| [1] |
XIAO Lin, YAN Xiangru, HE Yongjun, et al. A variable-gain fixed-time convergent and robust ZNN model for image fusion: Design, analysis, and verification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(6): 3415–3426. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3356530.
|
| [2] |
JIN Long, ZHANG Yunong, LI Shuai, et al. Modified ZNN for time-varying quadratic programming with inherent tolerance to noises and its application to kinematic redundancy resolution of robot manipulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(11): 6978–6988. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2590379.
|
| [3] |
ZHANG Zhijun, YANG Song, and ZHENG Lunan. A punishment mechanism-combined recurrent neural network to solve motion-planning problem of redundant robot manipulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(4): 2177–2185. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3111204.
|
| [4] |
LI Weibing, WU Haimei, and JIN Long. A lower dimension zeroing neural network for time-variant quadratic programming applied to robot pose control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(10): 11835–11843. doi: 10.1109/TII.2024.3413317.
|
| [5] |
廖伍代, 周军. 基于递归型神经网络动力学求解时变凸2次规划[J]. 运筹学学报, 2023, 27(1): 103–114. doi: 10.15960/j.cnki.issn.1007-6093.2023.01.007.LIAO Wudai and ZHOU Jun. Recurrent neural network dynamic for time-varying convex quadratic programming[J]. Operations Research Transactions, 2023, 27(1): 103–114. doi: 10.15960/j.cnki.issn.1007-6093.2023.01.007.
|
| [6] |
ZHANG Yunong, JIANG Danchi, and WANG Jun. A recurrent neural network for solving Sylvester equation with time-varying coefficients[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2002, 13(5): 1053–1063. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2002.1031938.
|
| [7] |
ZHANG Yunong, MA Weimu, and CAI Binghuang. From Zhang neural network to newton iteration for matrix inversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2009, 56(7): 1405–1415. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2008.2007065.
|
| [8] |
XU Feng, LI Zexin, NIE Zhuoyun, et al. Zeroing neural network for solving time-varying linear equation and inequality systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(8): 2346–2357. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2884543.
|
| [9] |
XIAO Lin, ZHANG Yongsheng, HU Zeshan, et al. Performance benefits of robust nonlinear zeroing neural network for finding accurate solution of Lyapunov equation in presence of various noises[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(9): 5161–5171. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2900659.
|
| [10] |
LI Shuai, CHEN Sanfeng, and LIU Bo. Accelerating a recurrent neural network to finite-time convergence for solving time-varying Sylvester equation by using a sign-Bi-power activation function[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2013, 37(2): 189–205. doi: 10.1007/s11063-012-9241-1.
|
| [11] |
JIN Jie, ZHU Jingcan, ZHAO Lv, et al. A robust predefined-time convergence zeroing neural network for dynamic matrix inversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(6): 3887–3900. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3179312.
|
| [12] |
LI Shuai and LI Yangming. Nonlinearly activated neural network for solving time-varying complex Sylvester equation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(8): 1397–1407. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2013.2285166.
|
| [13] |
LUO Jiawei and YANG Hui. A robust zeroing neural network model activated by the special nonlinear function for solving time-variant linear system in predefined-time[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2022, 54(3): 2201–2217. doi: 10.1007/s11063-021-10726-0.
|
| [14] |
CHEN Yuhuan, CHEN Jingjing, and YI Chenfu. A pre-defined finite time neural solver for the time-variant matrix equation E(t)X(t)G(t)=D(t)[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2024, 361(6): 106710. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2024.106710.
|
| [15] |
TANG Wensheng, CAI Hang, XIAO Lin, et al. A predefined-time adaptive zeroing neural network for solving time-varying linear equations and its application to UR5 robot[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2025, 36(3): 4703–4712. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3373040.
|
| [16] |
XIAO Lin, CAO Penglin, HE Yongjun, et al. Predefined-time noise immunity ZNN model for dynamic quaternion least squares problem and application to synchronization of hyperchaotic systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2024, 8(2): 1416–1426. doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2024.3352417.
|
| [17] |
ZENG Yuejie, XIAO Lin, LI Kenli, et al. Solving time-varying linear inequalities by finite-time convergent zeroing neural networks[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2020, 357(12): 8137–8155. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2020.06.004.
|
| [18] |
XIAO Lin, ZHANG Yongsheng, DAI Jianhua, et al. Comprehensive analysis of a new varying parameter zeroing neural network for time varying matrix inversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(3): 1604–1613. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.2989173.
|
| [19] |
XIAO Lin, LI Linju, HUANG Wenqian, et al. A new predefined time zeroing neural network with drop conservatism for matrix flows inversion and its application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(2): 752–761. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3225155.
|
| [20] |
CAO Mengrui, XIAO Lin, ZUO Qiuyue, et al. A fixed-time robust ZNN model with adaptive parameters for redundancy resolution of manipulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2024, 8(6): 3886–3898. doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2024.3377672.
|
| [21] |
XIAO Lin, SONG Wentong, LI Xiaopeng, et al. Design and analysis of a noise-resistant ZNN model for settling time-variant linear matrix inequality in predefined-time[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(10): 6840–6847. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3135383.
|
| [22] |
XIAO Lin, ZHANG Yongsheng, DAI Jianhua, et al. A new noise-tolerant and predefined-time ZNN model for time-dependent matrix inversion[J]. Neural Networks, 2019, 117: 124–134. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.05.005.
|
| [23] |
仲国民, 唐逸飞, 孙明轩. 用于有界噪声时变矩阵计算的终端零化神经网络[J]. 通信学报, 2024, 45(9): 55–67. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2024166.ZHONG Guomin, TANG Yifei, and SUN Mingxuan. Terminal zeroing neural network for time-varying matrix computing under bounded noise[J]. Journal on Communications, 2024, 45(9): 55–67. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2024166.
|
| [24] |
LI Weibing, YI Zilian, RAO Ruiqi, et al. A quadratic programming solution to position-level repetitive motion planning and obstacle avoidance of joint-constrained Robots[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2025, 72(2): 1860–1870. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2024.3406880.
|
| [25] |
ZHANG Yang and JIA Yingmin. Motion planning of redundant dual-arm robots with multicriterion optimization[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2023, 17(3): 4189–4199. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2023.3292430.
|
| [26] |
LIU Mei and SHANG Mingsheng. Orientation tracking incorporated multicriteria control for redundant manipulators with dynamic neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(4): 3801–3810. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3273253.
|
| [27] |
ZHONG Guomin, WANG Liming, and SUN Mingxuan. An initial-rectifying-constraint optimization scheme for repetitive motion planning by using prescribed-time zeroing neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22: 11087–11098. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2025.3531002.
|
| [28] |
SUN Mingxuan, ZHANG Yu, WU Yuxin, et al. On a finitely activated terminal RNN approach to time-variant problem solving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(12): 7289–7302. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3084740.
|
| [29] |
李杏, 仲国民. 用于时变矩阵计算的固定时间递归神经网络及其在重复运动规划中的应用[J]. 计算机科学, 2024, 51(8): 324–332. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.230500052.LI Xing and ZHONG Guomin. Fixed-time recurrent neural networks for time-variant matrix computing and its application in repeatable motion planning[J]. Computer Science, 2024, 51(8): 324–332. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.230500052.
|
| [30] |
汪黎明, 仲国民, 孙明轩, 等. 有限值终态零化神经网络及其在机器人运动规划中的应用[J]. 计算机科学, 2025, 52(5): 270–280. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.240400173.WANG Liming, ZHONG Guomin, SUN Mingxuan, et al. Finitely-valued terminal zeroing neural networks with application to robotic motion planning[J]. Computer Science, 2025, 52(5): 270–280. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.240400173.
|





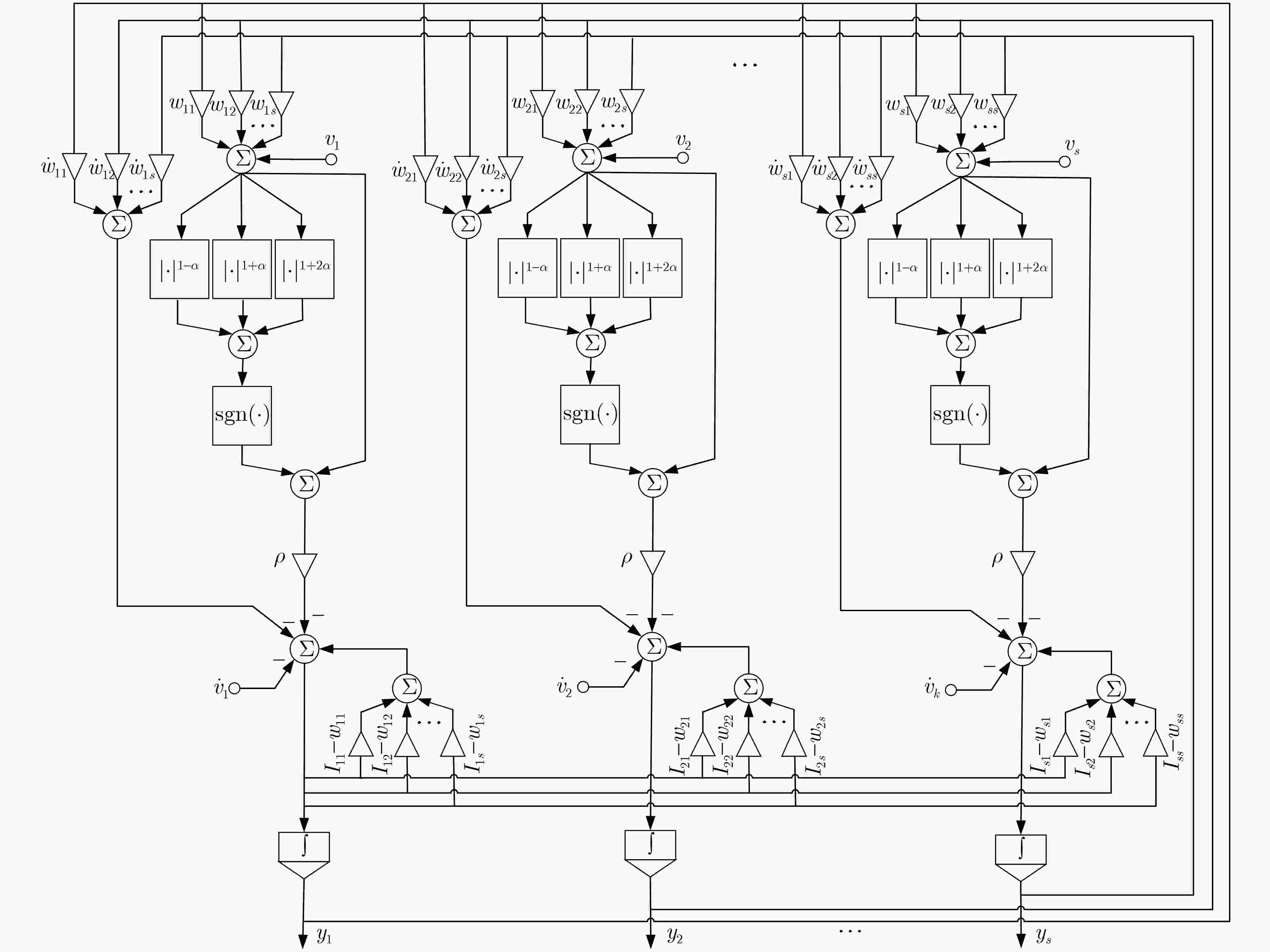
 下载:
下载:
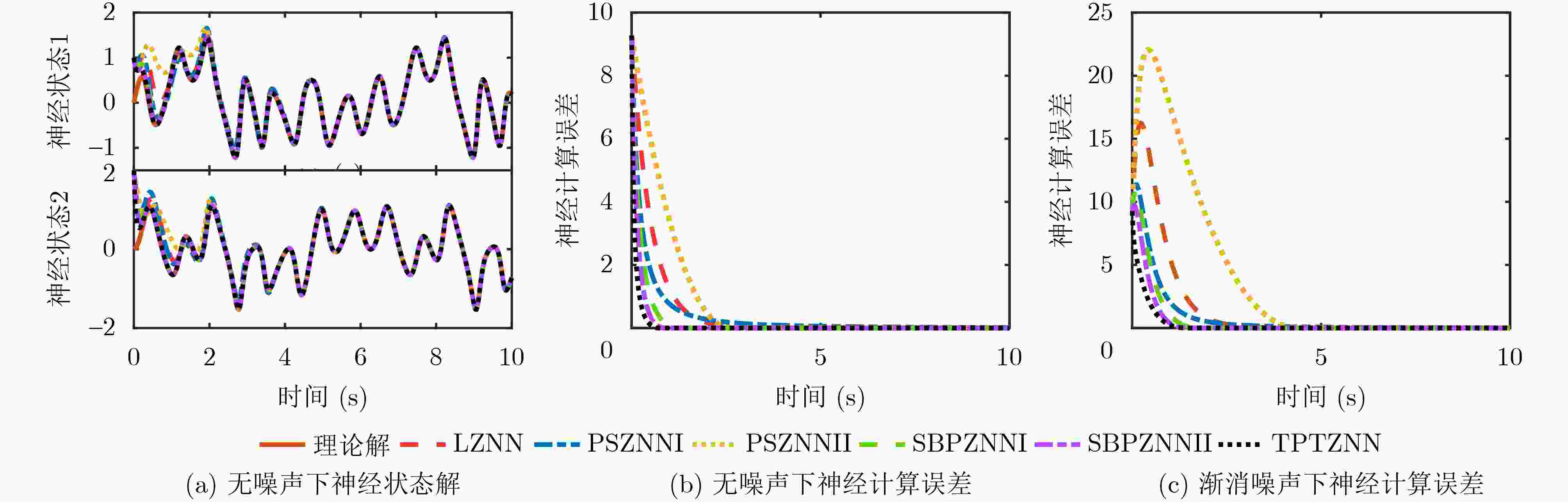

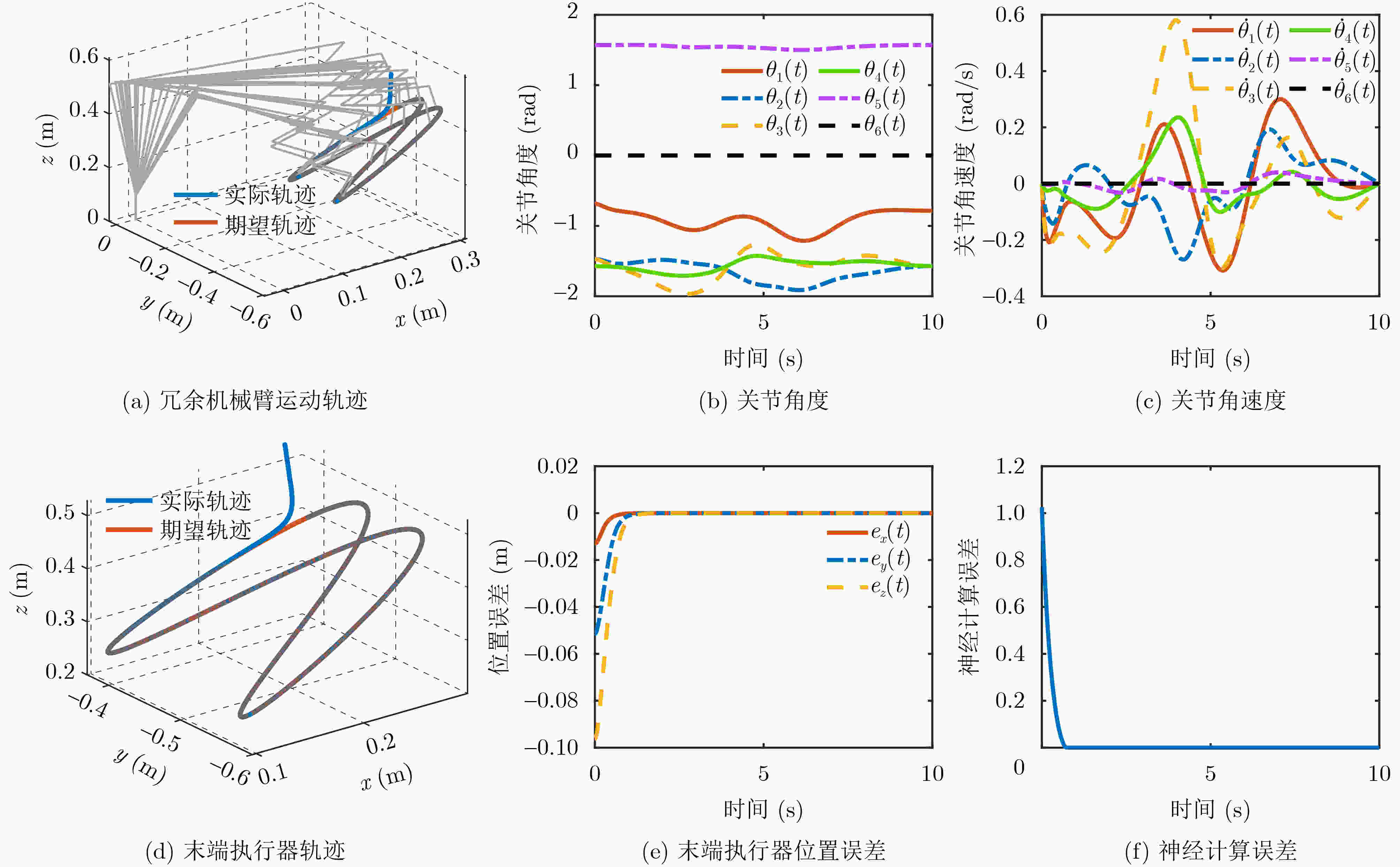
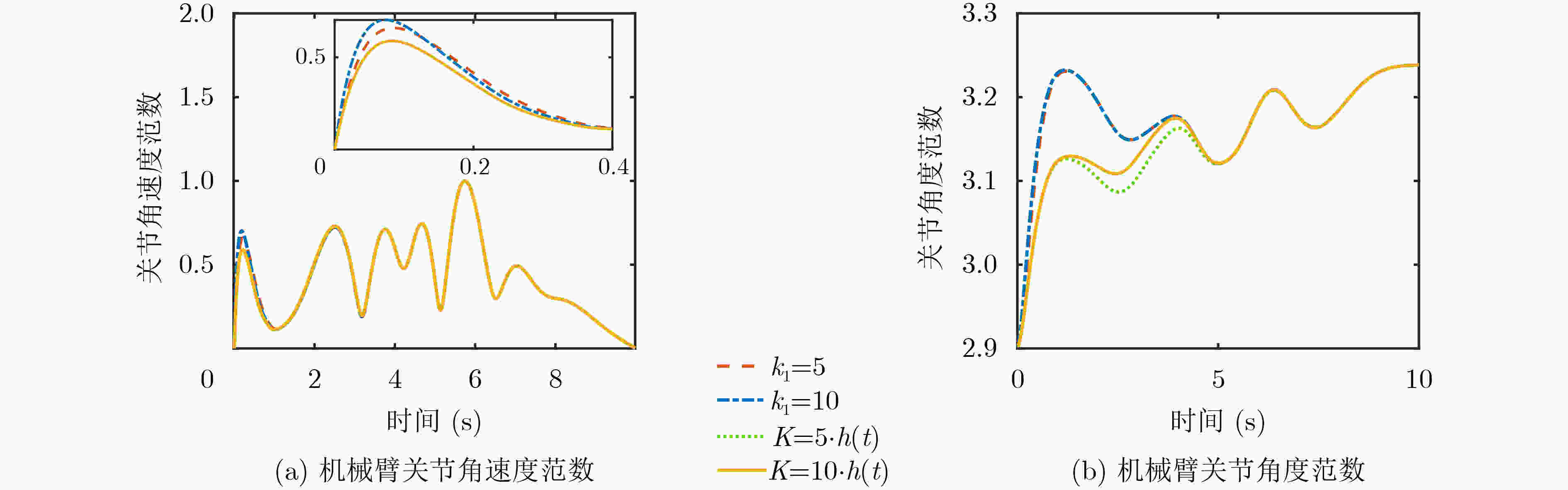


 下载:
下载:
