Exploration of Application of Artificial Intelligence Technology in Underwater Acoustic Network Routing Protocols
-
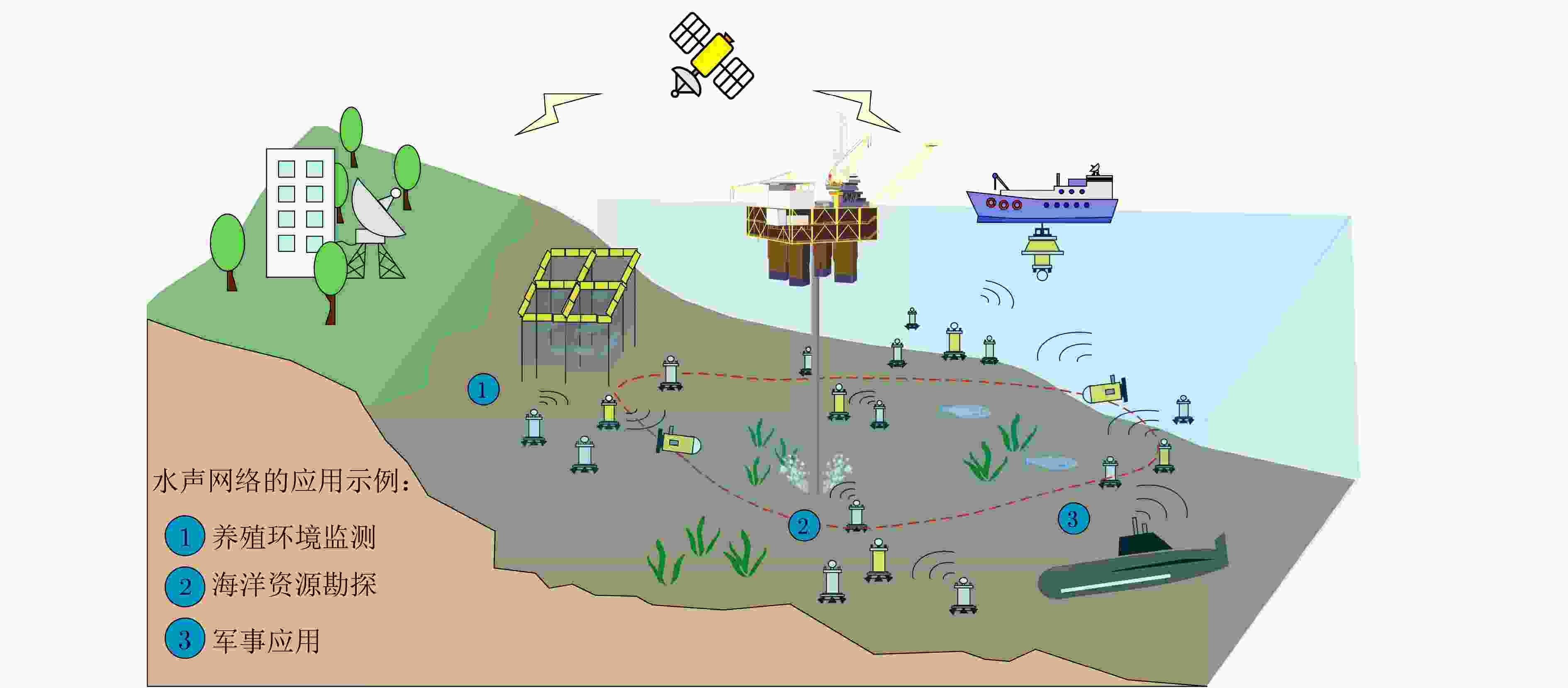
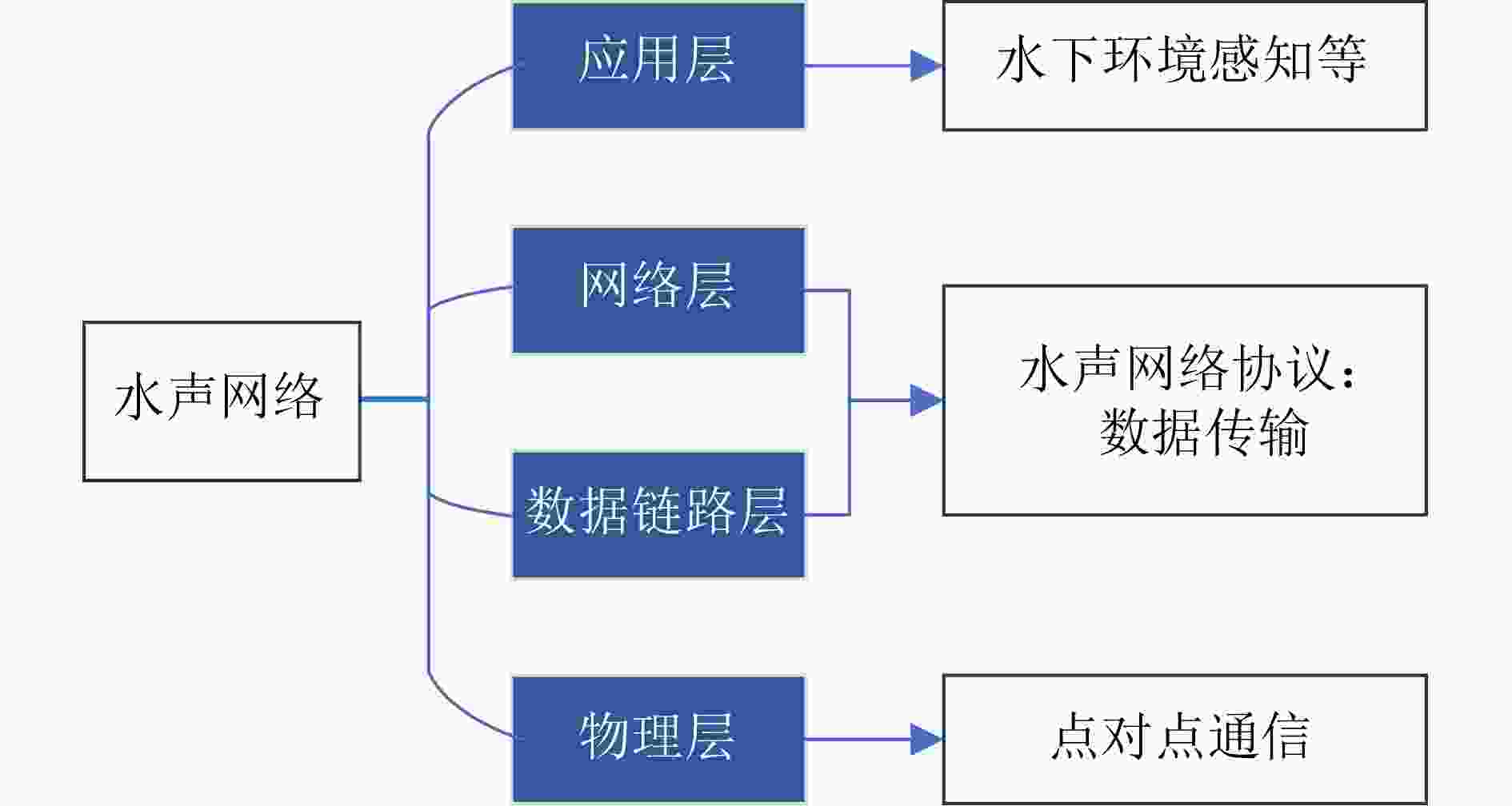
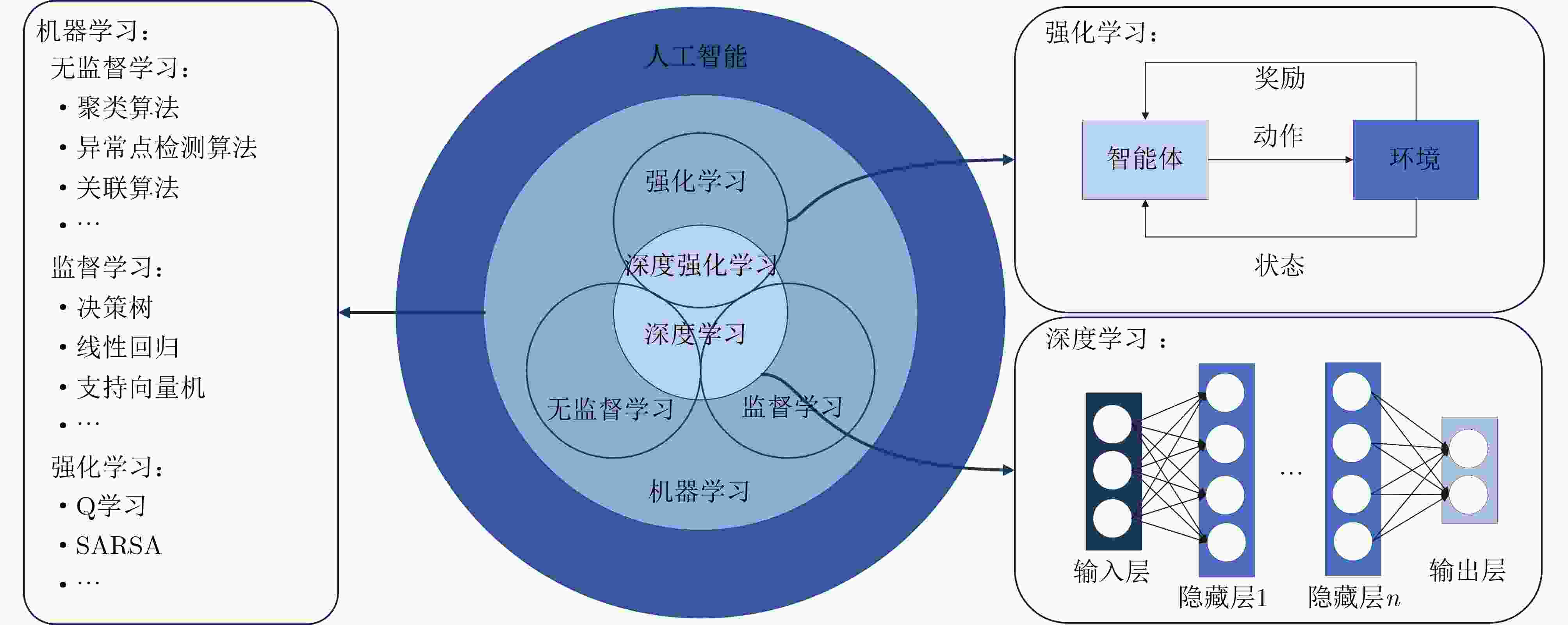
摘要: 随着海洋强国战略的发展,我国对海洋资源勘探、生态环境监测、军事安全应用等领域的海洋信息获取和数据传输需求迅速增加。水声网络作为水下数据传输的重要手段,其性能直接受到路由协议的影响。传统水声网络路由协议面临着动态海洋环境、节点能量有限以及网络安全等诸多挑战。近年来,人工智能技术凭借其强大的学习能力、数据洞察能力和适应性,逐渐被引入到水声网络路由协议中。该文综述了国内外人工智能技术在水声网络路由协议中的应用研究进展,详细分析了其在平面路由和层级路由中的应用情况。研究结果表明,人工智能技术能够有效优化路由决策,降低能耗,减少端到端时延,并在一定程度上提升网络安全性能。然而,当前的研究仍主要基于仿真,且在算法复杂度评估和硬件实现方面存在不足。未来的研究方向应包括开发更贴近实际海洋环境的仿真平台,进行海试实验以验证算法性能,同时降低人工智能算法的复杂度,以适应水声节点的硬件条件。该文旨在为水声网络路由协议中应用人工智能技术提供参考,并对未来研究方向提出建议。Abstract:
Significance In response to the strategic emphasis on maritime power, China has experienced growing demand for ocean resource exploration, ecological monitoring, and defense applications. Underwater acoustic networks provide an effective solution for data acquisition in these domains, with network performance largely dependent on the design and implementation of routing protocols. These protocols determine the transmission path and method, forming a foundation for optimizing underwater communication. Recent advances in Artificial Intelligence (AI) have prompted efforts to apply AI techniques to underwater acoustic network routing. By leveraging AI’s learning capacity, data insight capability, and adaptability, researchers aim to address challenges posed by dynamic underwater environments, energy limitations of nodes, and potential security threats. This paper examines the integration of AI technology into underwater acoustic network routing protocols and provides a critical evaluation of current research progress. Progress This paper reviews the application of AI technology in underwater acoustic network routing protocols, classifying existing approaches into flat and hierarchical routing categories. In flat routing, AI methods such as conventional heuristic algorithms, reinforcement learning, and deep learning have been applied to improve routing decisions. For hierarchical routing, AI is utilized not only for routing optimization but also for node clustering and layer structuring. These applications offer potential benefits, including enhanced routing efficiency, reduced energy consumption, improved end-to-end delay, and strengthened network security. Most performance evaluations are based on simulations. However, simulation environments vary considerably across studies, particularly in node quantity and density, ranging from small-scale to very large-scale networks. This variability complicates quantitative comparisons of performance metrics. Additionally, replicating these simulation scenarios in sea trials is limited by the logistical and financial constraints of deploying and recovering large numbers of nodes, thus impeding the validation of protocol performance under real-world conditions. The review further identifies critical challenges in applying AI to underwater acoustic networks. Many AI-based protocols operate under impractical assumptions, such as global knowledge of node positions and energy levels, which is rarely achievable in dynamic underwater settings. Maintaining such information requires substantial communication overhead, thereby increasing energy consumption and delay. Furthermore, the computational complexity of AI algorithms—particularly deep learning models—presents difficulties for implementation on underwater nodes with limited power, processing, and storage capacities. Few studies provide detailed complexity analyses, and hardware-based performance verifications remain scarce. This lack of real-world validation limits the assessment of the practical feasibility and effectiveness of AI-enabled routing protocols. Conclusions AI technology offers considerable potential for enhancing underwater acoustic network routing protocols by addressing key challenges such as environmental variability, energy constraints, and security threats. However, current research is constrained by several limitations. Many studies rely on unrealistic assumptions regarding the availability of complete node information, which is impractical in dynamic underwater settings. The acquisition and maintenance of such information entail substantial communication overhead, leading to increased energy consumption and delay. Moreover, the computational demands of AI algorithms—particularly deep learning models—often exceed the capabilities of resource-limited underwater nodes. Performance assessments remain predominantly simulation-based, with limited hardware implementation, thereby restricting the verification of real-world feasibility and effectiveness. Prospects Future research should prioritize the development of more accurate and realistic simulation platforms to support the evaluation of AI-based routing protocols. This includes the integration of advanced channel models and real-world observational data to improve simulation fidelity. Establishing standardized simulation conditions will also be essential for enabling consistent performance comparisons across studies. In parallel, greater emphasis should be placed on hardware implementation of AI algorithms, with efforts directed toward reducing algorithmic complexity and storage demands to accommodate the limitations of energy-constrained underwater nodes. Exploring cost-effective validation approaches, such as small-scale sea trials and semi-physical simulation frameworks, will be critical for assessing the practical performance and deployment feasibility of AI-enabled routing protocols. -
表 1 人工智能技术在水声网络平面路由协议中的应用探索
文献索引 算法类别 算法 年份 优化目标 验证方法 节点个数 网络范围 可靠性和
可扩展性能耗 端到端时延 网络安全性 [27] 常规智能算法 ACO&AFS 2020 √ √ √ × 仿真 20 14×5 km2 [28] ACO 2021 √ √ √ × 仿真 18 12×5 km2 [29] 2023 √ √ √ × 仿真 250 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [30] 2023 √ √ √ × 仿真 15~50 5×5×3 km3 [31] MO-CBACO 2023 √ √ √ √ 仿真 100~500 1×1 km2 [32] CSO 2020 √ √ × × 仿真 150~450 1.5×1.5×1.5 km3 [33] 博弈论 2020 √ √ √ × 仿真 200~400 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [34] 模糊控制 2021 √ √ √ × 仿真&湖试 仿真300–800&湖试5 仿真0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [35] GA&SA
&GSS2022 √ √ × √ 仿真 10~40 – [36] SVM 2023 √ √ √ × 仿真 100~500 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [37] GA&PSO 2024 √ √ √ × 仿真 80~160 1×1×1 km3 [38] 强化学习算法 RL 2019 √ √ √ × 仿真&海试 仿真6~40&海试6 仿真4×4×0.24 km3 [18] QL 2010 √ √ × × 仿真 250 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [39] 2019 √ √ √ × 仿真 100~300 5×5×2.5 km3 [40] 2020 √ √ √ × 仿真 200~800 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [41] 2021 √ √ √ × 仿真 100~500 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [42] 2021 √ √ × × 仿真 100 – [43] 2021 √ √ × × 仿真 18 14×5 km2 [44] 2021 √ √ √ × 仿真 50~600 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [45] 2022 √ √ √ × 仿真 100~500 4×4×5 km3 [46] 2023 √ √ √ × 仿真 10~40 6×6 km2 [47] 2023 √ √ √ × 仿真 40~90 4×4×4 km3 [48] 2024 √ × × √ 仿真 100~500 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [49] 2024 √ √ √ × 仿真 40~90 4×4×4 km3 [50] 深度学习与
深度强化学习DNN 2021 √ √ √ × 仿真 30 1.5×1.5 km2 [51] BP-NN 2023 √ √ × × 仿真 60 1×1 km2 [52] GNN 2024 √ √ √ × 仿真 50~250 5×5×3 km3 [53] GAN&QL 2024 √ √ √ √ 仿真 100 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [54] DQN 2019 √ √ √ × 仿真 80 5×4×4.5 km3 [55] 2021 √ √ √ × 仿真 100 0.5×0.4×0.45 km3 [56] 2022 √ √ × × 仿真 500~3 000 1×1×0.5 km3 [57] 2023 √ √ √ × 仿真 10~50 0.6×0.6×0.5 km3 表 2 人工智能技术在水声网络层级路由协议中的应用探索
文献索引 算法作用 算法 年份 优化目标 验证方法 节点个数 网络范围 可靠性和
可扩展性能耗 端到端
时延网络安
全性[59] 仅层级划分 K-Means 2020 √ √ × × 仿真 100 5×5 km2 [60] 2021 √ √ × × 仿真 200 0.02×0.02 km2 [61] 2022 √ √ × × 仿真 100 0.1×0.1×0.1 km3 [62] K-Means &QL 2021 √ √ × × 仿真 60 12.5×4 km2 [64] Birch 2021 √ √ × × 仿真 15000 0.8×0.8×0.8 km3 [65] MFO 2019 √ √ × × 仿真 40 (80) 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 (2×2×2 km3) [66] 模糊聚类&PSO 2019 √ √ × × 仿真 100 0.1×0.1×0.1 km3 [67] 2021 √ √ × × 仿真 100 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [68] DFO 2021 √ √ × × 仿真 20~200 0.5×2 km2 [69] 博弈论 2021 √ √ × × 仿真 100 0.1×0.1×0.1 km3 [70] PSO 2022 √ √ × × 仿真 100 0.1×0.1×0.1 km3 [71] GSO 2023 √ √ × × 仿真 20~200 0.5×2 km2 [72] DFO 2023 √ √ × × 仿真 100 0.2×0.2 km2 [73] 层级划分&
路由决策GA 2018 √ √ √ × 仿真 350 1×1×0.1 km3 [74] CSRO 2022 √ √ × × 仿真 300 – [75] QL 2022 √ √ × × 仿真 100 3×3×2.5 km3 [76] 2023 √ √ √ × 仿真 250 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [77] ChOA 2024 √ √ √ × 仿真 300 0.2×0.2 km2 [78] CKHA& GSO 2022 √ √ √ √ 仿真 300 2×2×2 km3 [79] EPO&GOA 2022 √ √ √ × 仿真 400 – [80] 仅路由决策 ACO 2020 √ √ √ × 仿真 300~500 5×5×1 km3 [81] GA 2020 √ √ √ × 仿真 200~300 5×5×1 km3 [82] BOA 2022 √ √ √ × 仿真 150~450 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [83] QL 2021 √ √ √ × 仿真 170 0.25×0.25×0.08 km3 [84] 2022 √ √ √ × 仿真 100~500 5×5×5 km3 [85] DBN 2021 √ √ × × 仿真 200 0.5×0.5×0.5 km3 [86] GMM-HMM-LSTM&PSO 2024 √ √ √ √ 仿真 50-200 2×2×1.5 km3 -
[1] 杨健敏, 王佳惠, 乔钢, 等. 水声通信及网络技术综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(1): 1–21. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230424.YANG Jianmin, WANG Jiahui, QIAO Gang, et al. Review of underwater acoustic communication and network technology[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(1): 1–21. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230424. [2] 乔钢, 刘凇佐, 刘奇佩. 水声通信网络协议、仿真与试验综述[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2017, 25(3): 151–160. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2017.02.002.QIAO Gang, LIU Songzuo, and LIU Qipei. Review of protocols, simulation and experimentation for underwater acoustic communication network[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2017, 25(3): 151–160. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2017.02.002. [3] 许肖梅. 水声通信与水声网络的发展与应用[J]. 声学技术, 2009, 28(6): 811–816. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1000-3630.2009.06.026.XU Xiaomei. Development and applications of underwater acoustic communication and networks[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2009, 28(6): 811–816. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1000-3630.2009.06.026. [4] RICE J and GREEN D. Underwater acoustic communications and networks for the US Navy's Seaweb program[C]. 2008 Second International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications, Cap Esterel, France, 2008: 715–722. doi: 10.1109/SENSORCOMM.2008.137. [5] 李风华, 路艳国, 王海斌, 等. 海底观测网的研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2019, 34(3): 321–330. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2019.03.010.LI Fenghua, LU Yanguo, WANG Haibin, et al. Research progress and development trend of seafloor observation network[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019, 34(3): 321–330. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2019.03.010. [6] 朱敏, 武岩波. 水声通信技术进展[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2019, 34(3): 289–296. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2019.03.006.ZHU Min and WU Yanbo. Development of underwater acoustic communication technology[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019, 34(3): 289–296. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2019.03.006. [7] KHAN H, HASSAN S A, and JUNG H. On underwater wireless sensor networks routing protocols: A review[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(18): 10371–10386. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2994199. [8] 温晓强, 孙运强, 申远哲, 等. 微小型无人潜航器水声通信系统研究[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2022, 41(5): 76–82. doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2203605.WEN Xiaoqiang, SUN Yunqiang, SHEN Yuanzhe, et al. Research on underwater acoustic communication system of micro-unmanned underwater vehicle[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2022, 41(5): 76–82. doi: 10.19652/j.cnki.femt.2203605. [9] 崔雍浩, 商聪, 陈锶奇, 等. 人工智能综述: AI的发展[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2019, 45(3): 225–231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2019.03.01.CUI Yonghao, SHANG Cong, CHEN Siqi, et al. Overview of AI: Developments of AI techniques[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2019, 45(3): 225–231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2019.03.01. [10] 孙志军, 薛磊, 许阳明, 等. 深度学习研究综述[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2012, 29(8): 2806–2810. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2012.08.002.SUN Zhijun, XUE Lei, XU Yangming, et al. Overview of deep learning[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2012, 29(8): 2806–2810. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2012.08.002. [11] 贺倩. 人工智能技术的发展与应用[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2017, 15(9): 32–37. doi: 10.16543/j.2095-641x.electric.power.ict.2017.09.006.HE Qian. Development and application of artificial intelligence technology[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2017, 15(9): 32–37. doi: 10.16543/j.2095-641x.electric.power.ict.2017.09.006. [12] BOYAN J A and LITTMAN M L. Packet routing in dynamically changing networks: A reinforcement learning approach[C]. The 7th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, Colorado, 1993: 671–678. [13] KUMAR S and MIIKKULAINEN R. Dual reinforcement Q-routing: An on-line adaptive routing algorithm[M]. DAGLI C H, AKAY M, ERSOY O, et al. Smart Engineering Systems: Neural Networks, Fuzzy Logic, Data Mining, and Evolutionary Programming. New York: ASME Press, 1997: 231–238. [14] DI CARO G and DORIGO M. Ant colonies for adaptive routing in packet-switched communications networks[C]. The 5th International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998: 673–682. doi: 10.1007/BFb0056909. [15] XIE Peng, CUI Junhong, and LAO Li. VBF: Vector-based forwarding protocol for underwater sensor networks[C]. The 5th International IFIP-TC6 Networking Conference on NETWORKING 2006. Networking Technologies, Services, Protocols; Performance of Computer and Communication Networks; Mobile and Wireless Communications Systems, Coimbra, Portugal, 2006: 1216–1221. doi: 10.1007/11753810_111. [16] YAN Hai, SHI Z J, and CUI Junhong. DBR: Depth-based routing for underwater sensor networks[C]. The 7th International IFIP-TC6 Networking Conference on NETWORKING 2008 Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks, Wireless Networks, Next Generation Internet. Singapore, 2008: 72–86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-79549-0_7. [17] HU Tiansi and FEI Yunsi. QELAR: A Q-learning-based energy-efficient and lifetime-aware routing protocol for underwater sensor networks[C]. 2008 IEEE International Performance, Computing and Communications Conference, Austin, USA, 2008: 247–255. doi: 10.1109/PCCC.2008.4745119. [18] HU Tiansi and FEI Yunsi. QELAR: A machine-learning-based adaptive routing protocol for energy-efficient and lifetime-extended underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2010, 9(6): 796–809. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2010.28. [19] 陈友淦, 许肖梅. 人工智能技术在水声通信中的研究进展[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2020, 41(10): 1536–1544. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202007110.CHEN Yougan and XU Xiaomei. Research progress in artificial intelligence technology for underwater acoustic communications[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2020, 41(10): 1536–1544. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202007110. [20] YILDIZ H U. Joint effects of void region size and sink architecture on underwater WSNs lifetime[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(10): 11046–11056. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3264159. [21] YADAV S, GARG N, AGGARWAL S G, et al. Recent Advances in Metrology: Select Proceedings of AdMet 2022[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2024: 309–320. [22] CHAUDHARY M, GOYAL N, BENSLIMANE A, et al. Underwater wireless sensor networks: Enabling technologies for node deployment and data collection challenges[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(4): 3500–3524. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2022.3218766. [23] LIU Zhixin, MENG Xiangyun, LIU Yang, et al. AUV-Aided hybrid data collection scheme based on value of information for internet of underwater things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(9): 6944–6955. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2021.3115800. [24] DONG Yanhan, CHEN Zheyang, SONG Zhixian, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface transmission for data importance classification in underwater acoustic networks with energy holes[C]. IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Zhengzhou, China, 2023: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/icspcc59353.2023.10400354. [25] 董阳泽, 许肖梅, 刘平香. 水声对抗中的水声网络及其对抗[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2011, 36(7): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2011.07.001.DONG Yangze, XU Xiaomei, and LIU Pingxiang. Counterworking to UAN in underwater acoustic warfare[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2011, 36(7): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2011.07.001. [26] 魏志强, 杨光, 丛艳平. 水下传感器网络安全研究[J]. 计算机学报, 2012, 35(8): 1594–1606. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2012.01594.WEI Zhiqiang, YANG Guang, and CONG Yanping. Security of underwater sensor networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2012, 35(8): 1594–1606. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2012.01594. [27] CHEN Yougan, ZHU Jianying, WAN Lei, et al. ACOA-AFSA fusion dynamic coded cooperation routing for different scale multi-hop underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 186773–186788. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3029533. [28] CHEN Yougan, TANG Yuying, FANG Xing, et al. PB-ACR: Node payload balanced ant colony optimal cooperative routing for multi-hop underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 57165–57178. doi: 10.1109/access.2021.3072283. [29] 袁青青, 袁丁, 严清. U-WSNs中基于蚁群算法的定向梯度传输机会路由协议[J]. 无线电工程, 2023, 53(7): 1502–1508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2023.07.002.YUAN Qingqing, YUAN Ding, and YAN Qing. Directional gradient transmission for opportunistic routing protocol based on ant colony algorithm in U-WSNs[J]. Radio Engineering, 2023, 53(7): 1502–1508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2023.07.002. [30] LI Chong, DU Xiujuan, and WANG Lijuan. IATLR: Improved ACO and TOPSIS-based layering routing protocol for underwater acoustic networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(3): 3262–3269. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2022.3230069. [31] ZHANG Mingyue, XIE Jianpeng, WANG Zongyang, et al. MO-CBACORP: A new energy-efficient secure routing protocol for underwater monitoring wireless sensor network[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 2023, 35(9): 101786. doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2023.101786. [32] KUMARI S, MISHRA P K, and ANAND V. Integrated load balancing and void healing routing with Cuckoo search optimization scheme for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2020, 111(3): 1787–1803. doi: 10.1007/s11277-019-06957-z. [33] WANG Qingwen, LI Jianghui, QI Qian, et al. A game-theoretic routing protocol for 3-D underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(10): 9846–9857. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2020.2988503. [34] HAN Duoliang, DU Xiujuan, LIU Xiuxiu, et al. FCLR: Fuzzy control-based layering routing protocol for underwater acoustic networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(23): 23590–23602. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2022.3218136. [35] UYAN O G, AKBAS A, and GUNGOR V C. A reliable and secure multi-path routing strategy for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. Computer Networks, 2022, 212: 109070. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2022.109070. [36] ZHANG Shuyun, CHEN Huifang, and XIE Lei. ASVMR: Adaptive support-vector-machine-based routing protocol in the underwater acoustic sensor network for smart ocean[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(9): 1736. doi: 10.3390/jmse11091736. [37] GAVALI A B, VAZE V M, and UBALE S A. HOCOR: Hybrid optimization-based cooperative opportunistic routing for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2024, 135(3): 1449–1472. doi: 10.1007/s11277-024-11106-2. [38] DI VALERIO V, LO PRESTI F, PETRIOLI C, et al. CARMA: Channel-aware reinforcement learning-based multi-path adaptive routing for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(11): 2634–2647. doi: 10.1109/jsac.2019.2933968. [39] JIN Zhigang, ZHAO Qinyi, and SU Yishan. RCAR: A reinforcement-learning-based routing protocol for congestion-avoided underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(22): 10881–10891. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2019.2932126. [40] LU Yongjie, HE Rongxi, CHEN Xiaojing, et al. Energy-efficient depth-based opportunistic routing with Q-learning for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(4): 1025. doi: 10.3390/s20041025. [41] ZHOU Yuan, CAO Tao, and XIANG Wei. Anypath routing protocol design via Q-Learning for underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(10): 8173–8190. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2020.3042901. [42] KHAN Z A, KARIM O A, ABBAS S, et al. Q-learning based energy-efficient and void avoidance routing protocol for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. Computer Networks, 2021, 197: 108309. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2021.108309. [43] CHEN Yougan, ZHENG Kaitong, FANG Xing, et al. QMCR: A Q-learning-based multi-hop cooperative routing protocol for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. China Communications, 2021, 18(8): 224–236. doi: 10.23919/jcc.2021.08.016. [44] ZHANG Ying, ZHANG Zheming, CHEN Lei, et al. Reinforcement learning-based opportunistic routing protocol for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(3): 2756–2770. doi: 10.1109/tvt.2021.3058282. [45] ZHU Rongxin, JIANG Qihang, HUANG Xiangdang, et al. A reinforcement-learning-based opportunistic routing protocol for energy-efficient and void-avoided UASNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(13): 13589–13601. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2022.3175994. [46] NANDYALA C S, KIM H W, and CHO H S. QTAR: A Q-learning-based topology-aware routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Computer Networks, 2023, 222: 109562. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2023.109562. [47] WANG Chao, SHEN Xiaohong, WANG Haiyan, et al. Reinforcement learning-based opportunistic routing protocol using depth information for energy-efficient underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(15): 17771–17783. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2023.3285751. [48] LI Feiyan, HAN Guangjie, LIN Chuan, et al. SDN-QLTR: Q-learning-assisted trust routing scheme for SDN-based underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(6): 10682–10694. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2023.3328356. [49] WANG Chao, SHEN Xiaohong, WANG Haiyan, et al. Multi-agent reinforcement learning-based routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks with value of information[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(5): 7042–7054. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2023.3345947. [50] HEMAVATHY N and INDUMATHI P. Deep learning-based hybrid dynamic biased track (DL-HDBT) routing for under water acoustic sensor networks[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2021, 12(1): 1211–1225. doi: 10.1007/s12652-020-02165-x. [51] ZHU Xiuling, CHEN Yougan, WAN Lei, et al. Dynamic layered routing protocols based on BP-NN for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2023, 211: 109454. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2023.109454. [52] ZHANG Shuyun, CHEN Huifang, and XIE Lei. GNN-IR: An intelligent routing method based on graph neural network in the underwater acoustic sensor network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(13): 21566–21582. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2024.3398375. [53] WANG Bin and BEN Kerong. GTR: GAN-based trusted routing algorithm for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(15): 4879. doi: 10.3390/s24154879. [54] SU Yishan, FAN Rong, FU Xiaomei, et al. DQELR: An adaptive deep Q-network-based energy- and latency-aware routing protocol design for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 9091–9104. doi: 10.1109/access.2019.2891590. [55] ANITHA D and KARTHIKA R A. DEQLFER—A deep extreme Q-learning firefly energy efficient and high performance routing protocol for underwater communication[J]. Computer Communications, 2021, 174: 143–153. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2021.04.030. [56] CHEN Yan, BAI Jie, and LI Yun. PDDQN-HHVBF routing protocol based on empirical priority DDQN to improve HHVBF[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11(23): 4031. doi: 10.3390/electronics11234031. [57] GENG Xuan and ZHANG Bin. Deep Q-network-based intelligent routing protocol for underwater acoustic sensor network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(4): 3936–3943. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2023.3234112. [58] 杨俊闯, 赵超. K-Means聚类算法研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(23): 7–14,63. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1908-0347.YANG Junchuang and ZHAO Chao. Survey on K-Means clustering algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019, 55(23): 7–14,63. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1908-0347. [59] WANG Meihuang, CHEN Yougan, SUN Xiang, et al. Node energy consumption balanced multi-hop transmission for underwater acoustic sensor networks based on clustering algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 191231–191241. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3032019. [60] OMEKE K G, MOLLEL M S, OZTURK M, et al. DEKCS: A dynamic clustering protocol to prolong underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(7): 9457–9464. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2021.3054943. [61] LI Luyao, QIU Yang, and XU Jing. A K-Means clustered routing algorithm with location and energy awareness for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Photonics, 2022, 9(5): 282. doi: 10.3390/photonics9050282. [62] ZHU Jianying, CHEN Yougan, SUN Xiang, et al. ECRKQ: Machine learning-based energy-efficient clustering and cooperative routing for mobile underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 70843–70855. doi: 10.1109/access.2021.3078174. [63] ZHANG Tian, RAMAKRISHNAN R, and LIVNY M. BIRCH: An efficient data clustering method for very large databases[J]. ACM SIGMOD Record, 1996, 25(2): 103–114. doi: 10.1145/235968.233324. [64] LIN Chuan, HAN Guangjie, WANG Tingting, et al. Fast node clustering based on an improved birch algorithm for data collection towards software-defined underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(22): 25480–25488. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2021.3055948. [65] DURRANI M Y, TARIQ R, AADIL F, et al. Adaptive node clustering technique for smart ocean under water sensor network (SOSNET)[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(5): 1145. doi: 10.3390/s19051145. [66] KRISHNASWAMY V and MANVI S S. Fuzzy and PSO based clustering scheme in underwater acoustic sensor networks using energy and distance parameters[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2019, 108(3): 1529–1546. doi: 10.1007/s11277-019-06483-y. [67] KRISHNASWAMY V and MANVI S S. Trusted node selection in clusters for underwater wireless acoustic sensor networks using fuzzy logic[J]. Physical Communication, 2021, 47: 101388. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2021.101388. [68] KHAN M F, BIBI M, AADIL F, et al. Adaptive node clustering for underwater sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(13): 4514. doi: 10.3390/s21134514. [69] XING Guanglin, CHEN Yumeng, HOU Rui, et al. Game-theory-based clustering scheme for energy balancing in underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(11): 9005–9013. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2021.3055857. [70] HOU Rui, FU Juan, DONG Mianxiong, et al. An Unequal clustering method based on particle swarm optimization in underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(24): 25027–25036. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2022.3195223. [71] BHARANY S, SHARMA S, ALSHARABI N, et al. Energy-efficient clustering protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks using optimized glowworm swarm optimization[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2023, 10: 1117787. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1117787. [72] KAVERIPAKAM S and CHINTHAGINJALA R. Clustering-based dragonfly optimization algorithm for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2023, 81: 580–598. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2023.09.047. [73] FAHEEM M, TUNA G, and GUNGOR V C. QERP: Quality-of-Service (QoS) aware evolutionary routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2018, 12(3): 2066–2073. doi: 10.1109/jsyst.2017.2673759. [74] ANURADHA D, SUBRAMANI N, KHALAF O I, et al. Chaotic search-and-rescue-optimization-based multi-hop data transmission protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(8): 2867. doi: 10.3390/s22082867. [75] SUN Yao, ZHENG Maochun, HAN Xiao, et al. Adaptive clustering routing protocol for underwater sensor networks[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2022, 136: 102953. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2022.102953. [76] YUAN Yufan, LIU Meiyan, ZHUO Xiaoxiao, et al. A Q-learning-based hierarchical routing protocol with unequal clustering for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(6): 6312–6325. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2022.3232614. [77] HE Shukun, LI Qinlin, KHISHE M, et al. The optimization of nodes clustering and multi-hop routing protocol using hierarchical chimp optimization for sustainable energy efficient underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Wireless Networks, 2024, 30(1): 233–252. doi: 10.1007/s11276-023-03464-9. [78] MOHAN P, SUBRAMANI N, ALOTAIBI Y, et al. Improved metaheuristics-based clustering with multihop routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(4): 1618. doi: 10.3390/s22041618. [79] SUBRAMANI N, MOHAN P, ALOTAIBI Y, et al. An efficient metaheuristic-based clustering with routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(2): 415. doi: 10.3390/s22020415. [80] XIAO Xingxing and HUANG Haining. A clustering routing algorithm based on improved ant colony optimization algorithms for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Algorithms, 2020, 13(10): 250. doi: 10.3390/a13100250. [81] XIAO Xingxing, HUANG Haining, and WANG Wei. Underwater wireless sensor networks: An energy-efficient clustering routing protocol based on data fusion and genetic algorithms[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 11(1): 312. doi: 10.3390/app11010312. [82] CHENTHIL T R and JESU JAYARIN P. An energy-aware multilayer clustering-based butterfly optimization routing for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2022, 122(4): 3105–3125. doi: 10.1007/s11277-021-09042-6. [83] ALSALMAN L and ALOTAIBI E. A balanced routing protocol based on machine learning for underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 152082–152097. doi: 10.1109/access.2021.3126107. [84] ZHU Rongxin, HUANG Xiwen, HUANG Xiangdang, et al. An on-site-based opportunistic routing protocol for scalable and energy-efficient underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(23): 12482. doi: 10.3390/app122312482. [85] 秦利娟, 刘鑫. 融合深度学习的UASN智能路由算法研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2021, 38(12): 118–121,266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2021.12.024.QIN Lijuan and LIU Xin. Intelligent routing algorithm for UASN based on deep learning[J]. Computer Simulation, 2021, 38(12): 118–121,266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2021.12.024. [86] ZHU Rongxin, BOUKERCHE A, and YANG Qiuling. An efficient secure and adaptive routing protocol based on GMM-HMM-LSTM for internet of underwater things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(9): 16491–16504. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2024.3354820. [87] STOJANOVIC M. On the relationship between capacity and distance in an underwater acoustic communication channel[J]. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 2007, 11(4): 34–43. doi: 10.1145/1347364.1347373. [88] YAN Honglu, MA Tianlong, PAN Chenyu, et al. Statistical analysis of time-varying channel for underwater acoustic communication and network[C]. 2021 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT), Islamabad, Pakistan, 2021: 55–60. doi: 10.1109/fit53504.2021.00020. [89] ZHONG Xuefeng, JI Fei, CHEN Fangjiong, et al. A new acoustic channel interference model for 3-D underwater acoustic sensor networks and throughput analysis[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(10): 9930–9942. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2020.2990414. [90] 张育芝, 张效民, 王安义, 等. 水声通信网络信道建模与仿真研究进展[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(4): 1249–1261. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.04.002.ZHANG Yuzhi, ZHANG Xiaomin, WANG Anyi, et al. Research progresses on channel modeling and simulation for underwater acoustic communication and networks[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(4): 1249–1261. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.04.002. [91] TOMASI B, TOSO G, CASARI P, et al. Impact of time-varying underwater acoustic channels on the performance of routing protocols[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2013, 38(4): 772–784. doi: 10.1109/joe.2013.2279735. [92] 刘奇佩, 刘琨, 罗逸豪, 等. Bellhop模型在水声网络仿真中的实现和应用[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2024, 32(1): 124–129. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2023-0015.LIU Qipei, LIU Kun, LUO Yihao, et al. Implementation and application of Bellhop model in underwater acoustic network simulation[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2024, 32(1): 124–129. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-3920.2023-0015. -





 下载:
下载:
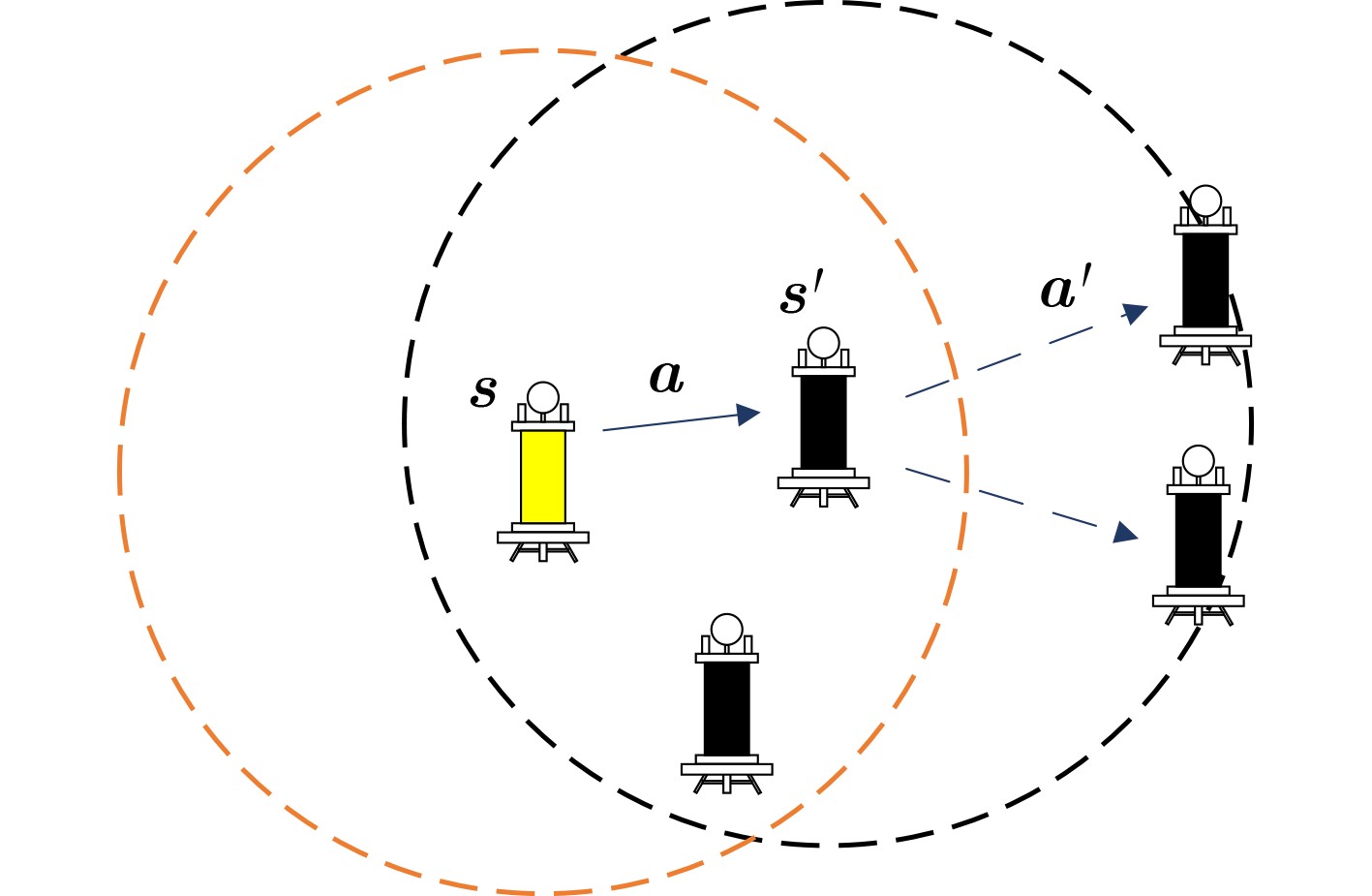
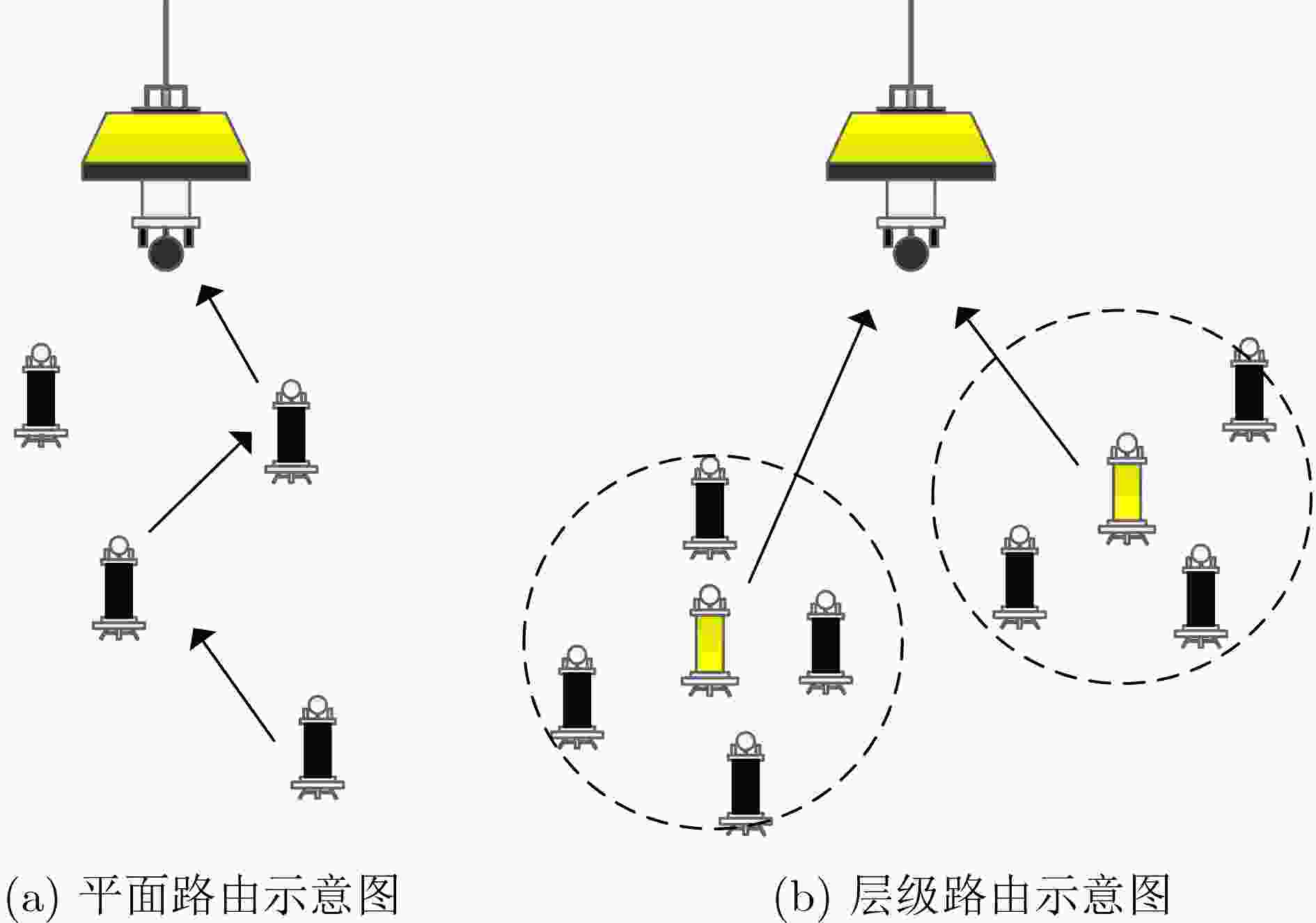
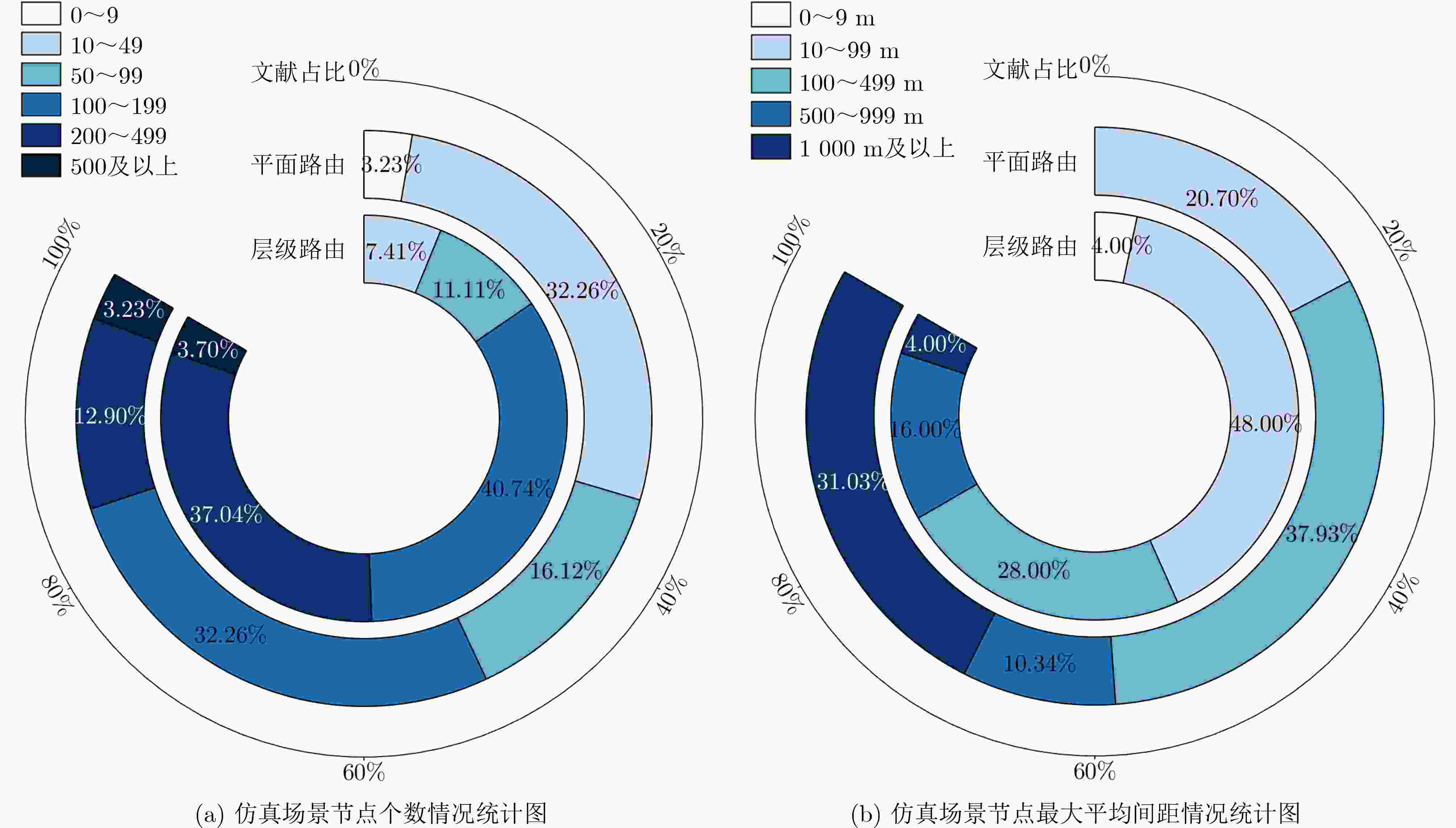


 下载:
下载:
