Resource Allocation for RIS-aided Cross-Model Communications
-
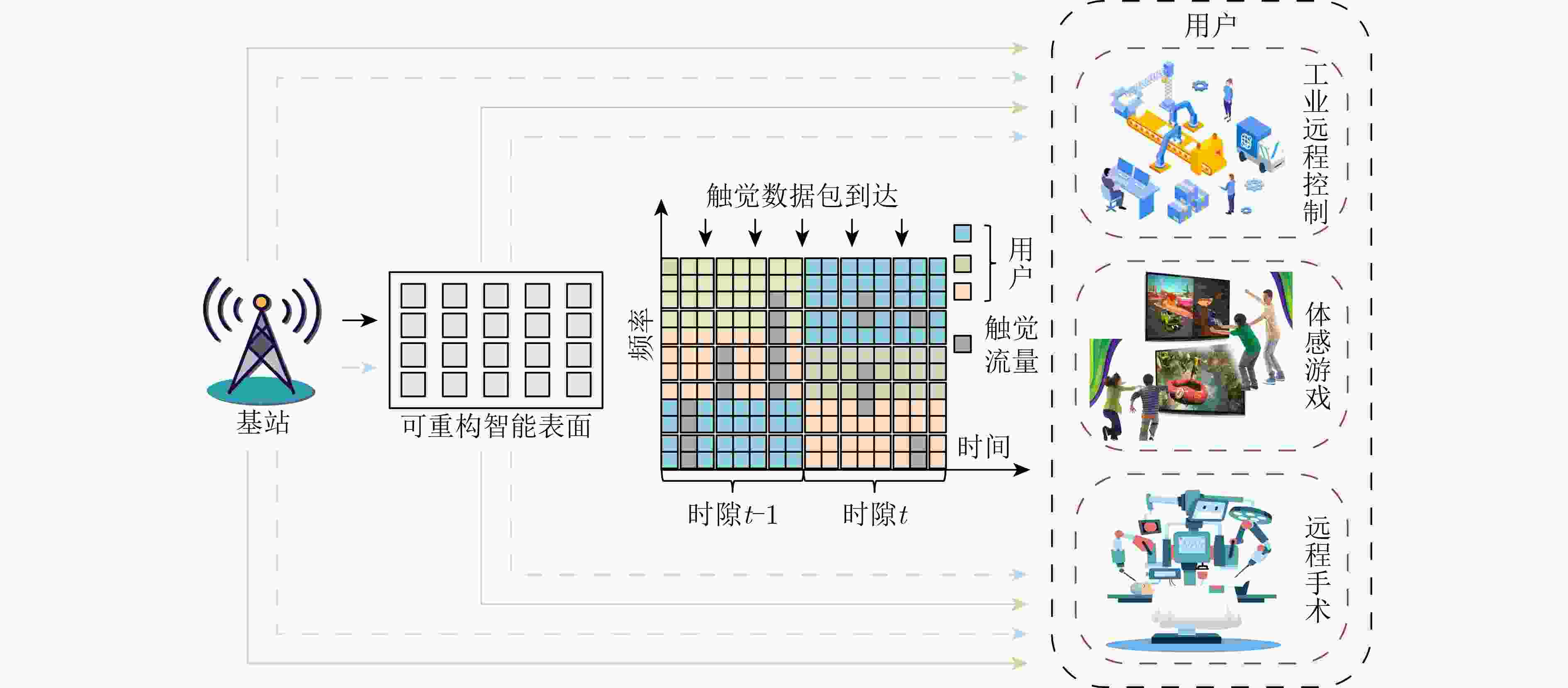
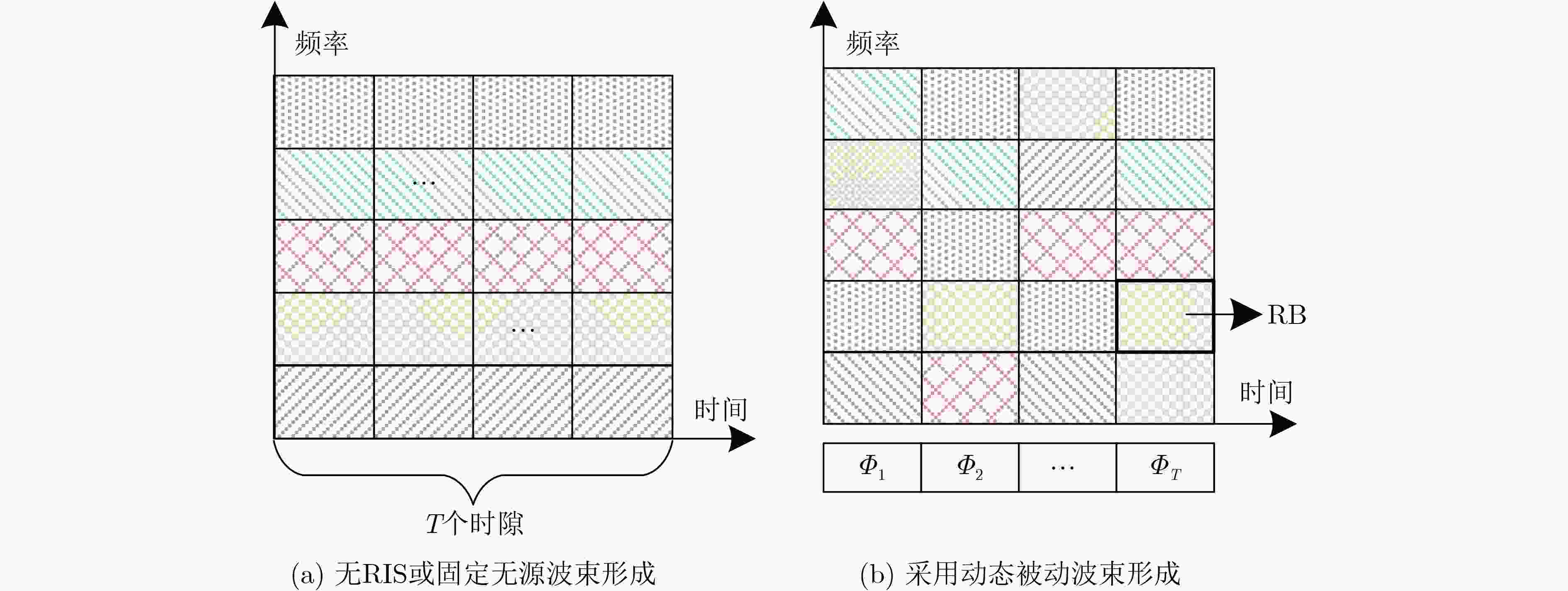
摘要: 针对视频和触觉业务共存的跨模态业务场景,该文构建了可重构智能表面(RIS)辅助的共存网络切片系统,用以提高视频业务和触觉业务的传输速率和可靠性。同时,为了有效降低触觉业务通过穿孔带给视频业务的资源损耗,提出了动态被动波束赋形方案,允许RIS在不同时隙进行动态调整。基于上述方案,该文在确保触觉业务传输的时延和可靠性满足约束的同时,构建最大化视频业务传输速率的优化问题,以满足跨模态业务共存需求,实现资源的合理分配。为求解此优化问题,该文将其建模为一个马尔可夫决策过程(MDP),通过深度确定性策略梯度(DDPG)算法来进行视频数据和触觉数据传输资源的联合优化。仿真结果显示,与现有方案相比,所提方案具有一定的优越性,在保证传输触觉业务可靠性的前提下,提高了约66.67%的视频业务和速率。Abstract:
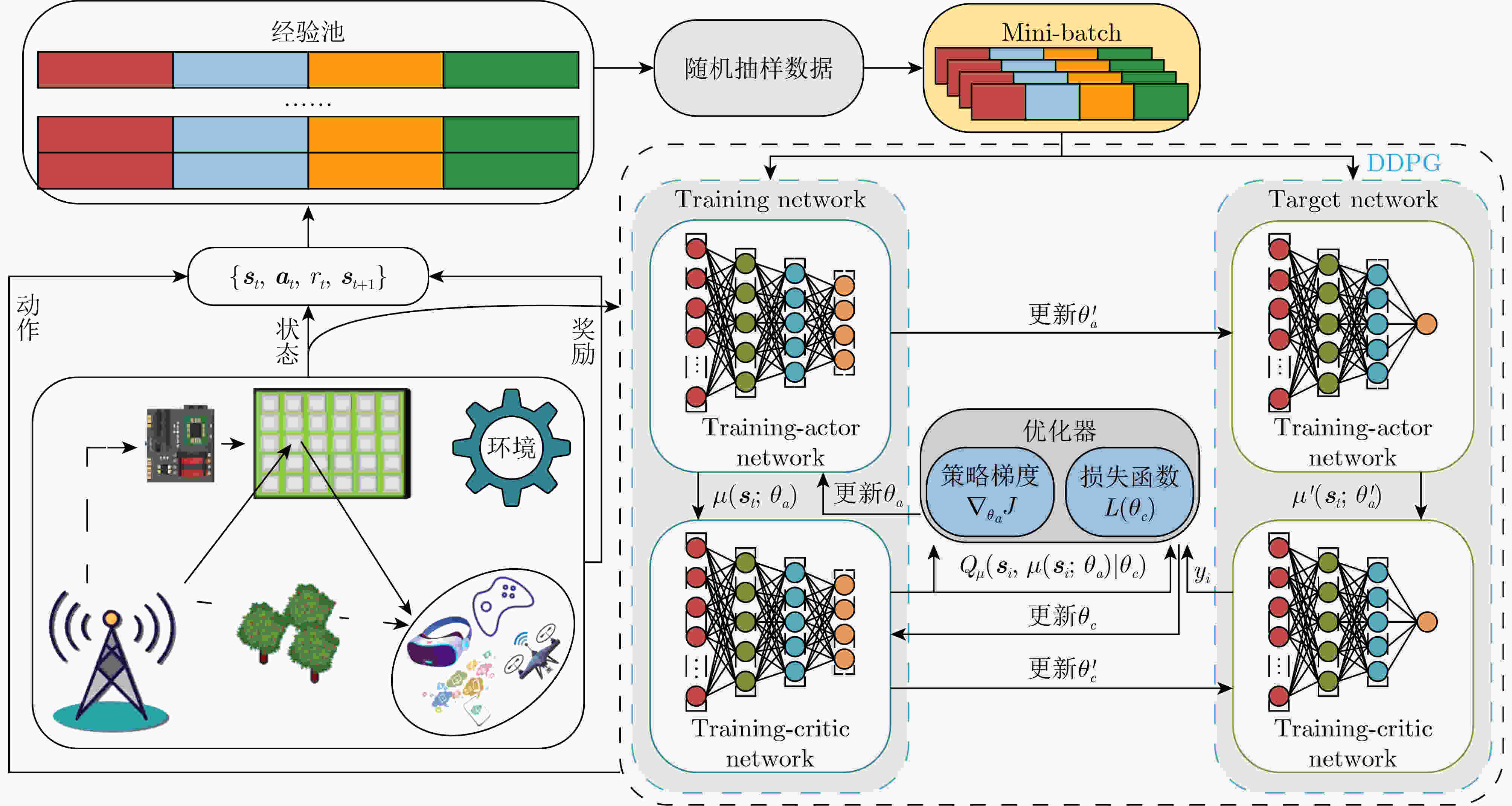
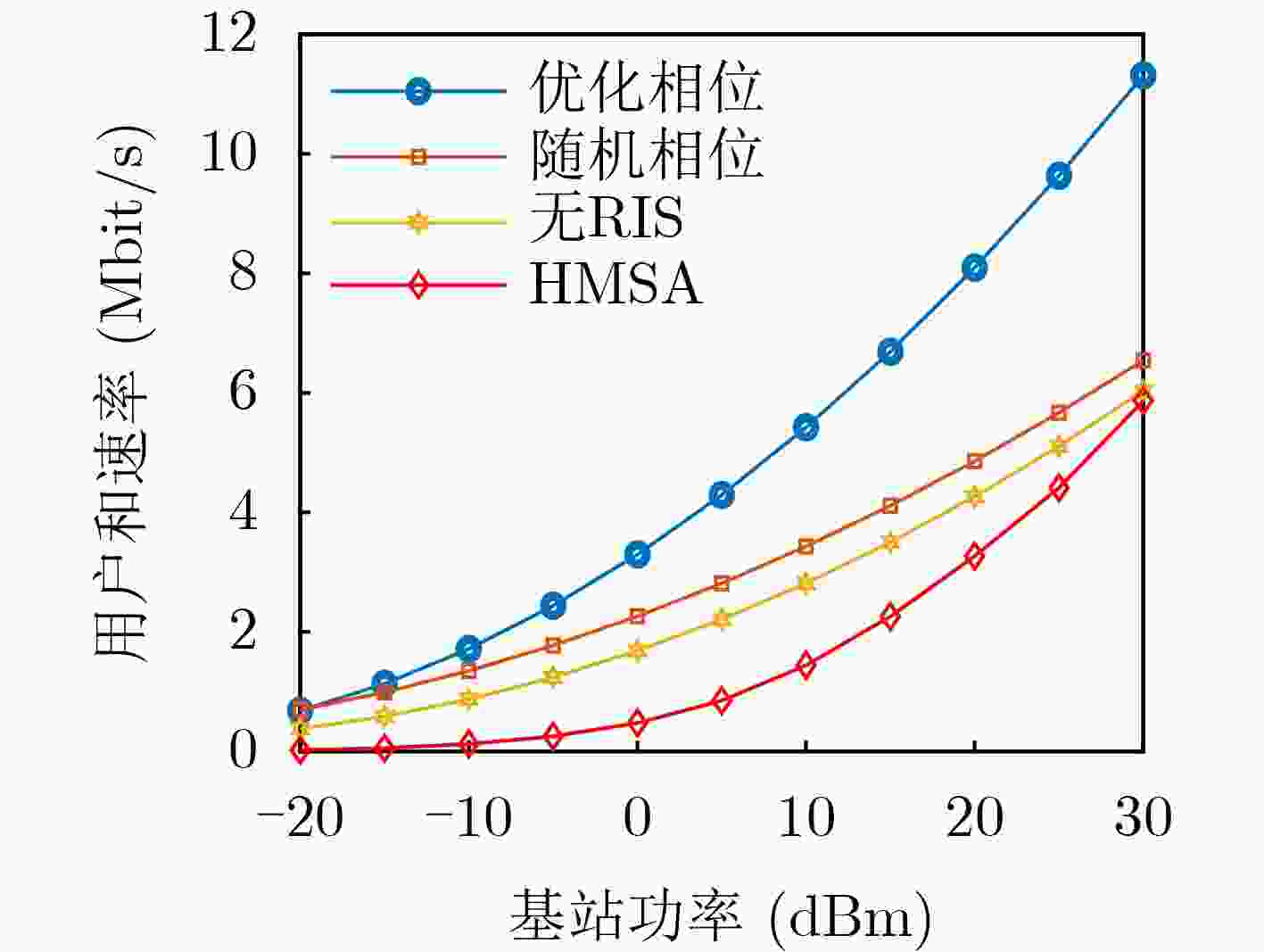
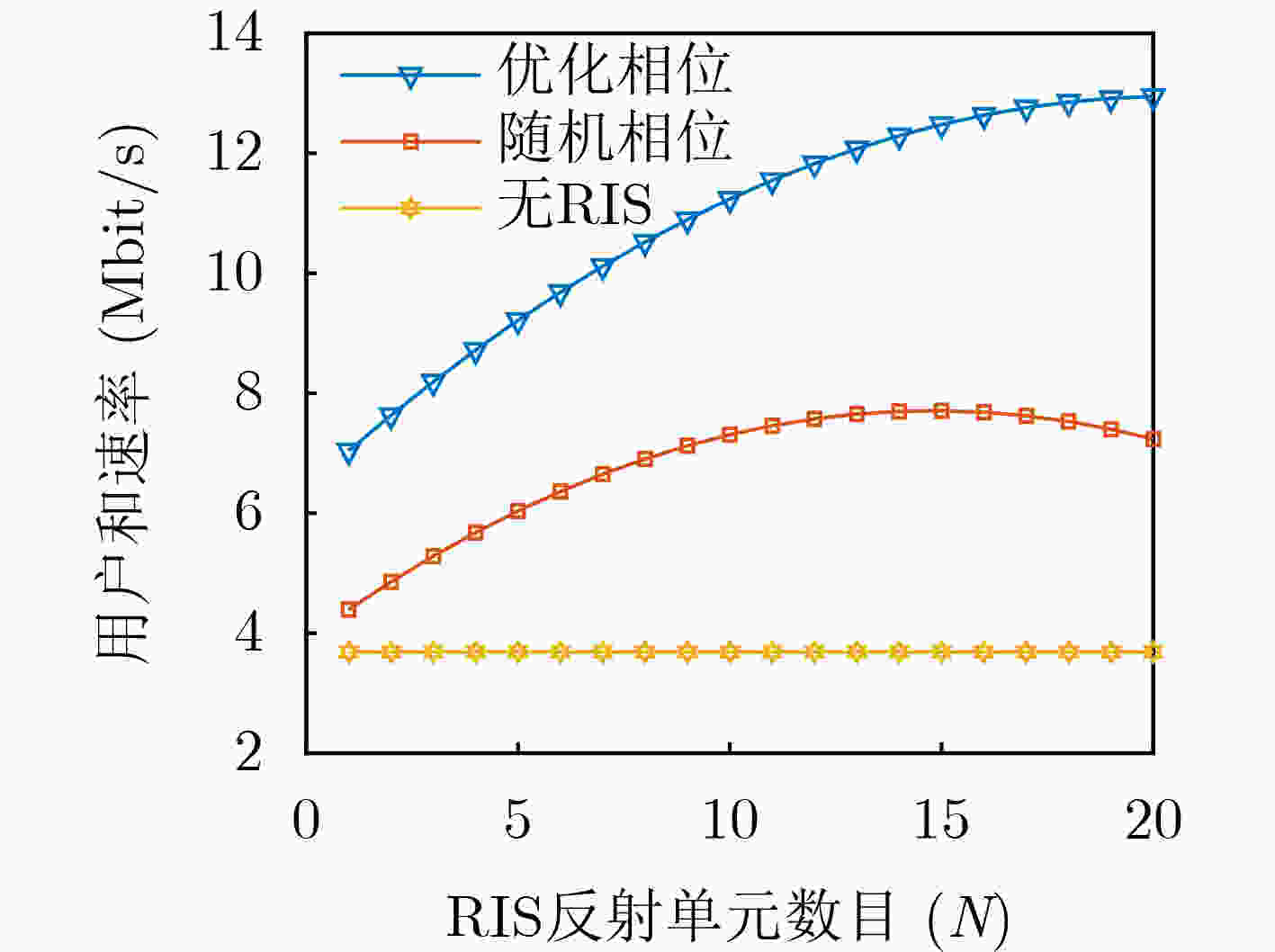
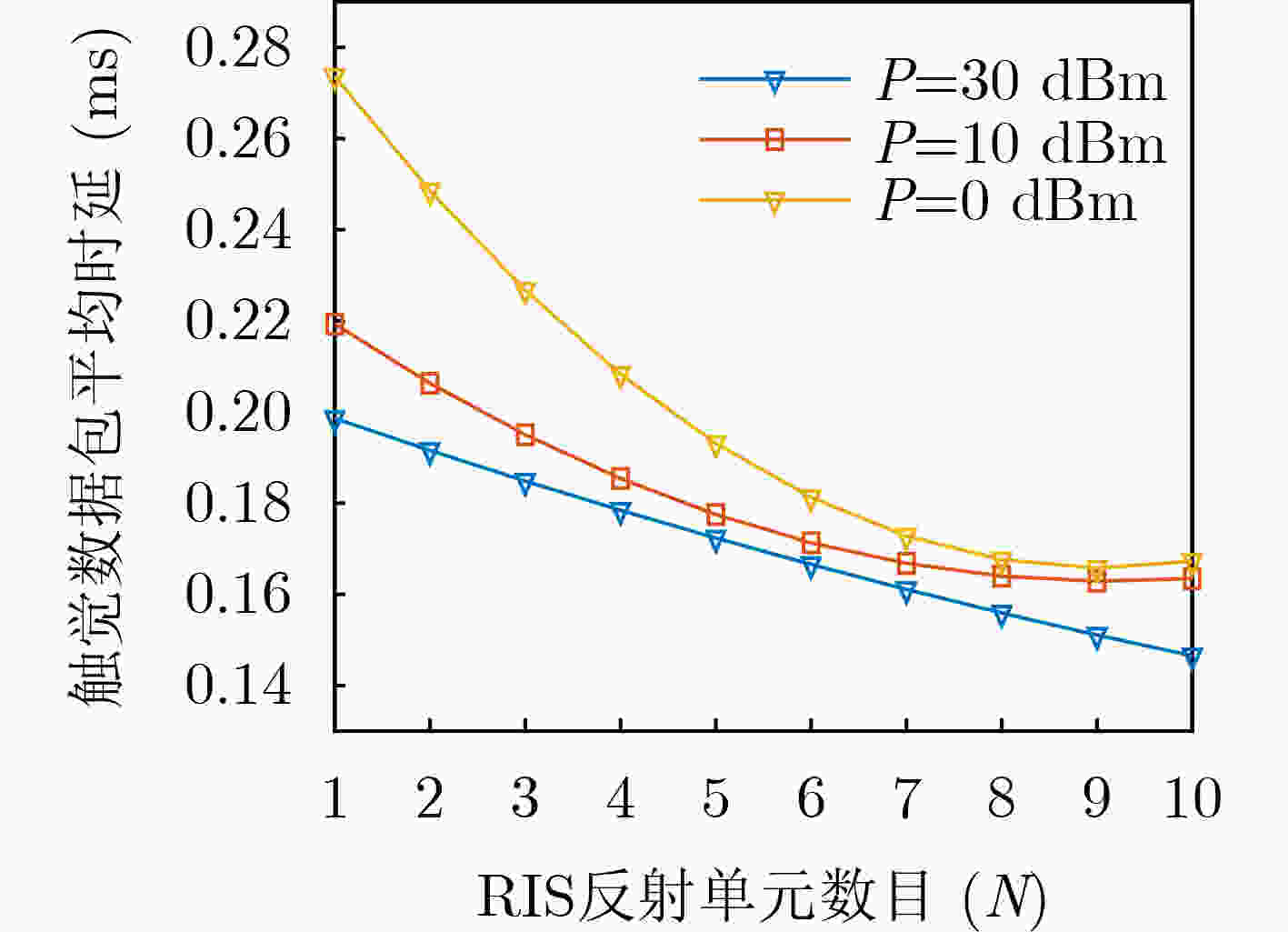
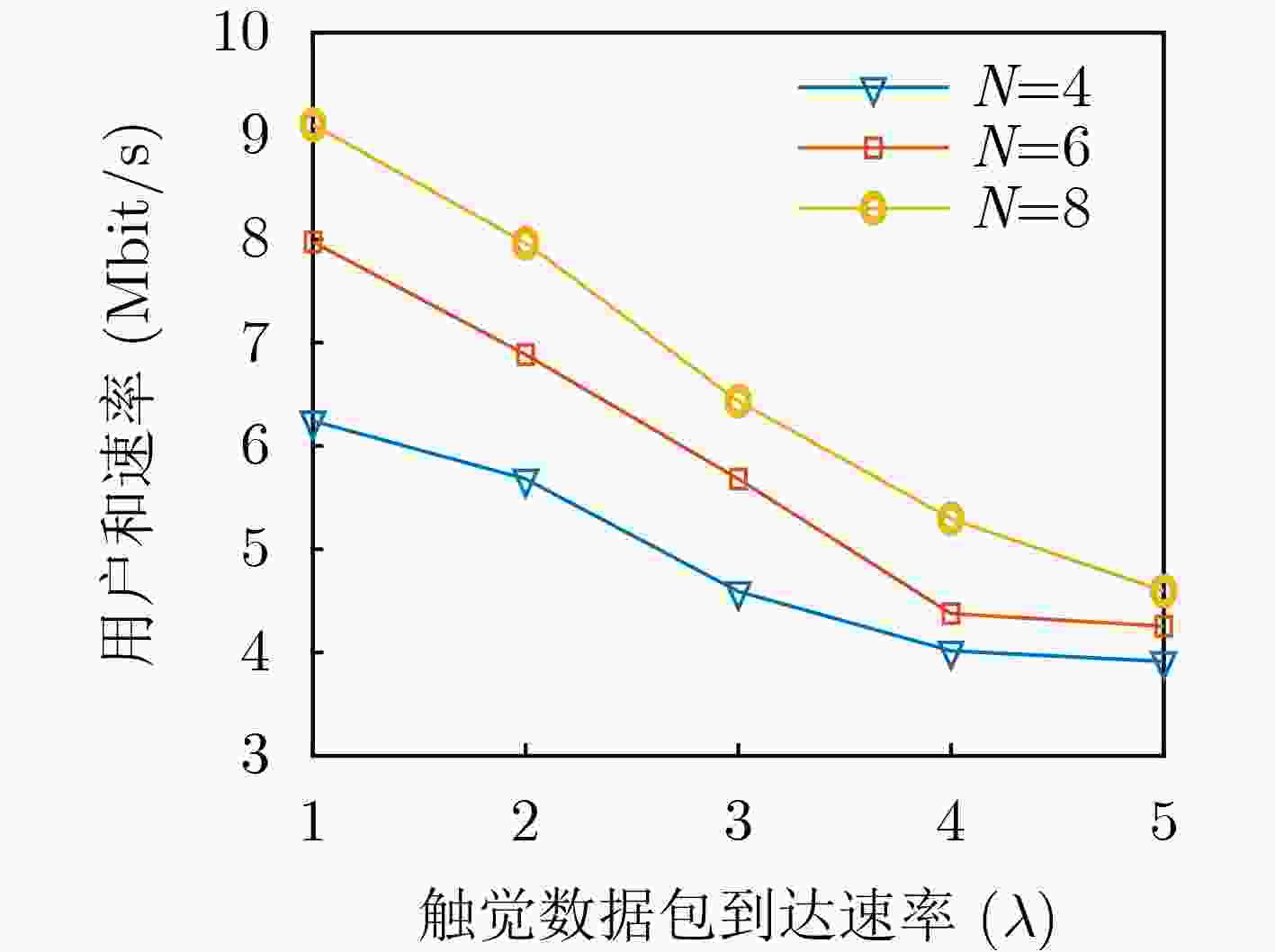
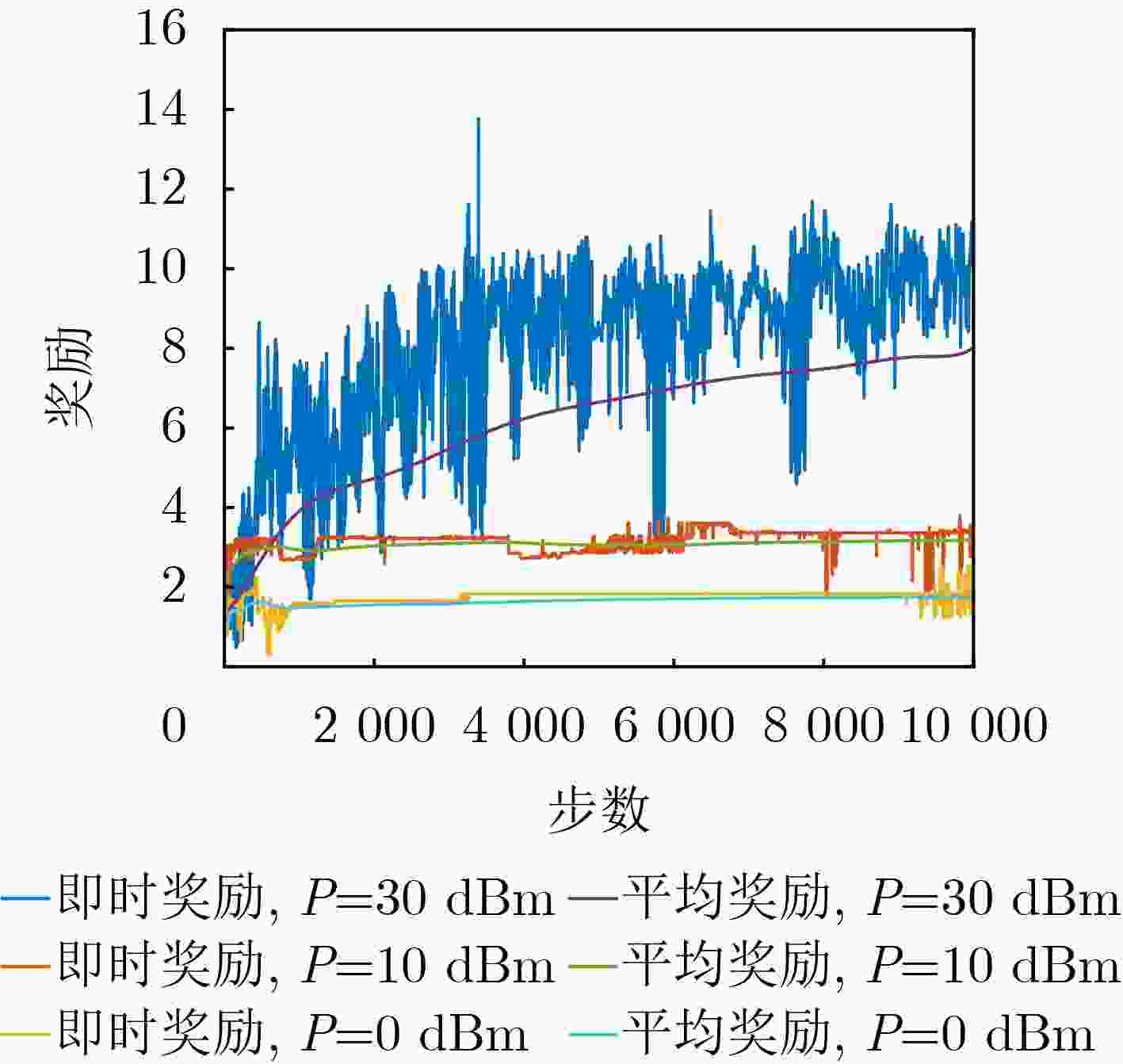
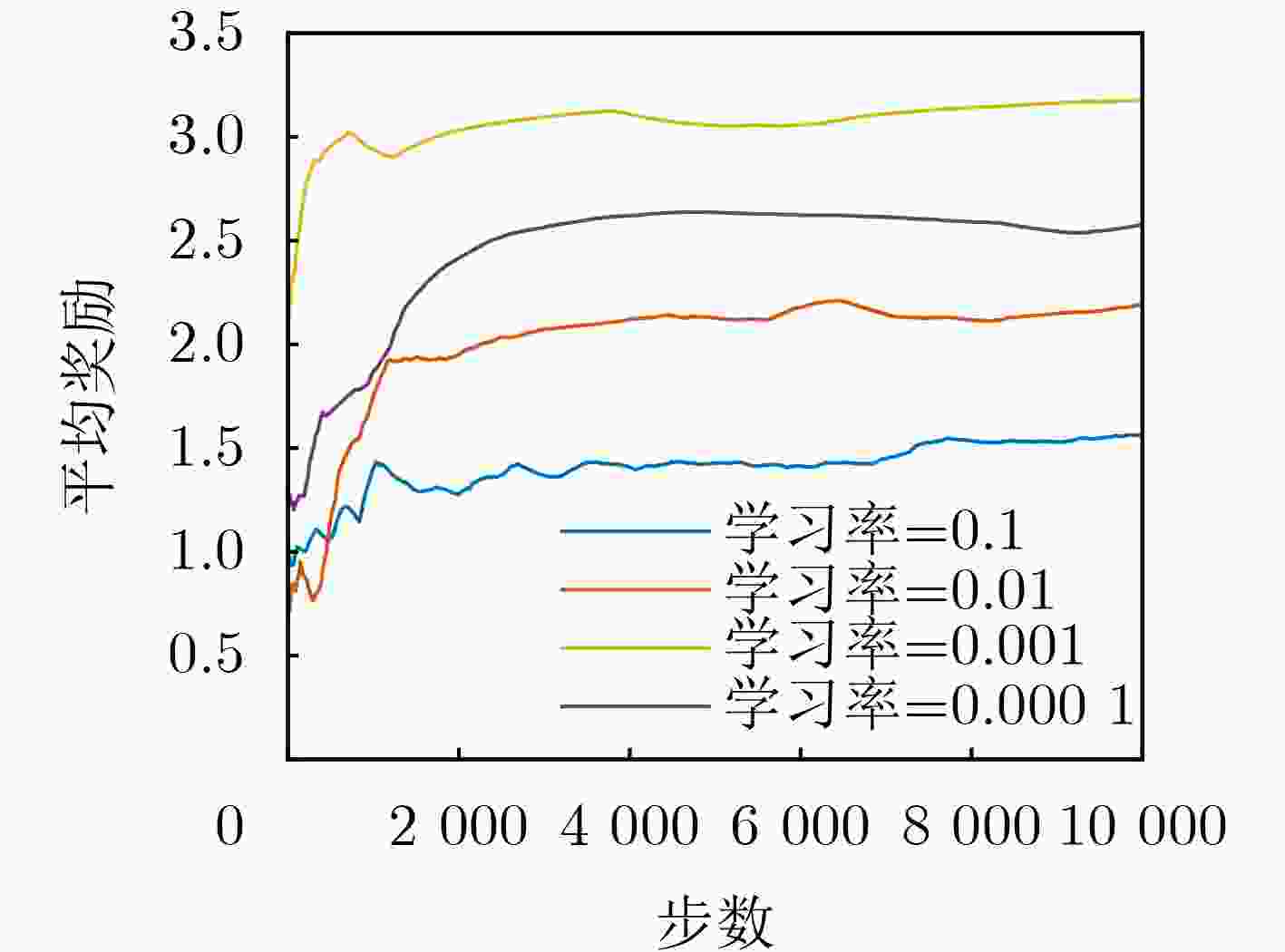
Objective The rapid development of digital and intelligent technologies has driven the increasing demand for cross-modal communication systems to support a wide range of applications, such as high-bandwidth video streaming, ultra-reliable low-latency haptic interactions, and immersive virtual reality experiences. These applications require the concurrent transmission of heterogeneous services, each with distinct and often conflicting resource demands. For instance, video services necessitate high data rates and large bandwidth allocations for smooth playback, while haptic services require ultra-low latency (<0.3 ms) and high reliability (>99.999%) for real-time interaction. Existing resource allocation schemes, typically designed for single-service scenarios or static optimization, do not effectively address the dynamic nature of wireless channels or the stringent requirements of multi-service coexistence. This paper proposes a dynamic resource allocation framework that utilizes Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) to optimize the transmission efficiency of video services and the reliability of haptic services, thereby enhancing spectrum utilization and improving the Quality of Experience (QoE) in cross-modal communication systems. Methods To address the resource competition between video and haptic services, this paper proposes an RIS-aided network slicing architecture. The RIS dynamically adjusts its phase shifts to reshape the wireless propagation environment, improving channel gain and reducing interference. A puncturing-based resource sharing mechanism is introduced, enabling haptic traffic to temporarily use resources allocated to video services during burst arrivals. This mechanism ensures the stringent latency and reliability requirements of haptic services are met without significantly affecting video service performance. The optimization problem is formulated as a Mixed-Integer Nonlinear Programming (MINLP) task, with the objective of maximizing the video service rate while satisfying the constraints of haptic services. To tackle the complexity of joint RIS phase optimization and resource allocation, the problem is modeled as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) with continuous state and action spaces. A Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm is employed, integrating actor-critic networks, experience replay, and target networks to learn optimal policies. The actor network generates decisions regarding resource block allocation, RIS phase shifts, and puncturing ratios, while the critic network evaluates the long-term reward, defined as the weighted sum of video throughput and haptic service satisfaction. Results and Discussions Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme. Compared to the HMSA scheme, the proposed method significantly improves the total transmission rate for users, particularly under varying Base Station (BS) power levels ( Fig. 4 ). The RIS phase optimization scheme outperforms both the random phase and no-RIS scenarios, highlighting the importance of dynamically adjusting RIS reflection coefficients to enhance channel gain (Fig. 5 ). Furthermore, the average delay of haptic data packets decreases as the number of RIS reflection units increases, and higher BS transmit power further reduces latency, confirming the synergy between RIS deployment and power allocation (Fig. 6 ). The user sum rate declines as the arrival rate of haptic data packets increases, due to intensified resource competition. However, deploying additional RIS reflection units mitigates this degradation, demonstrating the robustness of RIS-aided resource allocation (Fig. 7 ). The convergence behavior of the DDPG algorithm is analyzed, showing faster convergence in low-SNR environments (e.g., P = 0 dBm) compared to high-SNR scenarios (e.g., P = 30 dBm), where reward fluctuations are more pronounced (Fig. 8 ). Additionally, the learning rate is identified as a key hyperparameter, with a value of 0.001 providing the optimal balance between convergence speed and stability (Fig. 9 ). These results confirm that the proposed framework enhances video service throughput while ensuring the stringent reliability and low-latency requirements of haptic services, enabling efficient cross-modal resource coexistence.Conclusions This work presents an RIS-assisted dynamic resource allocation framework for cross-modal communication systems, effectively addressing the coexistence challenges of video and haptic services. Key innovations include the integration of RIS phase optimization with puncturing-based resource sharing and the application of DDPG to solve high-dimensional MINLP problems. The proposed scheme significantly enhances video throughput and haptic reliability, demonstrating its potential for 6G-enabled immersive applications. Future research will extend this framework to mobile user scenarios, multi-RIS collaborative systems, and multi-service coexistence environments with diverse QoS requirements. Specifically, the study will examine the impact of user mobility on RIS configuration and resource allocation strategies. Additionally, the benefits of deploying multiple RIS units in a coordinated manner will be explored to further enhance system performance and coverage. Finally, the framework will be expanded to support a broader range of services with varying latency, reliability, and bandwidth demands, paving the way for more versatile and efficient cross-modal communication systems. -
1 DDPG算法
初始化:${s_1}$,${\theta _a}$,${\theta _c}$,${\theta '_a} \leftarrow {\theta _a}$和${\theta '_c} \leftarrow {\theta _c}$,经验回放池$\mathbb{N}$,随
机噪声${{{\boldsymbol{N}}}_t}$while 迭代回合$ \le $最大迭代回合 do while $t \le T$ do • 根据状态${s_t}$和随机噪声${{{\boldsymbol{N}}}_t}$,通过actor网络计算动作
${{\boldsymbol{a}}_t} = \mu ({{\boldsymbol{s}}_t};{\theta _a}) + {{\boldsymbol N}_t}$• 执行动作${{\boldsymbol{a}}_t}$,获得奖赏值$r({{\boldsymbol{s}}_t},{{\boldsymbol{a}}_t})$和下一状态${{\boldsymbol{s}}_{t + 1}}$ • 将经验$({{\boldsymbol{s}}_t},{{\boldsymbol{a}}_t},{r_t},{{\boldsymbol{s}}_{t + 1}})$存储至经验回放池$\mathbb{N}$中 • 从经验回放池$\mathbb{N}$中随机采样${N_{{\mathrm{batch}}}}$个经验样本进行神经网
络训练• 通过式(26)的近似形式,计算得到当前训练critic网络的损
失函数• 通过损失函数$L({\theta _c})$关于${\theta _c}$的梯度更新critic网络的参数 • 通过式(23)更新actor网络的参数${\theta _a}$ • 使用式(29)和式(30)来更新目标actor网络和目标critic网络
的参数${\theta '_a}$和${\theta '_c}$• $t \leftarrow t + 1$ end while end while 表 1 仿真参数表
参数意义 设定数值 资源块RB总数$K$ 200 时隙个数$T$ 20 一个时隙的持续时间 1 ms 一个微小时隙的持续时间$\varDelta $ 0.125 ms 一个时隙内微小时隙个数${M}$ 8 RB的频率带宽$B$ 180 kHz 触觉数据包到达速率$\lambda $ 3 触觉数据包的大小$D_l^{m,t}$ 20 Byte 高斯随机噪声功率${\delta ^2}$ –93 dBm 触觉数据包的解码错误概率${\varepsilon _l}$ ${10^{ - 6}}$ -
[1] 李玉宏, 张朋, 金帝, 等. 应用对未来网络的需求与挑战[J]. 电信科学, 2019, 35(8): 2019203. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2019203.LI Yuhong, ZHANG Peng, JIN Di, et al. Application's needs and challenges for future networks[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2019, 35(8): 2019203. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2019203. [2] WEI Xin, WU Dan, ZHOU Liang, et al. Cross-modal communication technology: A survey[J]. Fundamental Research, 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2023.08.002. [3] WEI Xin, ZHANG Meng, and ZHOU Liang. Cross-modal transmission strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(6): 3991–4003. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3105130. [4] 陈鸣锴, 柳明浩, 王文俊, 等. 面向6G的跨模态语义编解码技术[J]. 信号处理, 2023, 39(7): 1141–1154. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2023.07.001.CHEN Mingkai, LIU Minghao, WANG Wenjun, et al. Codec for cross-modal semantic communication in 6G[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2023, 39(7): 1141–1154. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2023.07.001. [5] ALTAF KHATTAK S B, NASRALLA M M, and REHMAN I U. The role of 6G networks in enabling future smart health services and applications[C]. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference, Pafos, Cyprus, 2022: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/ISC255366.2022.9922093. [6] 李昂, 陈建新, 魏昕, 等. 面向6G的跨模态信号重建技术[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(6): 28–40. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022093.LI Ang, CHEN Jianxin, WEI Xin, et al. 6G-oriented cross-modal signal reconstruction technology[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(6): 28–40. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022093. [7] ZHOU Liang, WU Dan, CHEN Jianxin, et al. Cross-modal collaborative communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(2): 112–117. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.1900201. [8] STEINBACH E, STRESE M, EID M, et al. Haptic codecs for the tactile internet[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(2): 447–470. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2018.2867835. [9] ALSENWI M, TRAN N H, BENNIS M, et al. eMBB-URLLC resource slicing: A risk-sensitive approach[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(4): 740–743. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2900044. [10] SUN Haipeng, YANG Jin, SU Junhao, et al. Joint resource scheduling for coexistence of URLLC and eMBB in 5G wireless networks[C]. Proceedings of 2021 Computing, Communications and IoT Applications, Shenzhen, China, 2021: 53–58. doi: 10.1109/ComComAp53641.2021.9653121. [11] ZHAO Yunzhi, CHI Xuefen, QIAN Lei, et al. Resource allocation and slicing puncture in cellular networks with eMBB and URLLC terminals coexistence[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(19): 18431–18444. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3160647. [12] REN Rong, WANG Jie, YU Jingming, et al. Hybrid puncturing and superposition scheme for multiplexing uRLLC and eMBB services based on deep reinforcement learning[C]. Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 8th International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 2022: 806–810. doi: 10.1109/ICCC56324.2022.10065784. [13] GUO Jiangfeng, NIE Gaofeng, TIAN Hui, et al. Puncture-predictive fairness scheduling scheme for eMBB and URLLC based on TD3 algorithm[C]. Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China, Dalian, China, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICCC57788.2023.10233289. [14] ZHUANSUN Chenlu, YAN Kedong, ZHANG Gongxuan, et al. Hypergraph-based joint channel and power resource allocation for cross-cell M2M communication in IIoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(17): 15350–15361. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3263567. [15] WANG Lei, YIN Anmin, JIANG Xue, et al. Resource allocation for multi-traffic in cross-modal communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2023, 20(1): 60–72. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2022.3207776. [16] 文梦甜. 跨模态通信中传输策略优化研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京邮电大学, 2023. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2023.001196.WEN Mengtian. Research on optimization of transmission strategy in cross-modal communications[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2023.001196. [17] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107. [18] LIASKOS C, NIE Shuai, TSIOLIARIDOU A, et al. A new wireless communication paradigm through software-controlled metasurfaces[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(9): 162–169. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700659. [19] DI RENZO M, DEBBAH M, PHAN-HUY D T, et al. Smart radio environments empowered by reconfigurable AI meta-surfaces: An idea whose time has come[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2019, 2019: 129. doi: 10.1186/s13638-019-1438-9. [20] GHANEM W R, JAMALI V, and SCHOBER R. Joint beamforming and phase shift optimization for multicell IRS-aided OFDMA-URLLC systems[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Nanjing, China, 2021: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/WCNC49053.2021.9417582. [21] CAO Xuelin, YANG Bo, HUANG Chongwen, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted aerial-terrestrial communications via multi-task learning[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(10): 3035–3050. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3088634. [22] MELGAREJO D C, KALALAS C, DE SENA A S, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface-aided grant-free access for uplink URLLC[C]. Proceedings of the 2020 2nd 6G Wireless Summit, Levi, Finland, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/6GSUMMIT49458.2020.9083788. [23] ALMEKHLAFI M, ARFAOUI M A, ELHATTAB M, et al. Joint resource allocation and phase shift optimization for RIS-aided eMBB/URLLC traffic multiplexing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(2): 1304–1319. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3127265. [24] ZHOU Shuangquan, ZHANG Wenbin, XU Fanglei, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation in DDPG-based integrated satellite-terrestrial network[C]. Proceedings of 2023 IEEE Globecom Workshops, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2023: 147–152. doi: 10.1109/GCWkshps58843.2023.10464487. [25] SUTTON R S, MCALLESTER D, SINGH S, et al. Policy gradient methods for reinforcement learning with function approximation[C]. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver CO, USA, 1999: 1057–1063. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
