Adaptive Beamforming Based on Dual Convolutional Autoencoder
-
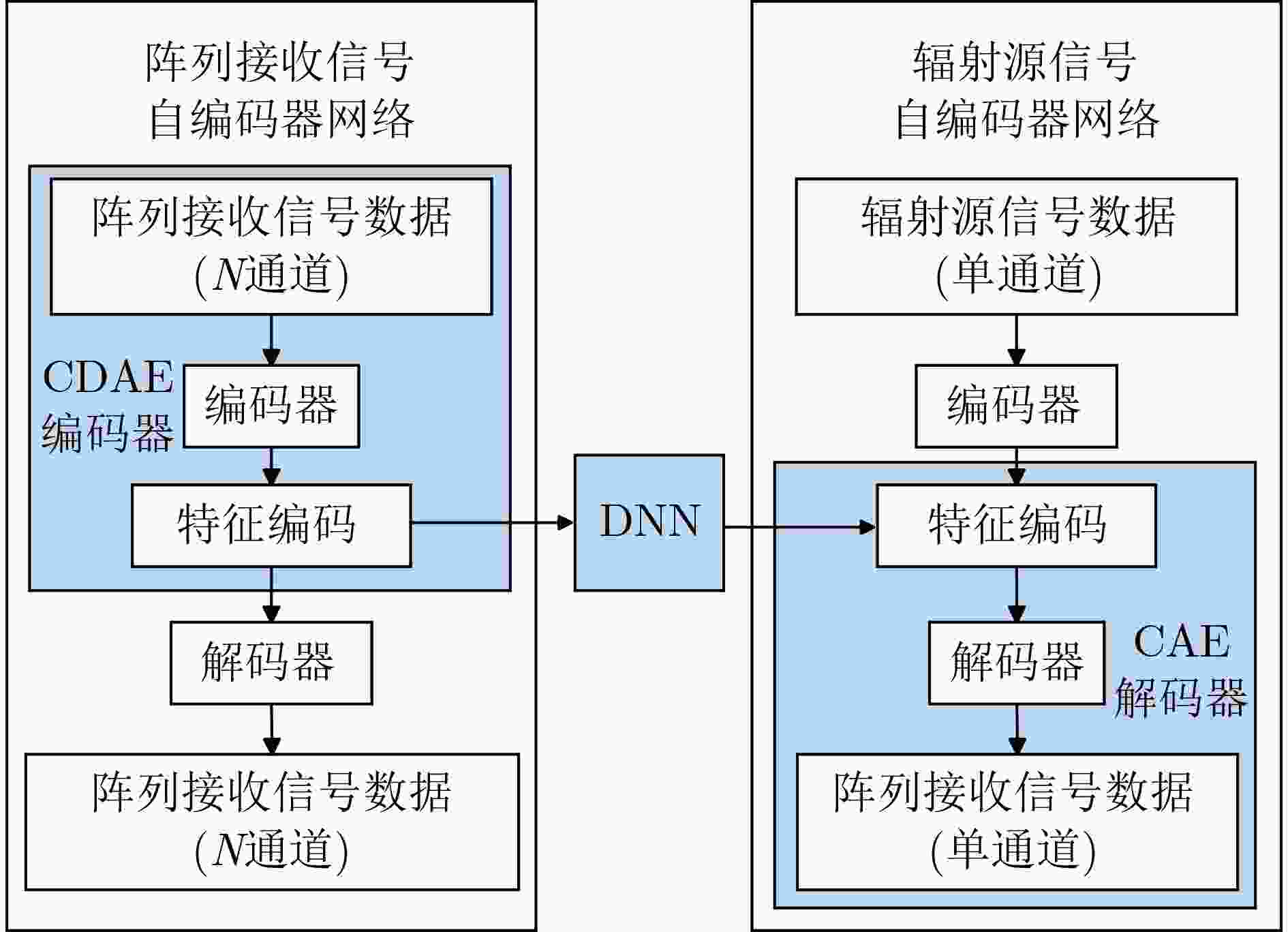
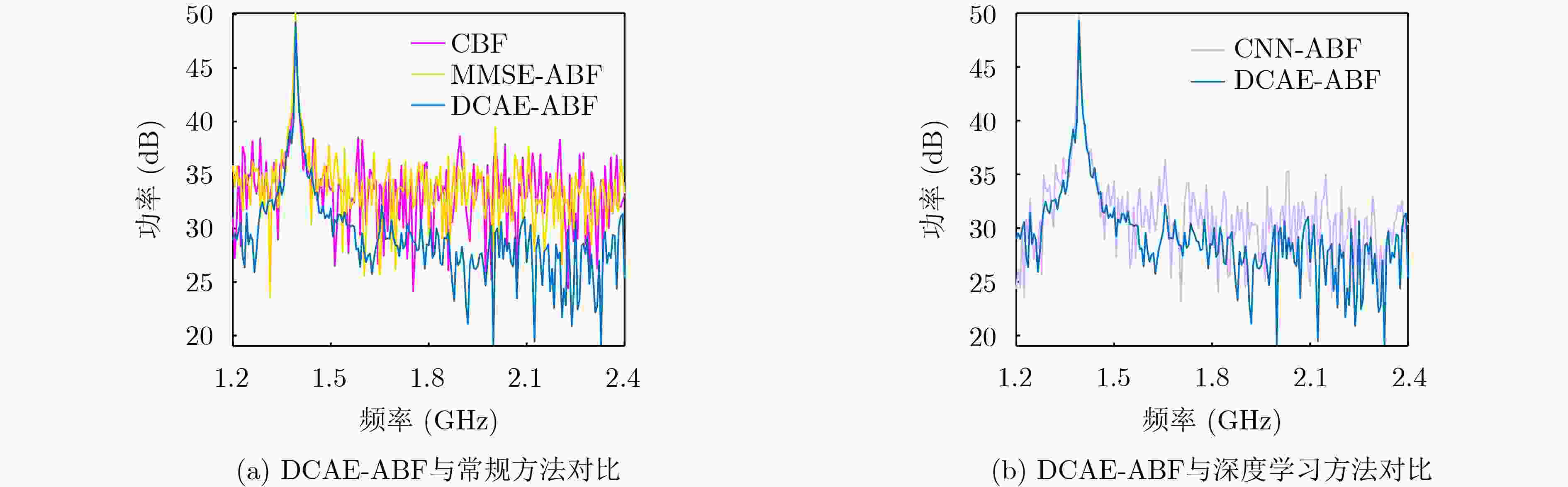
摘要: 在低信噪比环境下,阵列天线获取空域信号的来波方向极其困难,导致一般的波束形成方法无法准确形成正对入射信号的波束。针对上述问题,该文提出了一种基于双卷积自编码器的盲接收自适应波束形成(Dual Convolutional AutoEncoder-Adaptive Beamforming, DCAE-ABF)方法,该方法在基于大量空域统计信息的情况下,以时域-频域联合条件作为约束,利用两个独立的卷积自编码器(CAE)分别对阵列接收信号与辐射源信号进行特征提取,并使用深度神经网络(DNN)将两个CAE的特征编码进行连接,构建DCAE网络,实现在低信噪比环境下,面对未知频率和来波方向的入射信号时,也能够自适应形成正对入射信号的波束,达到盲接收的效果。仿真实验结果表明,在低信噪比环境下,单信号与双信号入射时所带来的信噪比增益均高于常规波束形成(CBF)方法与基于最小均方误差的自适应波束形成(Minimum Mean Square Error-Adaptive BeamForming, MMSE-ABF)方法,以及基于卷积神经网络的自适应波束形成方法(Convolutional Neural Networks- Adaptive BeamForming, CNN-ABF),且该增益在入射信号频率、角度变化时仍具有良好的稳定性。Abstract:
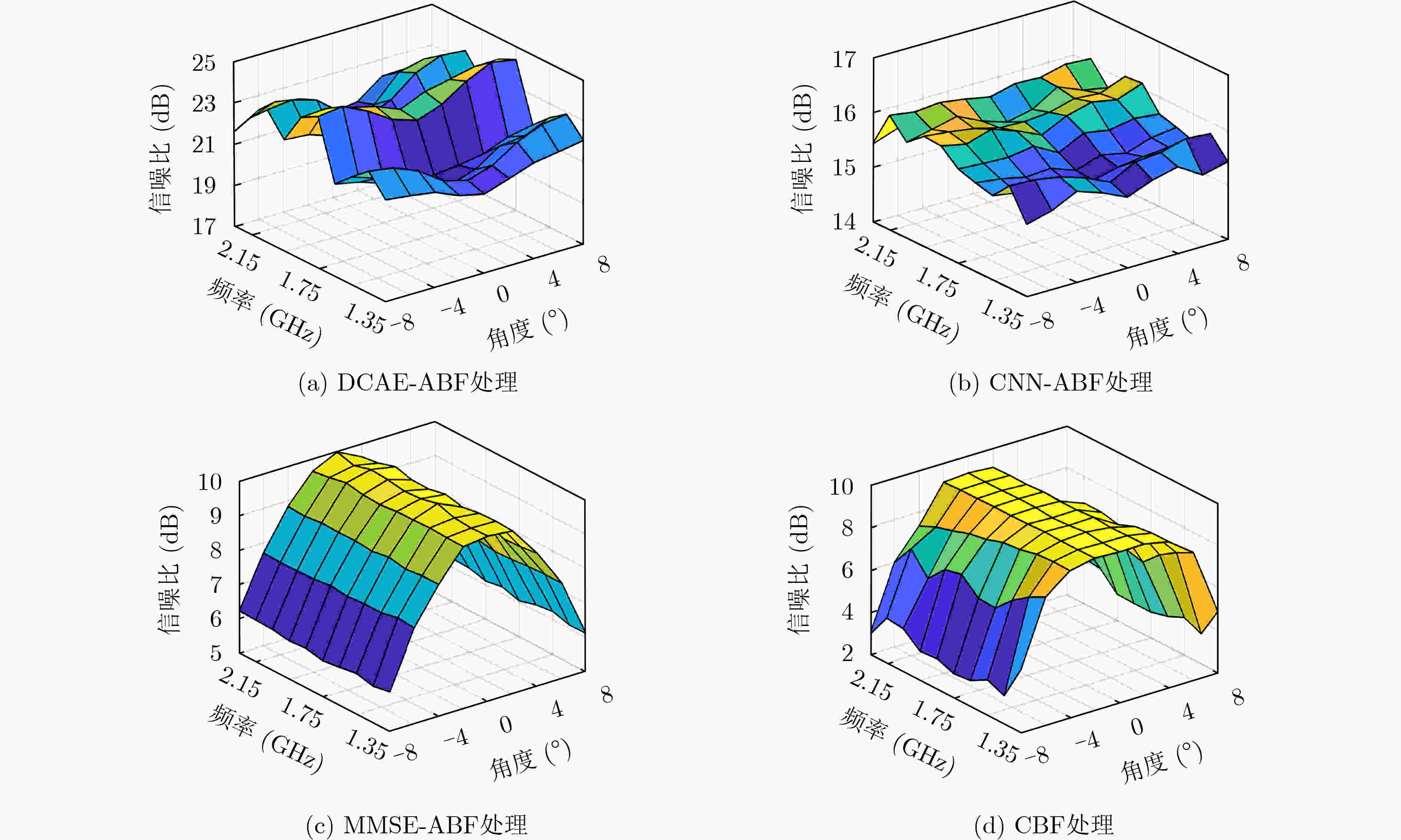
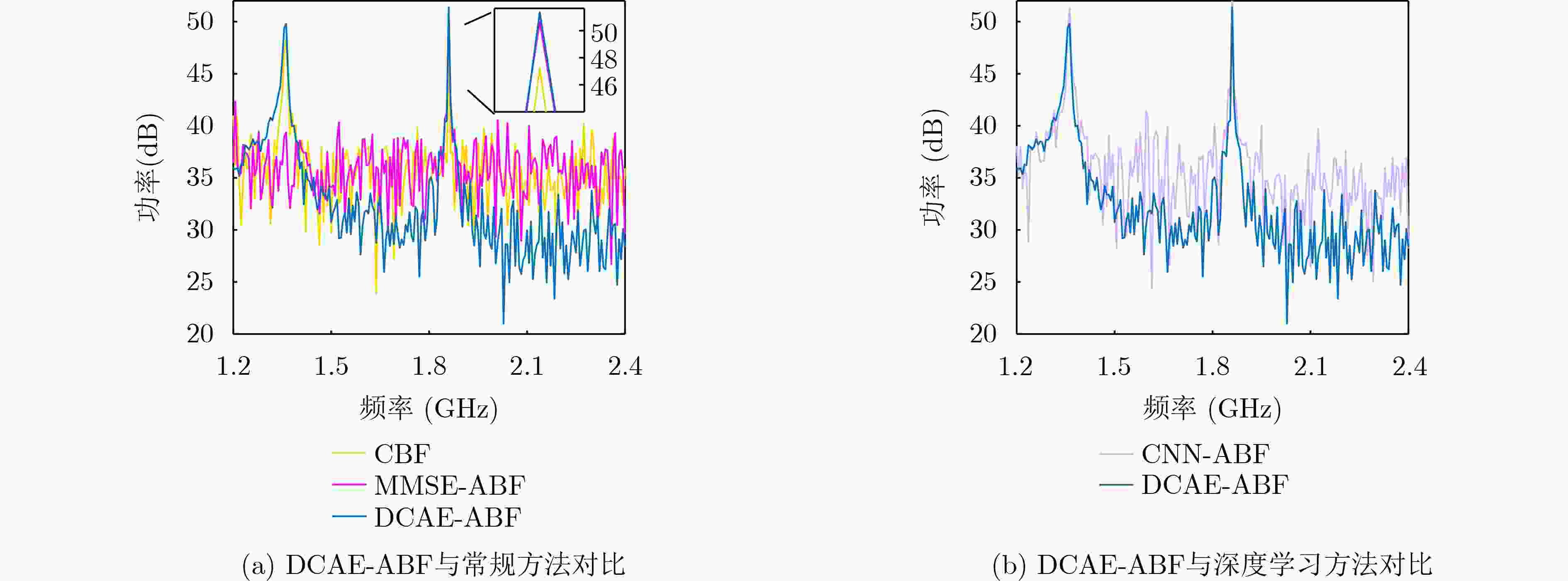
Objective Most traditional beamforming techniques and adaptive beamforming methods rely on reference signals. These methods require prior knowledge of the signal frequency and Direction of Arrival (DOA) at the array for beamforming. However, in low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) environments, obtaining the frequency and DOA of the incident signals is extremely challenging. This difficulty leads to significant performance degradation in reference-signal-based beamforming, limiting its applicability in tasks such as electronic reconnaissance and electronic countermeasures in low SNR conditions. This paper addresses the challenge of enabling antenna arrays to perform adaptive beamforming for incident signals with unknown frequencies and DOAs in low-SNR environments. Methods This paper proposes a Dual Convolutional AutoEncoder-Adaptive Beamforming (DCAE-ABF) method for blind reception. The approach leverages dual Convolutional Autoencoders (CAEs) to extract features from both the array-received signal and the radiation source signal, utilizing extensive air-domain statistical information with joint time-frequency domain constraints. A Deep Neural Network (DNN) connects the feature encodings from the two CAEs to construct the DCAE network. This method enables adaptive beamforming in low SNR environments, even when the incident signal’s frequency and DOA are unknown, facilitating blind reception. Results and Discussions Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed DCAE-ABF method can rapidly and accurately adjust the beam direction for incident signals with unknown frequencies and directions of arrival in a low SNR environment, effectively orienting the beam towards the incident signals for optimal reception. This method improves the output signal’s SNR, with the SNR gain significantly exceeding that of traditional beamforming techniques ( Fig. 4 ,Fig. 6 ). Furthermore, the SNR gain achieved by this method remains stable even when the frequency and angle of the incident signal vary (Fig. 5 ).Conclusions This paper presents an adaptive beamforming method based on dual convolutional autoencoders. The method outperforms the other three approaches discussed in this study when applied to incident signals with unknown directions of arrival in low SNR environments. Even when the DOA is unknown, the method effectively utilizes the spatial information accumulated during autoencoder training. It can extract features from the array signals and adaptively form beams directed at the incident signals, achieving optimal reception. This approach enables blind adaptive beamforming for signals with unknown frequencies and directions of arrival, significantly improving the SNR of the incident signals. -
表 1 超参数对输入测试结果带来的部分影响
自编码器层数 训练
时间CDAE
学习率DNN
学习率CAE
学习率信噪比
增益(dB)3层 适中 0.00007 0.0003 0.00003 20.9 0.00008 0.0004 0.00004 21.08 0.00009 0.0005 0.00005 21.56 0.0001 0.0006 0.00006 21.13 4层 较长 0.00007 0.0003 0.00003 16.12 0.00008 0.0004 0.00004 16.13 0.00009 0.0005 0.00005 16.17 0.0001 0.0006 0.00006 16.68 表 2 DCAE网络训练过程中的超参数
神经
网络初始
学习率学习率
衰减率网络层数 CDAE 0.00009 0.95 3层 DNN 0.0005 – 3层 CAE 0.00005 – 3层 表 3 DCAE网络的特征结构
输入形状 输出形状 阵列接收信号自编码器
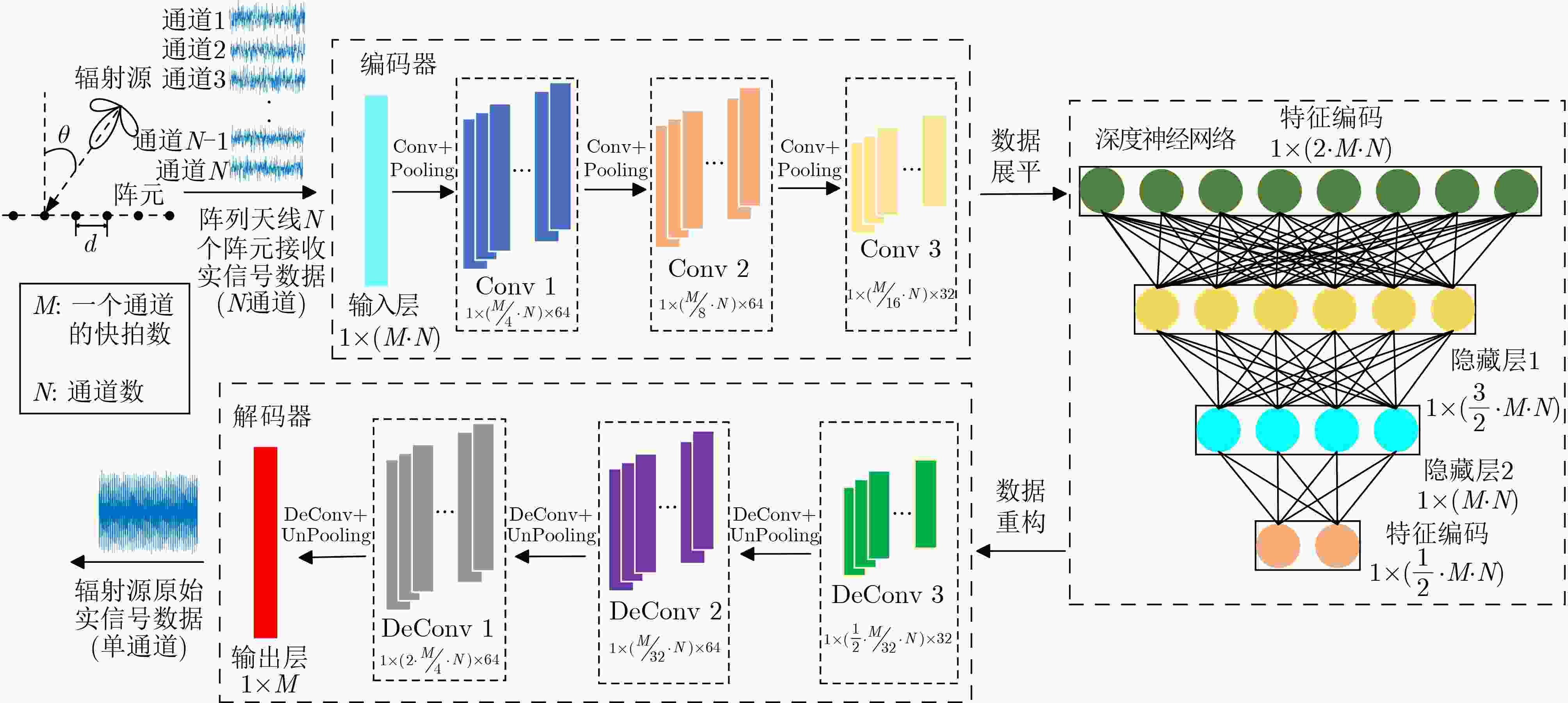
网络的解码器部分输入层 1× 3200 – 卷积层1 1× 3200 1× 3200 ×64池化层1 1× 3200 ×641×800×64 卷积层2 1×800×64 1×800×64 池化层2 1×800×64 1×400×64 卷积层3 1×400×64 1×400×32 池化层3 1×400×32 1×200×32 DNN连接部分 数据展平 1×200×32 1× 6400 全连接层1 1× 6400 1× 4800 全连接层2 1× 4800 1× 3200 全连接层3 1× 3200 1× 1600 数据重构 1× 1600 1×50×32 辐射源原始信号自编码器
网络的解码器部分反池化层1 1×50×32 1×100×32 反卷积层1 1×100×32 1×100×64 反池化层2 1×100×64 1×200×64 反卷积层2 1×200×64 1×200×64 反池化层3 1×200×64 1×400×64 反卷积层3 1×400×64 1×400 输出层 1×400 1×400 -
[1] 唐敏, 齐栋, 刘成城, 等. 基于多级阻塞的稳健相干自适应波束形成[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1705–1711. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180332.TANG Min, QI Dong, LIU Chengcheng, et al. New adaptive beamformer for coherent interference based on multistage blocking[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1705–1711. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180332. [2] 沈季, 万显荣, 易建新, 等. 复杂干扰场景下的稳健自适应波束形成[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(4): 941–949. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.04.01.SHEN Ji, WAN Xianrong, YI Jianxin, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming in complex interference scenarios[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(4): 941–949. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.04.01. [3] WU Xun, ZHANG Shurui, MA Xiaofeng, et al. The adaptive wideband beamforming using convolutional neural network[C]. Proceedings of 2022 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Harbin, China, 2022: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/ICMMT55580.2022.10022889. [4] 王兆彬, 巩朋成, 邓薇, 等. 联合协方差矩阵重构和ADMM的鲁棒波束形成[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2023, 55(4): 64–71. doi: 10.11918/202107104.WANG Zhaobin, GONG Pengcheng, DENG Wei, et al. Robust beamforming by joint covariance matrix reconstruction and ADMM[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2023, 55(4): 64–71. doi: 10.11918/202107104. [5] GODARA L C. Application of antenna arrays to mobile communications. II. Beam-forming and direction-of-arrival considerations[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1997, 85(8): 1195–1245. doi: 10.1109/5.622504. [6] ZAHARIS Z D, GRAVAS I P, LAZARIDIS P I, et al. An effective modification of conventional beamforming methods suitable for realistic linear antenna arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(7): 5269–5279. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.2977822. [7] SENTHILKUMAR K S, PIRAPAHARAN K, HOOLE P R P, et al. Single perceptron model for smart beam forming in array antennas[J]. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE), 2016, 6(5): 2300–2309. doi: 10.11591/ijece.v6i5.10719. [8] EL ZOOGHBY A H, CHRISTODOULOU C G, and GEORGIOPOULOS M. A neural network-based smart antenna for multiple source tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2000, 48(5): 768–776. doi: 10.1109/8.855496. [9] RAMEZANPOUR P, REZAEI M J, and MOSAVI M R. Deep‐learning‐based beamforming for rejecting interferences[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2020, 14(7): 467–473. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2019.0495. [10] SALLOMI A H and AHMED S. Multi-layer feed forward neural network application in adaptive beamforming of smart antenna system[C]. Proceedings of 2016 Al-Sadeq International Conference on Multidisciplinary in IT and Communication Science and Applications, Baghdad, Iraq, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/AIC-MITCSA.2016.7759925. [11] MOHAMMADZADEH S, NASCIMENTO V H, DE LAMARE R C, et al. Robust beamforming based on complex-valued convolutional neural networks for sensor arrays[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022, 29: 2108–2112. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2022.3212637. [12] MALLIORAS I, ZAHARIS Z D, LAZARIDIS P I, et al. A novel realistic approach of adaptive beamforming based on deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2022, 70(10): 8833–8848. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2022.3168708. [13] ZAHARIS Z D, SKEBERIS C, XENOS T D, et al. Design of a novel antenna array beamformer using neural networks trained by modified adaptive dispersion invasive weed optimization based data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2013, 59(3): 455–460. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2013.2244793. [14] 梁梦薇, 何劲, 舒汀, 等. 阵元位置互质的线性阵列: 阵列校正和波束形成[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(1): 240–248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221539.LIANG Mengwei, HE Jin, SHU Ting, et al. Linear coprime sensor location arrays: Array calibration and beamforming[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(1): 240–248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221539. [15] 陈鹏, 景晓簪, 陈洋, 等. 稳健的特征空间基变换自适应波束形成[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2023, 55(5): 71–77,113. doi: 10.11918/202112102.CHEN Peng, JING Xiaozan, CHEN Yang, et al. Robust eigenspace bases transition technique for adaptive beamforming[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2023, 55(5): 71–77,113. doi: 10.11918/202112102. [16] ZHU Yi, WU Xindong, QIANG Jipeng, et al. Representation learning via an integrated autoencoder for unsupervised domain adaptation[J]. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2023, 17(5): 175334. doi: 10.1007/s11704-022-1349-5. [17] LU Cai, MU Zuochen, ZONG Jingjing, et al. Unsupervised VSP up-and downgoing wavefield separation via dual convolutional autoencoders[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5900315. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3334309. [18] AL KASSIR H, ZAHARIS Z D, LAZARIDIS P I, et al. A review of the state of the art and future challenges of deep learning-based beamforming[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 80869–80882. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3195299. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
