FSG: Feature-level Semantic-aware Guidance for multi-modal Image Fusion Algorithm
-
摘要: 在自动驾驶领域,红外和可见光的融合图像因其能够提供显著目标和丰富的纹理细节而备受关注。然而现有的大部分融合算法单方面关注融合图像的视觉质量和评价指标,而忽略了高级视觉任务的需求。另外,虽然一些融合方法尝试结合高级视觉任务,但是其效果受限于语义先验和融合任务之间的交互不足且没有考虑到不同特征差异性的影响。因此,该文提出了特征级语义感知引导的多模态图像融合算法,使语义先验知识与融合任务进行充分交互,提高融合结果在后续的分割任务中的性能。对于语义特征和融合图像特征两者的差异性,提出了双特征交互模块,以实现不同特征的充分交互和选择。对于红外和可见光两种不同模态特征的差异性,提出了多源空间注意力融合模块,以实现不同模态信息的有效集成和互补。该文在3个公共数据集上进行了实验,结果表明该方法的融合结果优于其他方法且泛化能力较好,而且在各种融合算法联合分割任务的性能比较实验中也表明了该方法在分割任务中的优越性。Abstract:
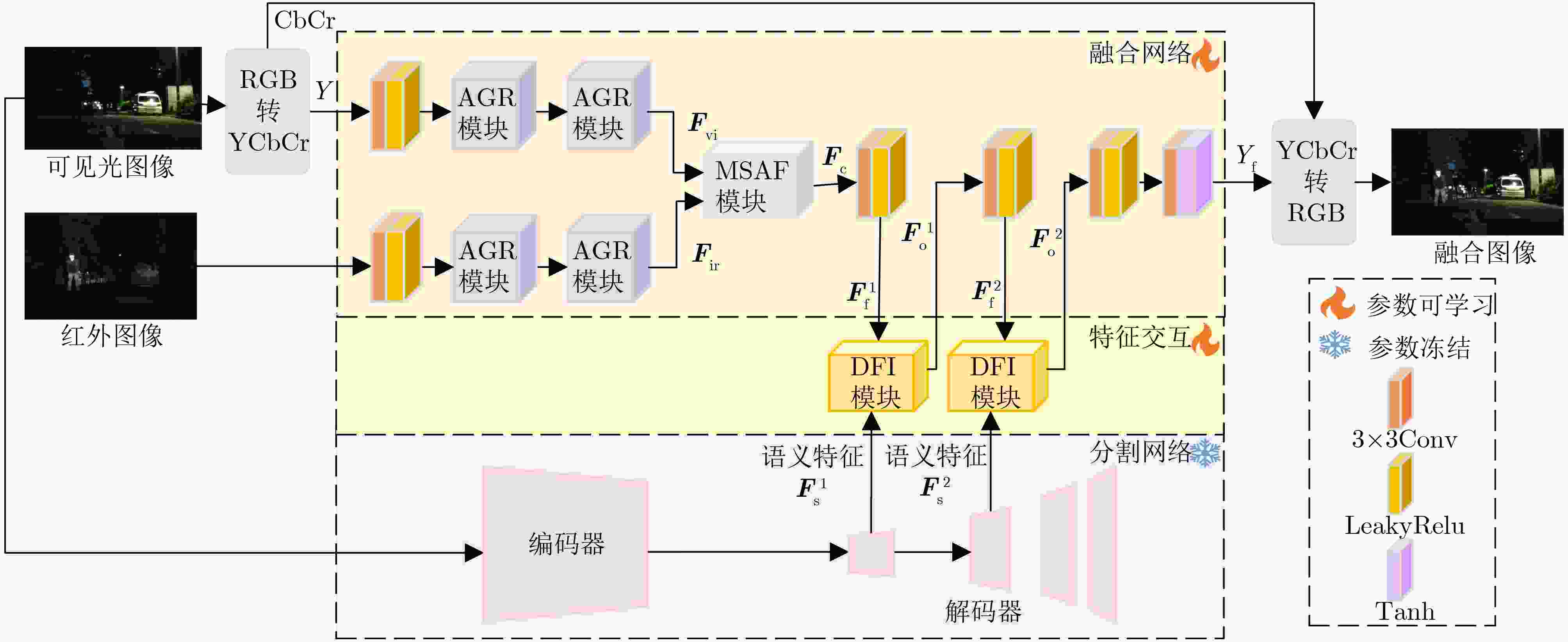
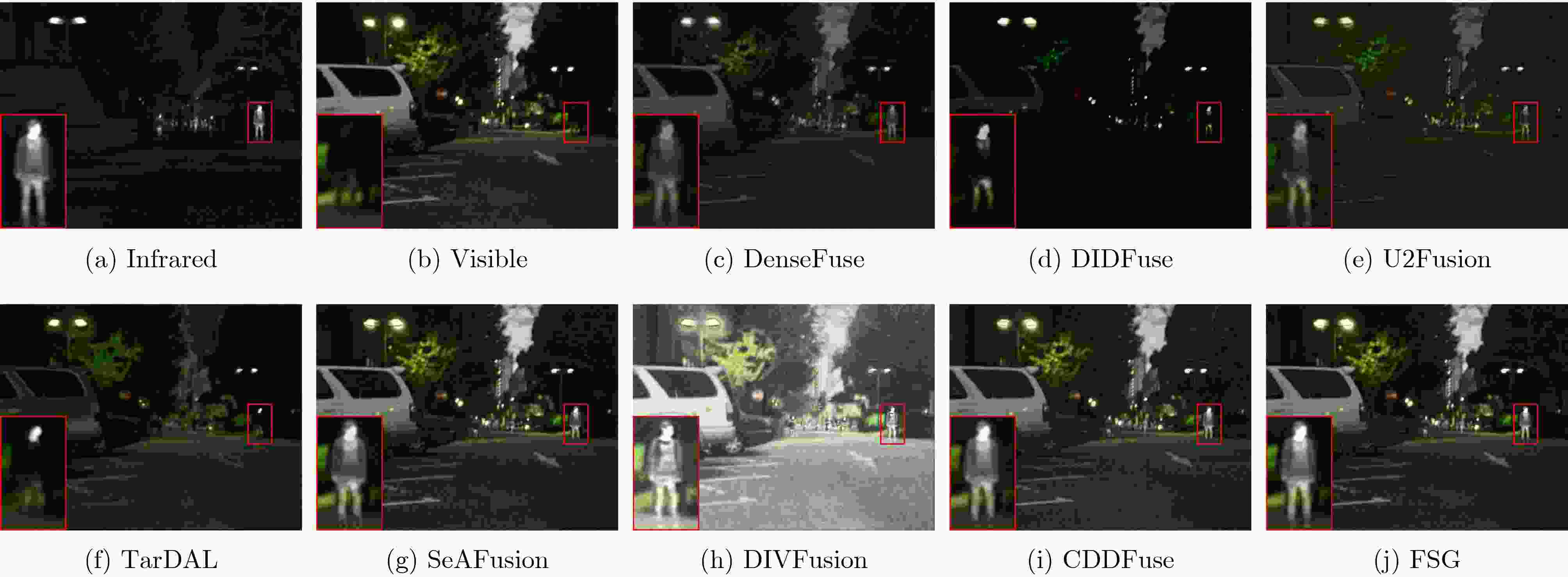
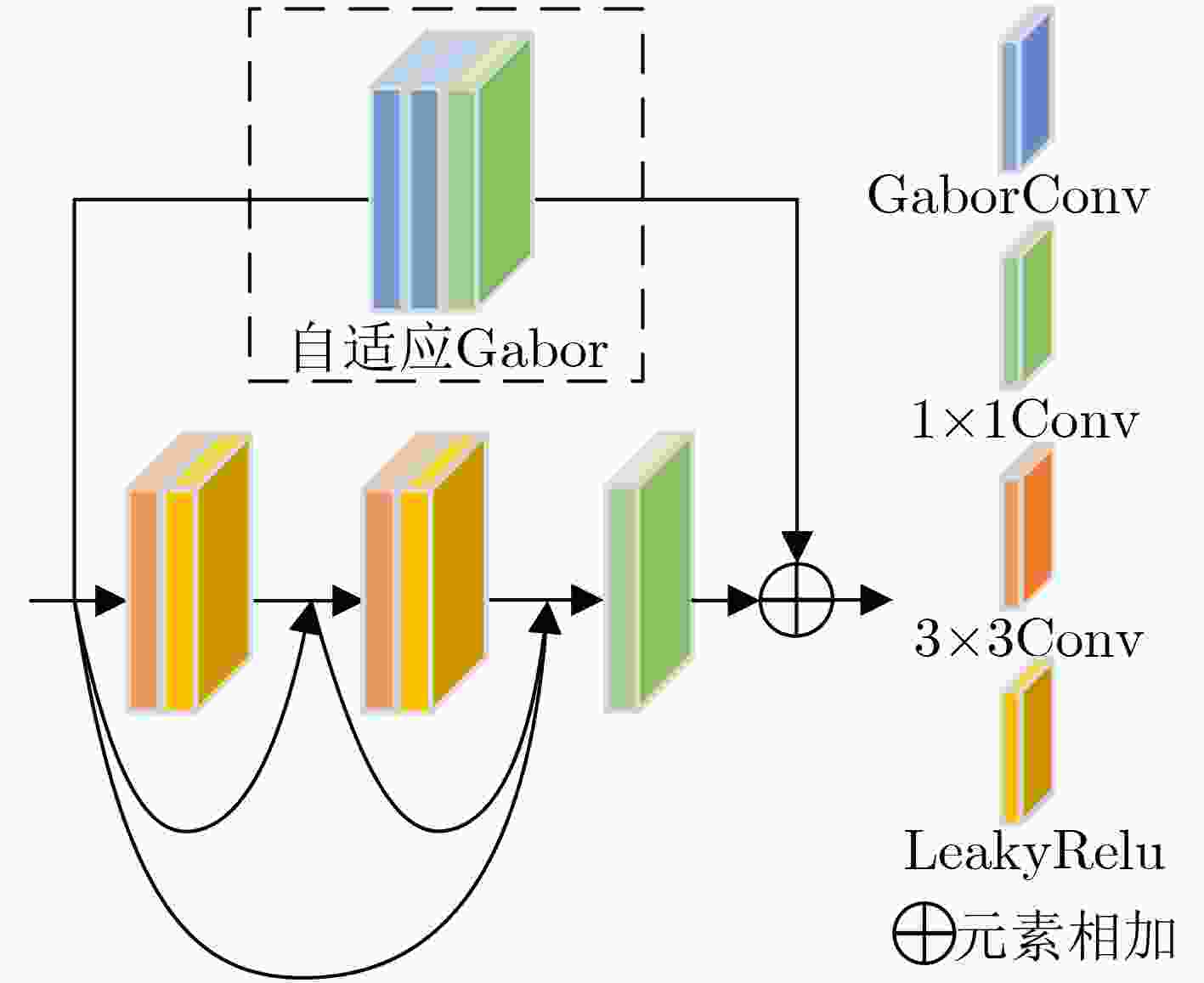
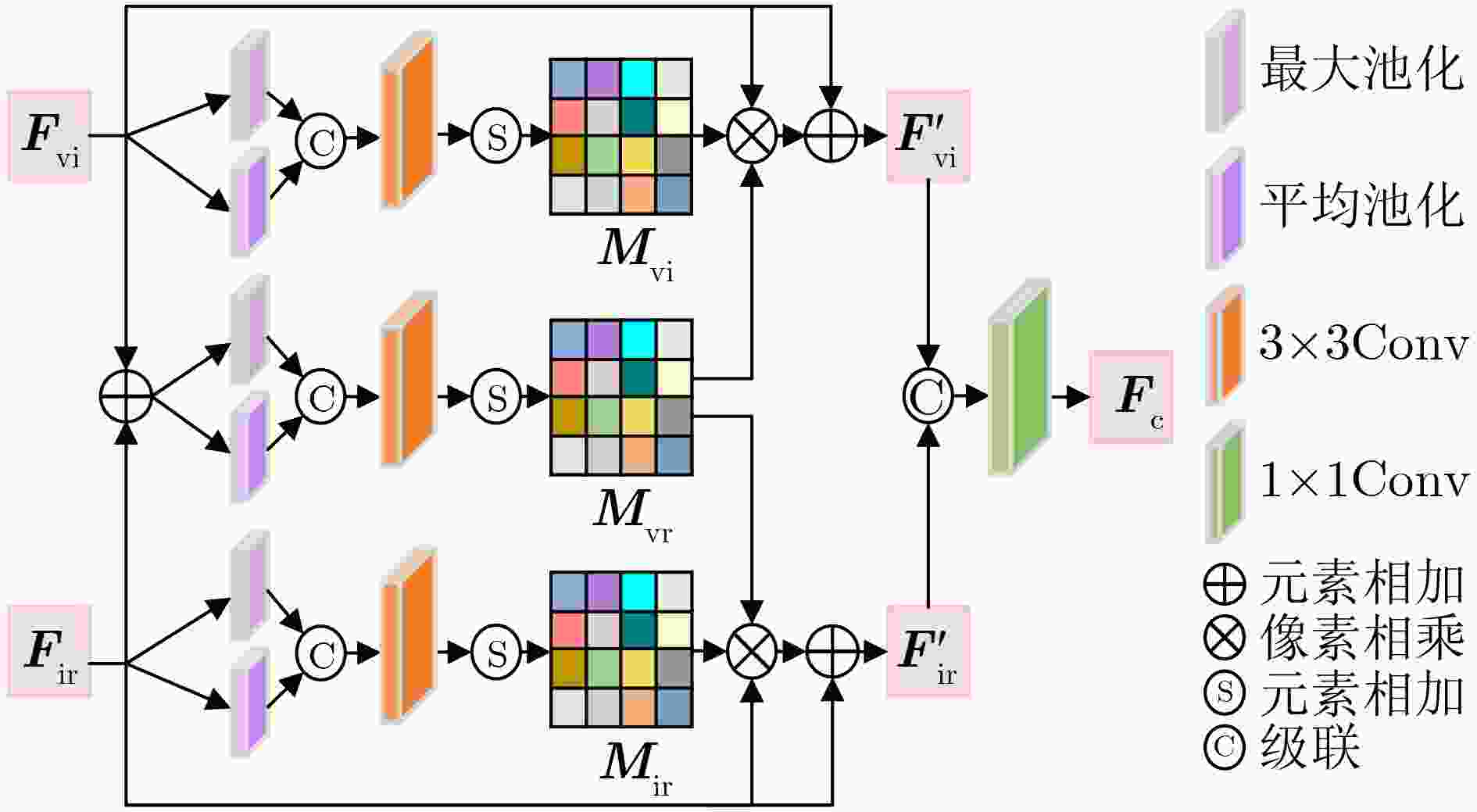
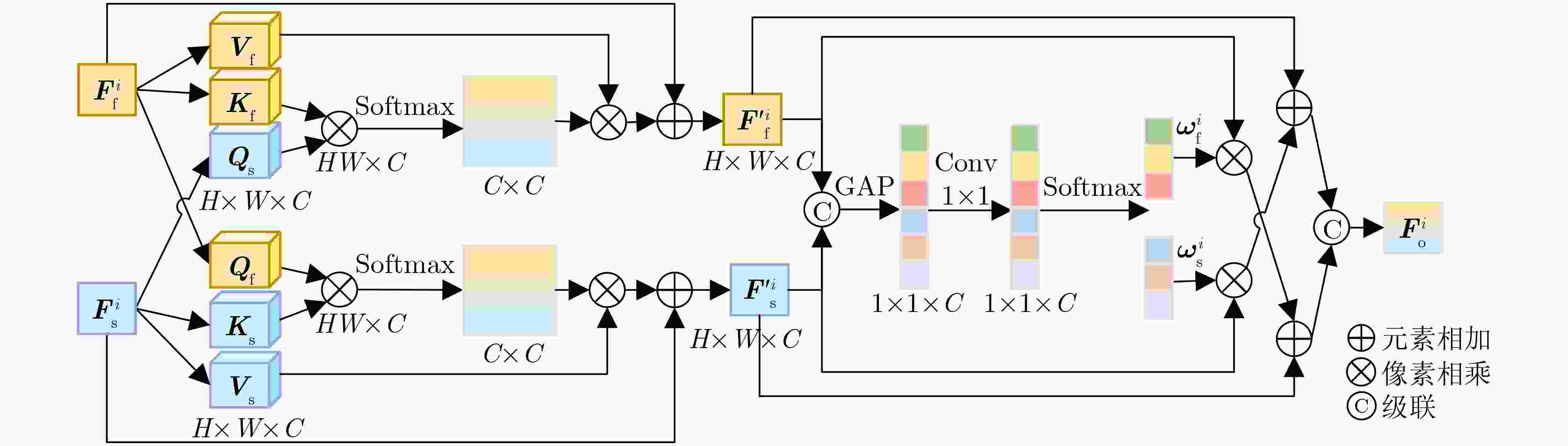
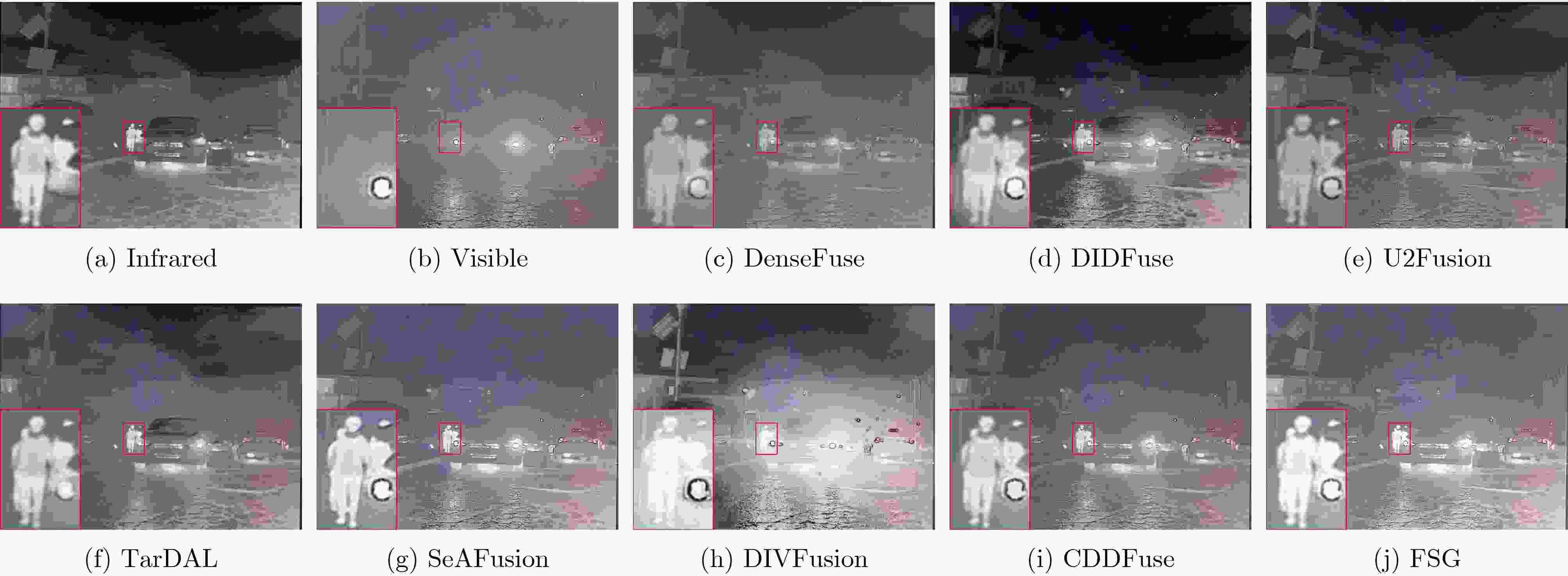
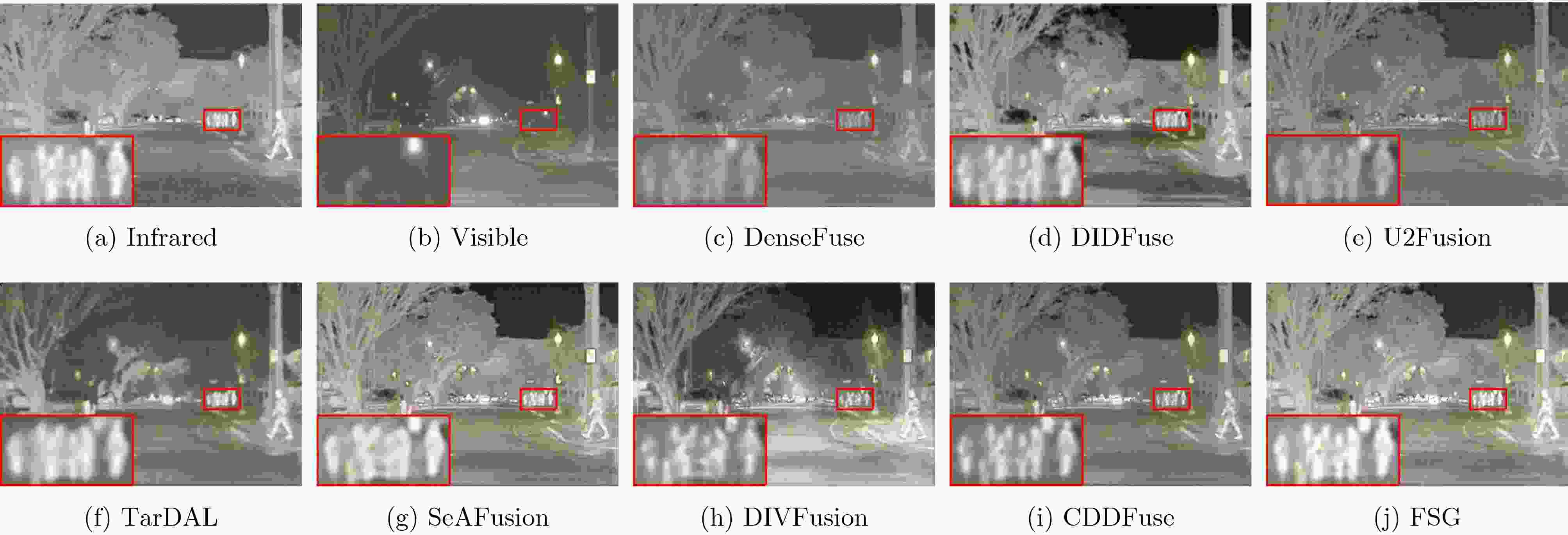
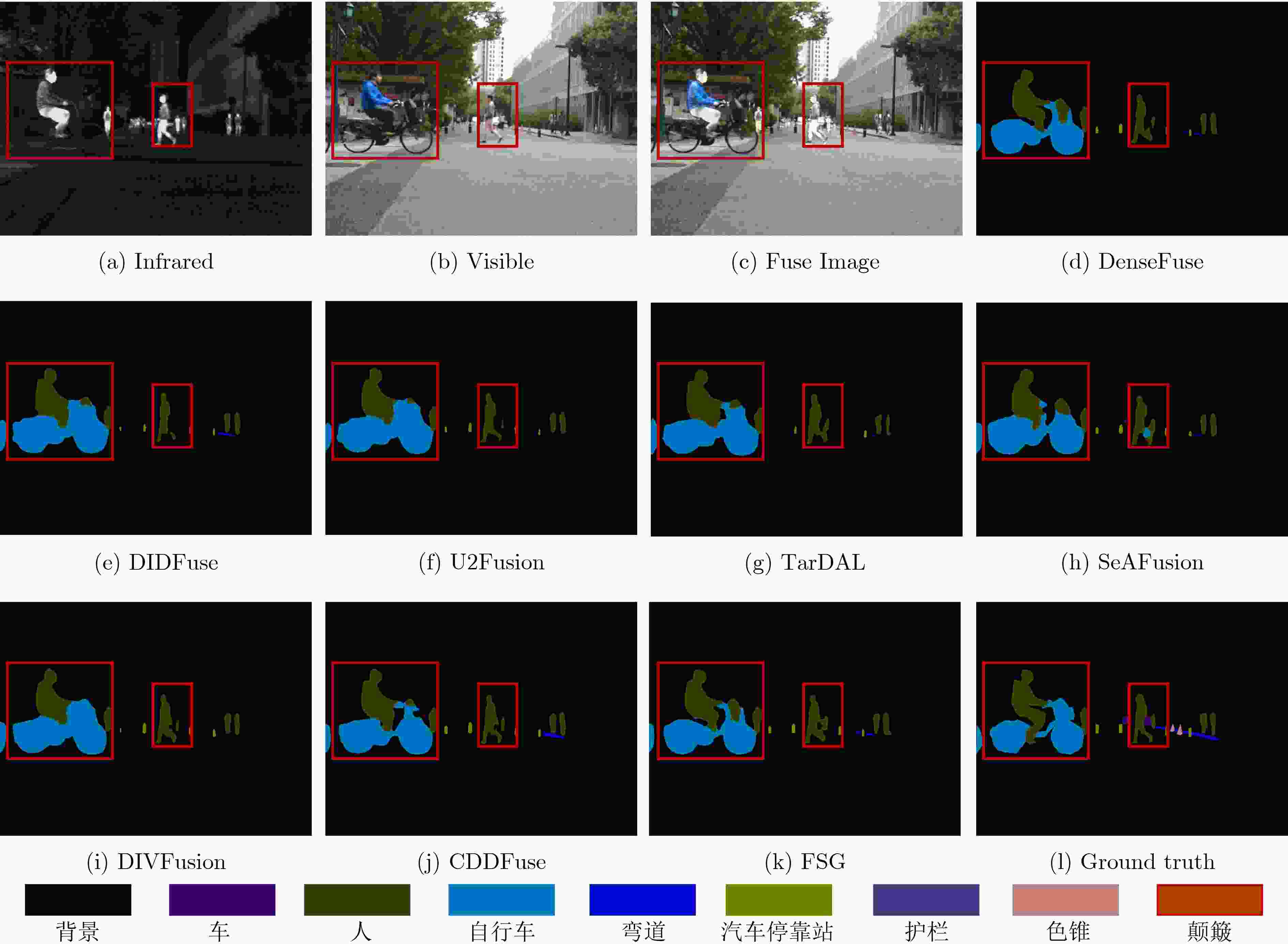
Objective Multimodal vision techniques offer greater advantages than unimodal ones in autonomous driving scenarios. Fused images from multiple modalities enhance salient radiation information from targets while preserving background texture and detail. Furthermore, such fused images improve the performance of downstream visual tasks, i.e., semantic segmentation, compared with visible-light images alone, thereby enhancing the decision accuracy of automated driving systems. However, most existing fusion algorithms prioritize visual quality and standard evaluation metrics, often overlooking the requirements of downstream tasks. Although some approaches attempt to integrate task-specific guidance, they are constrained by weak interaction between semantic priors and fusion processes, and fail to address cross-modal feature variability. To address these limitations, this study proposes a multimodal image fusion algorithm, termed Feature-level Semantic-aware Guidance (FSG), which leverages feature-level semantic information from segmentation networks to guide the fusion process. The proposed method aims to enhance the utility of fused images in advanced vision tasks by strengthening the alignment between semantic understanding and feature integration. Methods The proposed algorithm adopts a parallel fusion framework integrating a fusion network and a segmentation network. Feature-level semantic prior knowledge from the segmentation network guides the fusion process, aiming to enhance the semantic richness of the fused image and improve performance in downstream visual tasks. The overall architecture comprises a fusion network, a segmentation network, and a feature interaction mechanism connecting the two. Infrared and visible images serve as inputs to the fusion network, whereas only visible images, which are rich in texture and detail, are used as inputs to the segmentation network. The fusion network uses a dual-branch structure for modality-specific feature extraction, with each branch containing two Adaptive Gabor convolution Residual (AGR) modules. A Multimodal Spatial Attention Fusion (MSAF) module is incorporated to effectively integrate features from different modalities. In the reconstruction phase, semantic features from the segmentation network are combined with image features from the fusion network via a Dual Feature Interaction (DFI) module, enhancing semantic representation before generating the final fused image. Results and Discussions This study includes fusion experiments and joint segmentation task experiments. For the fusion experiments, the proposed method is compared with seven state-of-the-art algorithms: DenseFuse, DIDFuse, U2Fusion, TarDal, SeAFusion, DIVFusion, and CDDFuse, across three datasets: MFNet, M3FD, and RoadScene. Both subjective and objective evaluations are conducted. For subjective evaluation, the fused images generated by each method are visually compared. For objective evaluation, six metrics are employed: Mutual Information (MI), Visual Information Fidelity (VIF), Average Gradient (AG), Sum of Correlation Differences (SCD), Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM), and Gradient-based Similarity Measurement (QAB/F). The results show that the proposed method performs consistently well across all datasets, effectively preserves complementary information from infrared and visible images, and achieves superior scores on all evaluation metrics. In the joint segmentation experiments, comparisons are made on the MFNet dataset. Subjective evaluation is presented through semantic segmentation visualizations, and objective evaluation uses Intersection over Union (IoU) and mean IoU (mIoU) metrics. The segmentation results produced by the proposed method more closely resemble ground truth labels and achieve the highest or second-highest IoU scores across all classes. Overall, the proposed method not only yields improved visual fusion results but also demonstrates clear advantages in downstream segmentation performance. Conclusions This study proposes an FSG strategy for multimodal image fusion networks, designed to fully leverage semantic information to improve the utility of fused images in downstream visual tasks. The method accounts for the variability among heterogeneous features and integrates the segmentation and fusion networks into a unified framework. By incorporating feature-level semantic information, the approach enhances the quality of the fused images and strengthens their performance in segmentation tasks. The proposed DFI module serves as a bridge between the segmentation and fusion networks, enabling effective interaction and selection of semantic and image features. This reduces the influence of feature variability and enriches the semantic content of the fusion results. In addition, the proposed MSAF module promotes the complementarity and integration of features from infrared and visible modalities while mitigating the disparity between them. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method not only achieves superior visual fusion quality but also outperforms existing methods in joint segmentation performance. -
Key words:
- Image fusion /
- Joint segmentation task /
- Semantic awareness /
- Feature-level guidance
-
表 1 MFNet数据集上的融合结果的评价指标结果
方法 MI VIF AG SCD QAB/F SSIM DenseFuse 2.648 6 0.704 1 2.058 1 1.251 1 0.364 0 0.929 8 DIDFuse 2.052 5 0.372 4 2.110 4 1.088 2 0.203 8 0.838 6 U2Fusion 1.824 5 0.466 1 2.290 4 1.079 5 0.342 5 0.917 4 TarDAL 2.199 5 0.494 2 1.715 8 0.696 9 0.171 4 0.790 5 SeAFuison 3.743 5 0.829 6 3.705 2 1.534 7 0.607 7 0.790 5 DIVFusion 2.394 1 0.797 0 4.770 5 1.197 2 0.340 0 0.839 2 CDDFusion 4.893 8 0.889 2 3.333 1 1.489 7 0.671 3 0.964 7 FSG 4.724 9 1.000 1 3.763 2 1.701 2 0.672 5 0.978 9 表 2 M3FD数据集上的融合结果的评价指标结果
方法 MI VIF AG SCD QAB/F SSIM DenseFuse 2.933 8 0.675 7 2.611 2 1.497 6 0.370 7 0.924 1 DIDFuse 3.109 1 0.890 0 4.791 1 1.784 6 0.494 5 0.944 9 U2Fusion 2.806 8 0.723 3 3.912 1 1.580 3 0.537 2 0.966 5 TarDAL 3.569 7 0.746 6 2.601 9 1.286 3 0.290 4 0.873 0 SeAFuison 3.603 7 0.816 0 5.202 4 1.555 2 0.582 9 0.926 9 DIVFusion 2.789 6 1.016 0 5.306 2 1.537 7 0.428 2 0.884 5 CDDFusion 3.863 1 0.832 4 4.018 9 1.551 5 0.593 9 0.954 0 FSG 3.975 6 0.871 0 4.944 3 1.630 4 0.618 1 0.961 8 表 3 RoadScene数据集上的融合结果的评价指标结果
方法 MI VIF AG SCD QAB/F SSIM DenseFuse 3.105 3 0.748 6 2.950 2 1.169 5 0.415 2 0.906 2 DIDFuse 3.280 4 0.845 4 4.912 3 1.748 0 0.487 6 0.918 1 U2Fusion 2.906 2 0.738 2 4.218 5 1.089 9 0.530 8 0.945 1 TarDAL 3.416 3 0.794 9 3.594 1 1.359 2 0.397 0 0.848 4 SeAFuison 2.832 3 0.767 6 5.787 4 1.392 0 0.400 1 0.740 4 DIVFusion 2.968 6 0.793 1 4.394 7 1.412 2 0.336 9 0.773 2 CDDFusion 3.182 2 0.820 7 4.523 7 1.421 2 0.499 4 0.915 2 FSG 3.189 9 0.855 1 5.085 8 1.547 4 0.557 1 0.925 4 表 4 MFNet数据集上分割性能的评价指标比较,评价指标为IoU和mIoU (%)
背景 车 人 自行车 弯道 汽车停靠站 护栏 色锥 颠簸 mIoU Infrared 98.39 89.94 73.45 69.99 56.88 70.73 58.99 58.00 72.21 72.06 Visible 98.48 91.23 66.31 72.93 58.99 75.68 80.29 66.26 76.22 76.27 DenseFuse 98.68 92.06 75.97 72.84 61.47 78.40 80.80 67.50 79.60 78.59 DIDFuse 98.47 90.55 74.18 70.33 53.18 73.43 78.18 61.02 76.29 75.07 U2Fusion 98.66 91.56 75.9 72.72 59.87 77.52 84.42 67.05 77.55 78.36 TarDAL 98.47 90.70 71.67 70.44 55.15 74.77 80.98 62.17 76.02 75.60 SeAFuison 98.70 92.20 76.40 72.33 60.68 78.73 81.89 67.56 82.23 78.97 DIVFusion 98.56 91.52 74.51 72.04 57.38 74.74 76.25 64.84 73.80 75.96 CDDFuse 98.67 91.54 76.15 75.29 61.02 76.92 82.17 67.28 77.87 78.55 FSG 98.73 92.11 77.10 73.59 63.39 79.21 82.33 67.80 80.63 79.43 表 5 消融实验分割评价指标比较,评价指标为IoU和mIoU (%)
语义特征 DFI 模块 MSAF 模块 背景 车 人 自行车 弯道 汽车停靠站 护栏 色锥 颠簸 mIoU × × × 98.65 91.87 75.46 72.10 58.85 77.66 79.90 66.52 76.63 77.52 × × √ 98.63 91.58 75.49 71.86 60.04 77.22 81.94 66.38 79.72 78.10 √ × √ 98.71 91.99 76.95 72.78 63.02 78.68 81.94 68.01 80.63 79.19 √ √ × 98.68 92.05 75.88 72.26 60.43 78.31 80.90 67.30 79.11 78.32 √ √ √ 98.73 92.11 77.10 73.59 63.39 79.21 82.33 67.80 80.63 79.43 -
[1] LI Hui and WU Xiaojun. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(5): 2614–2623. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2887342. [2] ZHAO Zixiang, XU Shuang, ZHANG Chunxia, et al. DIDFuse: Deep image decomposition for infrared and visible image fusion[C]. The Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 2020: 970–976. doi: 10.24963/ijcai.2020/135. [3] XU Han, MA Jiayi, JIANG Junjun, et al. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(1): 502–518. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3012548. [4] TANG Linfeng, XIANG Xinyu, ZHANG Hao, et al. DIVFusion: Darkness-free infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 91: 477–493. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.10.034. [5] ZHAO Zixiang, BAI Haowen, ZHANG Jiangshe, et al. CDDFuse: Correlation-driven dual-branch feature decomposition for multi-modality image fusion[C]. The 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 5906–5916. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00572. [6] 杨莘, 田立凡, 梁佳明, 等. 改进双路径生成对抗网络的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(8): 3012–3021. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220819.YANG Shen, TIAN Lifan, LIANG Jiaming, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on improved dual path generation adversarial network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(8): 3012–3021. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220819. [7] LIU Xiangzeng, GAO Haojie, MIAO Qiguang, et al. MFST: Multi-modal feature self-adaptive transformer for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(13): 3233. doi: 10.3390/rs14133233. [8] LIU Qiao, PI Jiatian, GAO Peng, et al. STFNet: Self-supervised transformer for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2024, 8(2): 1513–1526. doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2024.3352490. [9] LIU Jinyuan, FAN Xin, HUANG Zhanbo, et al. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection[C]. The 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 5792–5801. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00571. [10] TANG Linfeng, YUAN Jiteng, and MA Jiayi. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 82: 28–42. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.12.004. [11] SUN Ke, XIAO Bin, LIU Dong, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5686–5696. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00584. [12] CORDTS M, OMRAN M, RAMOS S, et al. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 3213–3223. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.350. [13] HA Qishen, WATANABE K, KARASAWA T, et al. MFNet: Towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes[C]. 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, Canada, 2017: 5108-5115. doi: 10.1109/IROS.2017.8206396. [14] XU Han, MA Jiayi, LE Zhuliang, et al. FusionDN: A unified densely connected network for image fusion[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 12484–12491. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6936. [15] QU Guihong, ZHANG Dali, and YAN Pingfan. Information measure for performance of image fusion[J]. Electronics Letters, 2002, 38(7): 313–315. doi: 10.1049/el:20020212. [16] HAN Yu, CAI Yunze, CAO Yin, et al. A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity[J]. Information Fusion, 2013, 14(2): 127–135. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2011.08.002. [17] CUI Guangmang, FENG Huajun, XU Zhihai, et al. Detail preserved fusion of visible and infrared images using regional saliency extraction and multi-scale image decomposition[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 341: 199–209. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2014.12.032. [18] ASLANTAS V and BENDES E. A new image quality metric for image fusion: The sum of the correlations of differences[J]. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2015, 69(12): 1890–1896. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2015.09.004. [19] WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861. [20] BOBAN B and VLADIMIR P. Objective image fusion performance measures[J]. Vojnotehnički Glasnik, 2008, 56(2): 181–193. doi: 10.5937/vojtehg0802181B. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
