Locality-optimized Forward-secure Dynamic Searchable Symmetric Encryption
-
摘要: 对称可搜索加密是实现在云存储场景下加密搜索的一项重要原语。动态对称可搜索加密是支持动态增加和删除数据的对称可搜索加密,在多数场景相较静态方案更为实用。对称可搜索加密中局部性指的是搜索时服务器需要进行的非连续存储访问的次数,是影响搜索效率的重要指标之一。然而,动态对称可搜索加密中局部性与前向安全性的要求相矛盾。差的局部性导致了搜索时间随结果数量的简单线性增长,进而严重影响高频关键词的搜索效率。现有针对前向安全动态对称可搜索加密进行局部性优化的方案要么存在对两次搜索之间的更新次数的限制,要么更新效率和读效率较低。该文提出了新的局部性优化方案,能够转换任意符合要求的前向安全动态对称可搜索加密方案为优化局部性的前向安全动态对称可搜索加密方案,同时不损害更新效率和读效率在内的其他重要性能指标。方案基于客户端缓冲和分批打包,打包内同关键词更新可连续读取,有效限制了各关键词的局部性上界。同时,该文设计并使用了安全的打包格式,通过安全证明确保了转换后方案在保证前向安全的同时不会引入额外信息泄露。理论和实验分析证明了该方案在极大提升高频关键词搜索效率的同时,不对更新效率以及其他关键词的搜索效率产生显著的负面影响。Abstract:
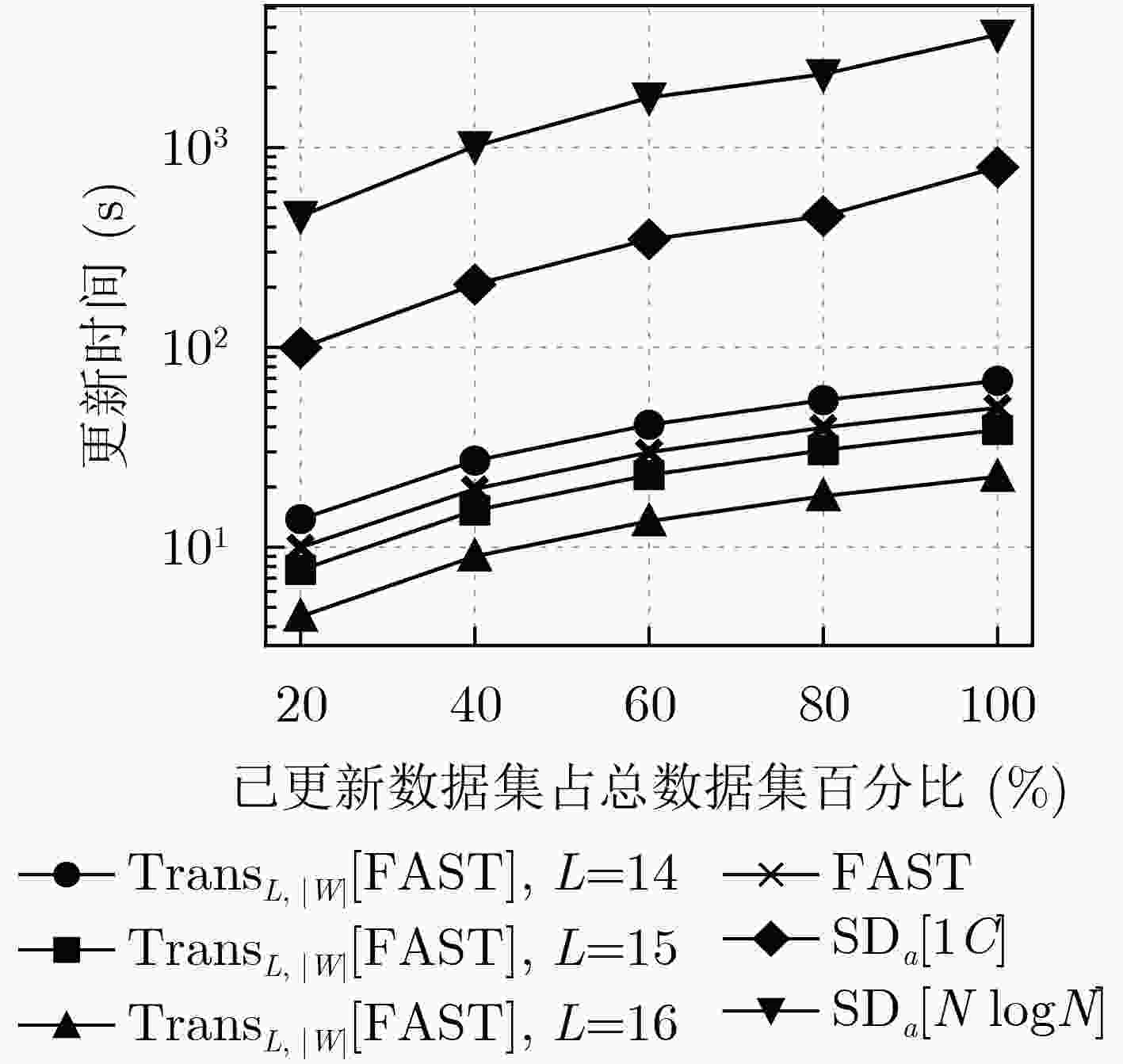
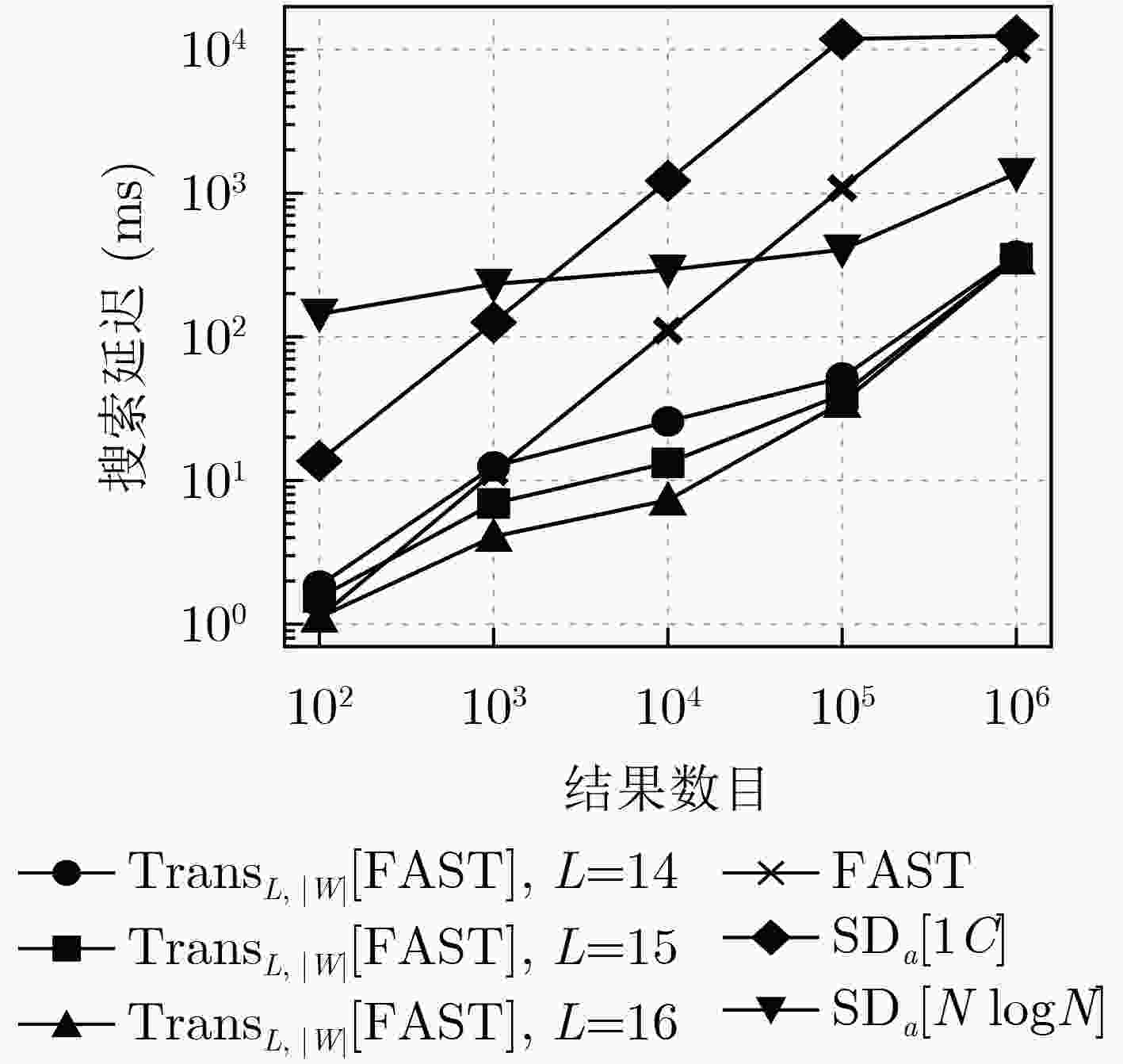
Objective With the rapid development of cloud computing, more individuals and enterprises are outsourcing data storage, raising significant concerns regarding data privacy. Traditional encryption methods preserve confidentiality but render the data unsearchable, severely limiting usability. Searchable Symmetric Encryption (SSE) addresses this limitation by enabling efficient keyword searches over encrypted data, and dynamic SSE further enhances practicality by supporting data updates. However, a critical challenge in dynamic SSE is the trade-off between forward security—ensuring that past queries cannot retrieve results from newly added data—and locality. Locality, defined as the number of non-contiguous storage accesses during a search, is a key metric for I/O efficiency and directly affects search performance. Poor locality causes search latency to increase linearly with keyword frequency, creating a significant performance bottleneck. Existing schemes either constrain the number of updates between searches or degrade update and read efficiency, limiting real-world applicability. This study proposes a novel scheme that transforms existing forward-secure dynamic SSE into locality-optimized variants without compromising key performance metrics such as update and read efficiency. Methods The proposed scheme improves locality by reorganizing SSE updates into batched operations. Instead of uploading each update individually, the client temporarily stores updates in a local buffer. Once a predefined threshold is reached, the accumulated updates are uploaded as a single package. Within each package, updates corresponding to the same keyword are stored contiguously to minimize non-contiguous storage accesses, thereby enhancing locality. The transformed scheme retains the use of the underlying forward-secure dynamic SSE to store essential metadata required for extracting the contents of each package during a search, thereby preserving forward security. However, search operations may reveal the storage positions of updates for some keywords within a package, potentially constraining the inferred distribution of updates for other keywords. To address this issue, a secure packaging algorithm is designed to mitigate such leakage and maintain the overall security of the scheme. Results and Discussion By implementing client-side buffering and batched updating, the proposed scheme transforms compatible forward-secure dynamic SSE schemes into locality-optimized variants. The integration of a secure packaging algorithm into the batching process ensures that forward security is preserved, as confirmed by a formal security proof, without introducing additional information leakage. A comprehensive evaluation is conducted, comparing a typical forward-secure dynamic SSE scheme (referred to as the original scheme), its transformed variants under various buffer sizes, and an existing locality-optimized forward-secure dynamic SSE scheme. Both theoretical and experimental analyses are performed. Theoretical analysis indicates that although the transformed scheme imposes an upper bound on locality, it maintains similar computational complexity to the original scheme in other critical aspects, such as update and read efficiency. Moreover, its update complexity and read performance outperform those of the existing locality-optimized scheme ( Table 1 ). Experimental results yield three main findings. (1) Although client-side buffering requires additional storage, the overall client storage remains comparable to that of the original scheme (Table 2 ). (2) Update times are similar to the original scheme and are reduced to between 1% and 10% of those observed in the existing locality-optimized solution (Fig. 4 ). (3) For low-frequency keywords, search latency moderately increases—by up to 70%—relative to the original scheme. In contrast, for high-frequency keywords, latency is substantially reduced, ranging from 23.1% to 3.5% of that in the original scheme. Overall, the transformed scheme consistently achieves lower search latency than the existing solution (Fig. 5 ).Conclusions This study proposes a novel scheme that transforms forward-secure dynamic SSE into locality-optimized variants through client-side buffering and batched updating, without degrading core performance metrics (e.g., update and read efficiency). A secure packaging algorithm is introduced, and a formal security proof demonstrates that the scheme preserves forward security without incurring additional information leakage. Both theoretical and experimental results show that the scheme significantly improves locality and search efficiency for high-frequency keywords, while maintaining comparable update and read performance for other keywords. A notable limitation is that the scheme requires predefining the total number or an upper bound on different keywords, which restricts flexibility in dynamic environments. Addressing this limitation remains a key direction for future research. Additionally, extending the scheme to operate under malicious server assumptions or to support further security properties, such as backward security, also warrants investigation. -
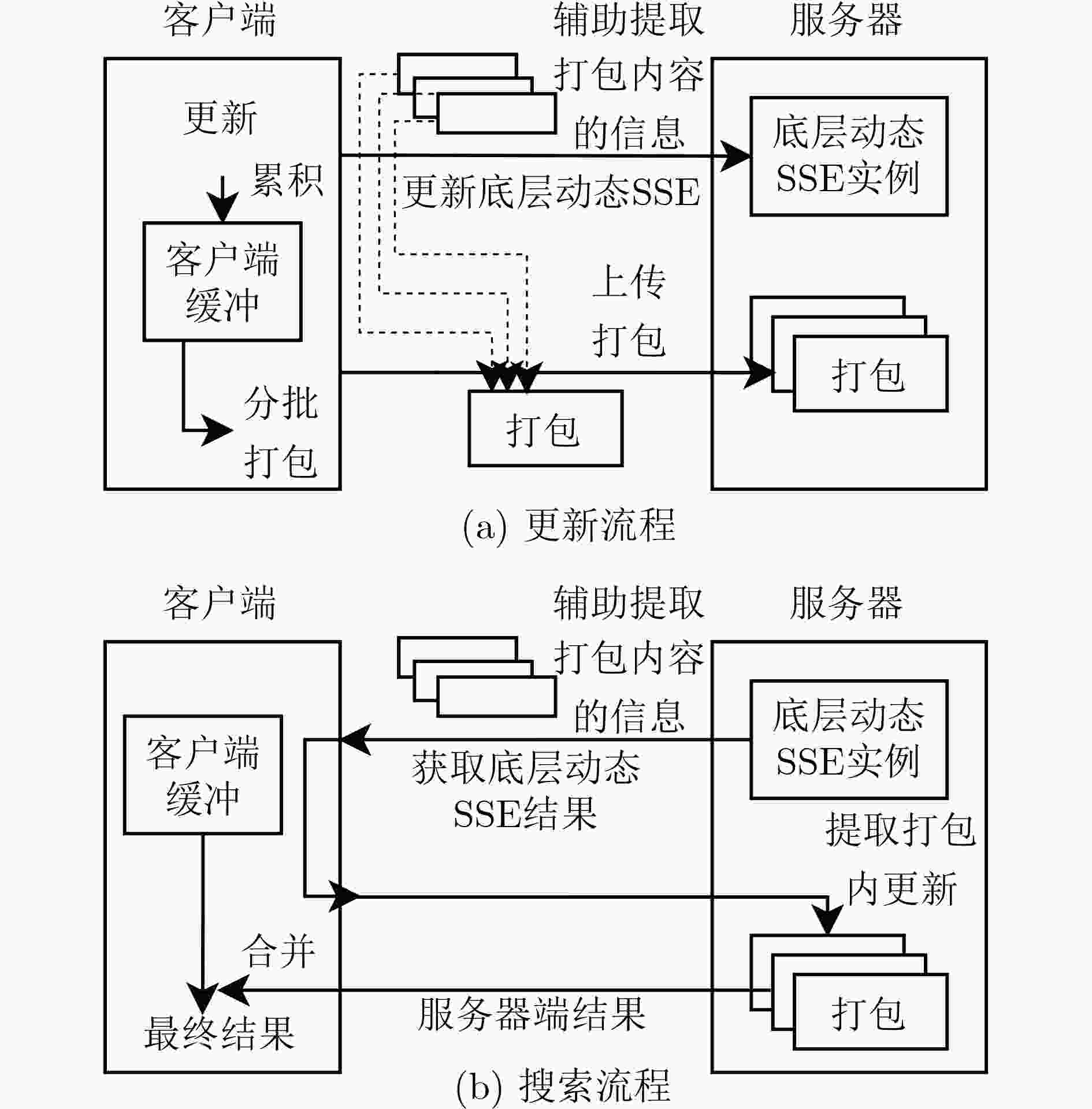
1 初始化$ {\text{Tran}}{{\text{s}}_{L,|W|}}[{\varPi }].{\text{Setup}}(\lambda ; \bot ) $
输入:安全参数$ \lambda $ 输出:客户端输出密钥$ K = {K_{\varPi }} $、状态$ {\text{st}} = (e,{\text{Buffer}},{\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }}) $;
服务器输出加密数据库$ {\text{EDB = (Packs,ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }}) $(1) $ (({K_{\varPi }},{\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }}{\text{);ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }}) \leftarrow {\varPi }.{\text{Setup}}(\lambda ; \bot ) \text{;} $ (2) $ {\text{Buffer}} \leftarrow \varnothing $(关键词到更新列表的映射),$e \leftarrow 0$; (3) $ {\text{Packs}} \leftarrow \langle \rangle $(空列表); (4) 客户端存储密钥$ K = {K_{\varPi }} $、状态$ {\text{st}} = (e,{\text{Buffer}},{\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }}) $,服
务器存储加密数据库$ {\text{EDB = (Packs,ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }}) $。2 更新$ {\text{Tran}}{{\text{s}}_{L,|W|}}[{\varPi }].{\text{Update}}({K_{\varPi }},(e,{\text{Buffer}},{\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }}) $,${\text{id}},w,{\text{op}} $;$({\text{Packs}},{\text{ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }})) $
输入:客户端输入更新的关键词$ w $、文档标识符$ {\text{id}} $、操作符$ {\text{op}} $、密钥$ K = {K_{\varPi }} $、状态$ {\text{st}} = (e,{\text{Buffer}},{\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }}) $;服务器输入加密数据库
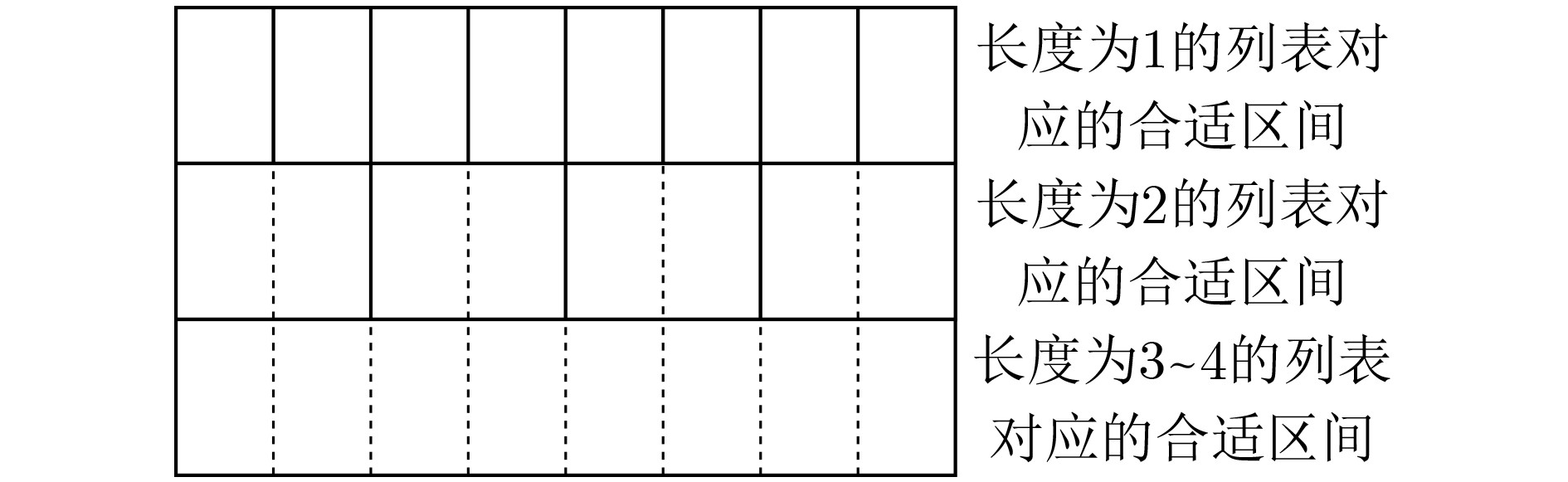
$ {\text{EDB = (Packs,ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }}) $输出:客户端和服务器分别输出可能更新的上述状态和加密数据库客户端执行: (1) $ {\text{Buffer}}[w] \leftarrow {\text{Buffer}}[w]||\langle ({\text{id}},{\text{op}})\rangle \text{;} $ (2) if $\sum\nolimits_{w \in W} {|{\text{Buffer}}[w]|} \lt {2^{L - 1}}$,结束; (3) $e \leftarrow e + 1 , P \leftarrow {\text{InitPack}}(L) \text{;} $ (4) foreach $ w \in \{ w'\mid {\text{Buffer}}[w'] \ne \langle \rangle \} $,设$ {\text{Buffer}}[w] = {\langle ({\text{i}}{{\text{d}}_i},{\text{o}}{{\text{p}}_i})\rangle _i} $: (a) ${t_{e,w}}{\mathop {\leftarrow} \limits^{{S\mkern-10.5mu/}} } {\{ 0,1\} ^\lambda } $; (b) $ (l,r){\mathop {\leftarrow} \limits^{{S\mkern-10.5mu/}} } {\text{SuitableIntervals}}(|{\text{Buffer}}[w]|) \cap {\text{UnusedIntervals}}(P) $,其中$ {\text{UnusedIntervals}}(P) $表示$ P $中在本次算法执行中未被本行选取过 的区间; (c) 设$ (l,r) $在$ {{P}} $中对应的子数组为$ {\text{Arr}} $; (d) for $ j \leftarrow 1 $to$ {2^{l - 1}} $: (i) if $ j \le |{\text{Buffer}}[w]| $, $ {\text{Arr}}[j] \leftarrow H({t_{e,w}}||j) \oplus ({\text{i}}{{\text{d}}_j}||{\text{o}}{{\text{p}}_j}) $;else $ {\text{Arr}}[j] \leftarrow H({t_{e,w}}||j) \oplus \bot $。 (e) $({\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }};{\text{ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }}) \leftarrow {\varPi }.{\text{Update}}({K_{\varPi }},{\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }},e||l||r||{t_{e,w}},w',{\text{add';ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }}) 。 $ (5) $ {\text{Buffer}} \leftarrow \varnothing \text{;} $ (6) 设$ m $为步骤(4)中处理的关键词数; (7) for $ i \leftarrow 1 $ to $ |W| - m $: (a) $ ({\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }};{\text{ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }}) \leftarrow {\varPi }.{\text{Update}}({K_{\varPi }},{\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }}, \bot ,'{\text{dummy}}','{\text{add}}';{\text{ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }}) $。其中$ {{'{\mathrm{dummy}}'}} $表示一个弃用关键词。 (8) 生成随机比特串填充$ P $中$ {\text{UnusedIntervals}}(P) $对应的部分; (9) 将$ P $发送给服务器。服务器执行: (10) $ {\text{Packs}} \leftarrow {\text{Packs}}||\langle P\rangle $。 3 搜索$ {\text{Tran}}{{\text{s}}_{L,|W|}}[{\varPi }].{\text{Search}}({K_{\varPi }},(e,{\text{Buffer}},{\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }}),w;({\text{Packs}},{\text{ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }})) $
输入:客户端输入搜索的关键词$ w $,密钥$ K = {K_{\varPi }} $、状态$ {\text{st}} = (e,{\text{Buffer}},{\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }}) $;服务器输入加密数据库$ {\text{EDB = (Packs,ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }}) $ 输出:客户端输出搜索结果即对应关键词$ w $的文档标识符集合$ {\text{DB}}(w) $、可能更新的上述状态;服务器输出可能更新的上述加密数据库客户
端执行:(1) $(({\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }},{\text{ID}}');{\text{ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }}) \leftarrow {\varPi }.{\text{Search}}({K_{\varPi }},{\text{s}}{{\text{t}}_{\varPi }},w;{\text{ED}}{{\text{B}}_{\varPi }}) $ (2) 将$ {\text{ID}}' $发送给服务器。服务器执行: (3) 设$ {\text{ID}}' ={\{ ({e_i}'||{l_i}'||{r_i}'||t{'_{{e_i},w}})\} _{i = 1,2,\cdots,b}} $,将其按$ {e_i}' $正序排列,得到$ {\langle ({e_i},{l_i},{r_i},{t_{{e_i},w}})\rangle _{i = 1,2,\cdots,b}} $; (4) ${\text{ID}} \leftarrow \varnothing \text{;}$ (5) for $i \leftarrow 1$ to $|b|$,设$ ({l_i},{r_i}) $在$ {\text{Packs}}[{e_i}] $中对应的子数组为$ {\text{Ar}}{{\text{r}}_i} $: (a) for $j \leftarrow 1$ to $|{\text{Ar}}{{\text{r}}_i}|$: (i) if $ {\text{Ar}}{{\text{r}}_i}[j] \oplus H({t_{{e_i},w}}||j) = \bot $,break; (ii) 设$ {\text{id||op}} = {\text{Ar}}{{\text{r}}_i}[j] \oplus H({t_{{e_i},w}}||j) $; (iii) if $ {{{\mathrm{op }}= ' {\mathrm{add}}'}} $, $ {\text{ID}} \leftarrow {\text{ID}} \cup \{ {\text{id}}\} $;else $ {\text{ID}} \leftarrow {\text{ID}} \setminus \{ {\text{id}}\} $。 (6) 将$ {\text{ID}} $返回给客户端。客户端执行: (7) for $i = 1$ to $|{\text{Buffer}}[w]|$,设$ {\text{(id,op)}} = {\text{Buffer}}[w][i] $; (a) if $ {\text{op =}} ' {\mathrm{add}}' $, $ {\text{ID}} \leftarrow {\text{ID}} \cup \{ {\text{id}}\} $;else $ {\text{ID}} \leftarrow {\text{ID}} \setminus \{ {\text{id}}\} $ (8) 输出$ {\text{ID}} $为最终搜索结果。 表 1 复杂度对比
方案 搜索复杂度 局部性 读效率 更新复杂度 客户端存储 ${\text{FAST}}$[4] $O(|{\text{DB}}(w)|)$ $O(|{\text{DB}}(w)|)$ $O(1)$ $O(1)$ $O(|W|)$ $ {\text{Tran}}{{\text{s}}_{L,|W|}}{\text{[FAST]}} $ $O(|{\text{DB}}(w)|)$ $O(\min (|{\text{DB}}(w)|,N/|W|))$ $O(1)$ $O(\log_2 |W|)$ $O(|W|)$ ${\text{S}}{{\text{D}}_a}[1C]$/${\text{L-S}}{{\text{D}}_d}[1C]$[14] $O(|{\text{DB}}(w)|{\log _2}N)$ $O({\log _2}N)$ $O({\log _2}N)$ $ O({\log _2}N) $/$ O(\log _2^2N) $ $O({\log _2}N)$ ${\text{S}}{{\text{D}}_a}[N{\text{log}}N]$/${\text{L-S}}{{\text{D}}_d}[N{\text{log}} N]$[14] $O(|{\text{DB}}(w)| + {\log _2}N)$ $O({\log _2}N)$ $O({\log _2}N)$ $ O(\log _2^2N) $/$O(\log _2^3N)$ $O({\log _2}N)$ 表 2 客户端存储对比
方案 客户端存储大小 ${\text{FAST}}$[4] 390.6 kB ${\text{Tran}}{{\text{s}}_{L,|W|}}{\text{[FAST]}},L = 14$ 618.9 kB ${\text{Tran}}{{\text{s}}_{L,|W|}}{\text{[FAST]}},L = 15$ 690.9 kB ${\text{Tran}}{{\text{s}}_{L,|W|}}{\text{[FAST]}},L = 16$ 834.9 kB $ {\text{S}}{{\text{D}}_a}[1C] $[14] 128 B ${\text{S}}{{\text{D}}_a}[N\log N]$[14] 128 B -
[1] 肖人毅. 云计算中数据隐私保护研究进展[J]. 通信学报, 2014, 35(12): 168–177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2014.12.020.XIAO Renyi. Survey of privacy preserving data queries in cloud computing[J]. Journal on Communications, 2014, 35(12): 168–177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436x.2014.12.020. [2] LI Feng, MA Jianfeng, MIAO Yinbin, et al. A survey on searchable symmetric encryption[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2024, 56(5): 119. doi: 10.1145/3617991. [3] DENNING P J. The locality principle[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2005, 48(7): 19–24. doi: 10.1145/1070838.1070856. [4] SONG Xiangfu, DONG Changyu, YUAN Dandan, et al. Forward private searchable symmetric encryption with optimized I/O efficiency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2020, 17(5): 912–927. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2018.2822294. [5] BOST R, MINAUD B, and OHRIMENKO O. Forward and backward private searchable encryption from constrained cryptographic primitives[C]. The 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 1465–1482. doi: 10.1145/3133956.3133980. [6] CASH D and TESSARO S. The locality of searchable symmetric encryption[C]. The 33rd International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques Advances in Cryptology, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014: 351–368. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-55220-5_20. [7] ASHAROV G, NAOR M, SEGEV G, et al. Searchable symmetric encryption: Optimal locality in linear space via two-dimensional balanced allocations[C]. The 48th ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Cambridge, USA, 2016: 1101–1114. doi: 10.1145/2897518.2897562. [8] DEMERTZIS I and PAPAMANTHOU C. Fast searchable encryption with tunable locality[C]. Proceedings of 2017 ACM International Conference on Management of Data, Chicago, USA, 2017: 1053–1067. doi: 10.1145/3035918.3064057. [9] ASHAROV G, SEGEV G, and SHAHAF I. Tight tradeoffs in searchable symmetric encryption[C]. Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 2018: 407–436. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-96884-1_14. [10] BOST R. ∑oφoς: Forward secure searchable encryption[C]. 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 2016: 1143–1154. doi: 10.1145/2976749.2978303. [11] STEFANOV E, PAPAMANTHOU C, and SHI E. Practical dynamic searchable encryption with small leakage[C]. The 21st Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2014. doi: 10.14722/ndss.2014.23298. [12] ZHANG Yupeng, KATZ J, and PAPAMANTHOU C. All your queries are belong to us: The power of File-Injection attacks on searchable encryption[C]. The 25th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, Austin, USA, 2016: 707–720. [13] POWERS D M W. Applications and explanations of Zipf’s law[C]. The Joint Conferences on New Methods in Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning, Sydney, Australia, 1998: 151–160. [14] MONDAL P, CHAMANI J G, DEMERTZIS I, et al. I/O-efficient dynamic searchable encryption meets forward & backward privacy[C]. The 33rd USENIX Security Symposium, Philadelphia, USA, 2024: 2527–2544. [15] SONG D X, WAGNER D, and PERRIG A. Practical techniques for searches on encrypted data[C]. 2000 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, Berkeley, USA, 2000: 44–55. doi: 10.1109/SECPRI.2000.848445. [16] CURTMOLA R, GARAY J, KAMARA S, et al. Searchable symmetric encryption: Improved definitions and efficient constructions[C]. The 13th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Alexandria, USA, 2006: 79–88. doi: 10.1145/1180405.1180417. [17] LI Feng, MA Jianfeng, MIAO Yinbin, et al. Beyond volume pattern: Storage-efficient Boolean searchable symmetric encryption with suppressed leakage[C]. The 28th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security Computer Security, Hague, Netherlands, 2024: 126–146. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-50594-2_7. [18] HALTIWANGER J and HOANG T. Exploiting update leakage in searchable symmetric encryption[C]. The 17th ACM Conference on Data and Application Security and Privacy, Porto, Portugal, 2024: 115–126. doi: 10.1145/3626232.3653260. [19] ZHAO Chenbin, DU Ruiying, HE Kun, et al. Efficient verifiable dynamic searchable symmetric encryption with forward and backward security[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(3): 2633–2645. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3470772. [20] LI Dexin, ZHAO Xingwen, LI Hui, et al. Volume-hiding multidimensional verifiable dynamic searchable symmetric encryption scheme for cloud computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(23): 37437–37451. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3408812. [21] ZUO Cong, LAI Shangqi, SUN Shifeng, et al. Searchable encryption for conjunctive queries with extended forward and backward privacy[J]. Proceedings on Privacy Enhancing Technologies, 2025, 2025(1): 440–455. doi: 10.56553/popets-2025-0024. [22] MIERS I and MOHASSEL P. IO-DSSE: Scaling dynamic searchable encryption to millions of indexes by improving locality[C]. The 24th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2017. doi: 10.14722/ndss.2017.23394. [23] MINAUD B and REICHLE M. Dynamic local searchable symmetric encryption[C]. The 42nd Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 2022: 91–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-15985-5_4. [24] XU Peng, SUSILO W, WANG Wei, et al. ROSE: Robust searchable encryption with forward and backward security[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 1115–1130. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2022.3155977. [25] DOU Haochen, DAN Zhenwu, XU Peng, et al. Dynamic searchable symmetric encryption with strong security and robustness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2024, 19: 2370–2384. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2024.3350330. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
