellite-terrestrial wireless networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2024. doi: 10.26969/d.cnki.gbydu.2024.000013. [91] 夏元清, 谢超, 高寒, 等. 天空地一体化网络环境下多运动体系统跨域协同控制与智能决策[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(5): 1176–1199. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.1774.XIA Yuanqing, XIE Chao, GAO Han, et al. Cross-domain cooperative control and intelligent decision-making of multi-dynamic agents in space-air-ground integrated network environment: A review[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(5): 1176–1199. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.1774. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
